Buryatia
| Republic of Buryatia | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Республика Бурятия (Russian) Буряад Республика (Buryat) |
|||
| — Republic — | |||
|
|||
| Anthem: Anthem of the Republic of Buryatia | |||
 |
|||
| Coordinates: 53°48′N 109°20′E / 53.800°N 109.333°ECoordinates: 53°48′N 109°20′E / 53.800°N 109.333°E | |||
| Political status | |||
| Country | |||
| Federal district | Siberian[1] | ||
| Economic region | East Siberian[2] | ||
| Established | May 30, 1923 | ||
| Capital | Ulan-Ude | ||
| Government (as of August 2010) | |||
| - Head[3] | Vyacheslav Nagovitsyn[4] | ||
| - Legislature | People's Khural[3] | ||
| Statistics | |||
| Area (as of the 2002 Census)[5] | |||
| - Total | 351,300 km2 (135,637.7 sq mi) | ||
| Area rank | 15th | ||
| Population (2010 Census)[6] | |||
| - Total | 972,021 | ||
| - Rank | 54th | ||
| - Density[7] | 2.77 /km2 (7.2 /sq mi) | ||
| - Urban | 58.4% | ||
| - Rural | 41.6% | ||
| Time zone(s) | IRKT (UTC+09:00)[8] | ||
| ISO 3166-2 | RU-BU | ||
| License plates | 03 | ||
| Official languages | Russian;[9] Buryat[10] | ||
| Official website | |||
The Republic of Buryatia (Russian: Респу́блика Буря́тия, tr. Respublika Buryatiya, IPA: [rʲɪsˈpublʲɪkə bʊˈrʲætʲɪjə]; Buryat: Буряад Республика, Buryaad Respublika) is a federal subject of Russia (a republic). Its capital is the city of Ulan-Ude. Its area is 351,300 square kilometers (135,600 sq mi) with a population of 972,021 (2010 Census).[6]
Geography

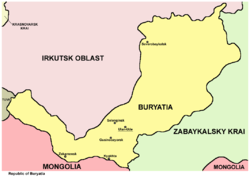
The republic is located in the south-central region of Siberia along the eastern shore of Lake Baikal.
- Area: 351,300 km²
- Borders:
- Internal: Irkutsk Oblast (W/NW/N), Zabaykalsky Krai (NE/E/SE/S), Tuva Republic (W)
- International: Mongolia (S/SE)
- Water: Lake Baikal (N)
- Highest point: Mount Munku-Sardyk (3,491 m)
Rivers
Major rivers include:
- Barguzin River
- Irkut River
- Kitoy River
- Oka River
- Selenga River
- Uda River
- Upper Angara River
- Vitim River
Lakes
- Lake Baikal - Buryatia covers 60% percent of the lake's shoreline
- Lake Gusinoye
Mountains
Over 80% of the republic's territory is located in the mountainous region, including the Baikal Mountains on the northern shores of Lake Baikal.
Natural resources
The republic's natural resources include gold, tungsten, zinc, uranium, and more.
Climate
- Average annual temperature: −1.6 °C (29.1 °F)
- Average January temperature: −22 °C (−8 °F)
- Average July temperature: +18 °C (64 °F)
- Average annual precipitation: 244 millimeters (9.6 in)
Administrative divisions
Demographics
Population: 972,021 (2010 Census);[6] 981,238 (2002 Census);[11] 1,041,119 (1989 Census).[12]
| 17-12-1926 | 17-01-1939 | 17-01-1959 | 15-01-1970 | 17-01-1979 | 17-01-1989 | 09-10-2002 | 14-10-2010 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total population | 491,236 | 545,766 | 673,326 | 812,251 | 899,398 | 1,038,252 | 981,238 | 972,021 |
| Average annual population growth | +1.7% | +1.1% | +1.5% | -0.4% | -0.1% | |||
| Males | 248,513 | 467,984 | ||||||
| Females | 242,723 | 513,254 | ||||||
| Females per 1000 males | 977 | 1,097 | ||||||
| Proportion urban | 9.3% | 59.6% | ||||||
| Territory (km2) | 368,392 | 351,334 | 351,334 | 351,334 | 351,334 | 351,334 | 351,334 | 351,334 |
| Population density/km2 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.3 | 2.6 | 3.0 | 2.8 | 2.8 |
Vital statistics
| Average population (x 1000) | Live births | Deaths | Natural change | Crude birth rate (per 1000) | Crude death rate (per 1000) | Natural change (per 1000) | Fertility rates | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1970 | 816 | 14,766 | 6,301 | 8,465 | 18.1 | 7.7 | 10.4 | |
