Retroperitoneal hemorrhage
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Retroperitoneal hemorrhage | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources | |
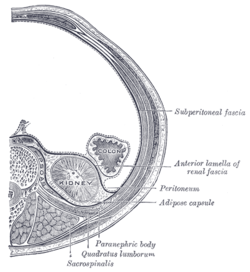 Transverse section, showing the relations of the capsule of the kidney. (Peritoneum is labeled at center right. Retroperitoneal space is behind peritoneum.) | |
| ICD-10 | R58, R93.5 |
| ICD-9 | 793.6459.0 |
| DiseasesDB | 11455 |
Retroperitoneal hemorrhage (or retroperitoneal hematoma) refers to an accumulation of blood found in the retroperitoneal space.
It can present with Grey Turner's sign (flank bruising).
Causes include:
- anticoagulation[1]
- a ruptured aortic aneurysm
- a ruptured renal aneurysm[2]
- acute pancreatitis
- malignancy[3]
References
- ↑ John P. McGahan; Barry B. Goldberg (January 2008). Diagnostic ultrasound. Informa Health Care. pp. 772–. ISBN 978-1-4200-6978-5. Retrieved 20 April 2010.
- ↑ Case Rep Vasc Med. 2013;2013:452317 http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/452317
- ↑ Marilyn J. Siegel (1 November 2007). Pediatric Body CT. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 353–. ISBN 978-0-7817-7540-3. Retrieved 20 April 2010.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.