Respiratory bronchiole
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Respiratory bronchiole | |
|---|---|
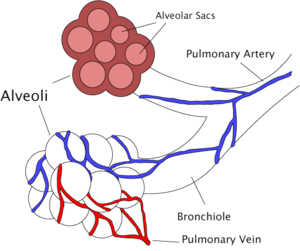 | |
| Diagram of the alveoli with both cross-section and external view. | |
 | |
| Schematic longitudinal section of a primary lobule of the lung (anatomical unit); r. b respiratory bronchiole; al. d alveolar duct; at atria; a. s alveolar sac; 'a' alveolus or air cell; p. a.: pulmonary artery; p. v pulmonary vein; l lymphatic; l. n lymph node. | |
| Latin | bronchioli respiratorii |
| Gray's | subject #240 1098 |
| Code | TH H3.05.02.0.00018 |
The respiratory bronchioles are the narrowest airways of the lungs, one fiftieth of an inch across.[1] The bronchi divide many times before evolving into the bronchioles. The bronchioles deliver air to the exchange surfaces of the lungs.[2] They are interrupted by alveoli which are thin walled evaginations. Alveolar ducts are distal continuations of the respiratory bronchioles.
Additional images
-

Part of a secondary lobule from the depth of a human lung, showing parts of several primary lobules.
References
External links
- Diagram at davidson.edu
- Respiratory+bronchioles at eMedicine Dictionary
- BU Histology Learning System: 13606loa
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.