| 1975 | 862 | 17,751 | 7,586 | 10,165 | 20.6 | 8.8 | 11.8 | |
| 1980 | 921 | 19,859 | 8,734 | 11,125 | 21.6 | 9.5 | 12.1 | |
| 1985 | 993 | 23,975 | 9,529 | 14,446 | 24.1 | 9.6 | 14.5 | |
| 1990 | 1,050 | 19,185 | 9,602 | 9,583 | 18.3 | 9.1 | 9.1 | 2,18 |
| 1991 | 1,052 | 16,868 | 9,753 | 7,115 | 16.0 | 9.3 | 6.8 | 2,03 |
| 1992 | 1,049 | 13,944 | 10,347 | 3,597 | 13.3 | 9.9 | 3.4 | 1,87 |
| 1993 | 1,043 | 11,981 | 12,388 | - 407 | 11.5 | 11.9 | -0.4 | 1,65 |
| 1994 | 1,039 | 12,327 | 13,650 | -1,323 | 11.9 | 13.1 | -1.3 | 1,66 |
| 1995 | 1,035 | 12,311 | 12,588 | - 277 | 11.9 | 12.2 | -0.3 | 1,60 |
| 1996 | 1,031 | 12,159 | 12,441 | - 282 | 11.8 | 12.1 | -0.3 | 1,57 |
| 1997 | 1,025 | 11,555 | 12,111 | - 556 | 11.3 | 11.8 | -0.5 | 1,51 |
| 1998 | 1,017 | 11,746 | 11,481 | 265 | 11.6 | 11.3 | 0.3 | 1,53 |
| 1999 | 1,009 | 11,468 | 13,114 | -1,646 | 11.4 | 13.0 | -1.6 | 1,42 |
| 2000 | 1,001 | 11,654 | 13,155 | -1,501 | 11.6 | 13.1 | -1.5 | 1,42 |
| 2001 | 992 | 11,678 | 13,858 | -2,180 | 11.8 | 14.0 | -2.2 | 1,44 |
| 2002 | 983 | 12,830 | 14,404 | -1,574 | 13.1 | 14.7 | -1.6 | 1,52 |
| 2003 | 977 | 13,177 | 15,056 | -1,879 | 13.5 | 15.4 | -1.9 | 1,51 |
| 2004 | 973 | 13,399 | 14,868 | -1,469 | 13.8 | 15.3 | -1.5 | 1,49 |
| 2005 | 969 | 13,551 | 15,144 | -1,593 | 14.0 | 15.6 | -1.6 | 1,41 |
| 2006 | 966 | 14,193 | 13,930 | 263 | 14.7 | 14.4 | 0.3 | 1,41 |
| 2007 | 965 | 15,460 | 12,802 | 2,658 | 16.0 | 13.3 | 2.8 | 1,60 |
| 2008 | 966 | 16,372 | 12,948 | 3,424 | 16.9 | 13.4 | 3.5 | 1,68 |
| 2009 | 968 | 16,729 | 12,466 | 4,263 | 17.3 | 12.9 | 4.4 | 2,03 |
| 2010 | 972 | 16,535 | 12,386 | 4,149 | 17.0 | 12.7 | 4.3 | 1,99 |
| 2011 | 972 | 16,507 | 12,299 | 4,208 | 17.0 | 12.7 | 4.3 | 2,03 |
| 2012 | 972 | 17,006 | 12,064 | 4,942 | 17.5 | 12.4 | 5.1 | 2.14 |
| 2013 | 973 | 17,145 | 11,538 | 5,607 | 17.6 | 11.8 | 5.8 | 2.19(e) |
Demographics for 2007
Source:[14]
| District | Births | Deaths | Growth | Pp (2007) | BR | DR | NGR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Republic of Buryatia | 12,337 | 9,833 | 2,504 | 960,000 | 17.13 | 13.66 | 0.35% |
| Ulan-Ude | 4,260 | 3,517 | 743 | 373,300 | 15.22 | 12.56 | 0.27% |
| Bichursky District | 339 | 318 | 21 | 26,900 | 16.80 | 15.76 | 0.10% |
| Dzhidinsky District | 512 | 309 | 203 | 30,800 | 22.16 | 13.38 | 0.88% |
| Yeravninsky District | 244 | 191 | 53 | 18,600 | 17.49 | 13.69 | 0.38% |
| Zaigrayevsky District | 714 | 630 | 84 | 48,700 | 19.55 | 17.25 | 0.23% |
| Zakamensky District | 492 | 322 | 170 | 30,400 | 21.58 | 14.12 | 0.75% |
| Ivolginsky District | 498 | 320 | 178 | 31,000 | 21.42 | 13.76 | 0.77% |
| Kabansky District | 702 | 779 | -77 | 64,400 | 14.53 | 16.13 | -0.16% |
| Kizhinginsky District | 303 | 192 | 111 | 18,700 | 21.60 | 13.69 | 0.79% |
| Kyakhtinsky District | 629 | 393 | 236 | 40,500 | 20.71 | 12.94 | 0.78% |
| Mukhorshibirsky District | 338 | 319 | 19 | 28,000 | 16.10 | 15.19 | 0.09% |
| Pribaykalsky District | 423 | 357 | 66 | 28,900 | 19.52 | 16.47 | 0.30% |
| Selenginsky District | 628 | 522 | 106 | 47,500 | 17.63 | 14.65 | 0.30% |
| Tarbagataysky District | 205 | 216 | -11 | 16,900 | 16.17 | 17.04 | -0.09% |
| Tunkinsky District | 304 | 249 | 55 | 23,000 | 17.62 | 14.43 | 0.32% |
| Khorinsky District | 314 | 222 | 92 | 19,200 | 21.81 | 15.42 | 0.64% |
| Barguzinsky District | 367 | 272 | 95 | 25,600 | 19.11 | 14.17 | 0.49% |
| Bauntovsky Evenkiysky District | 126 | 92 | 34 | 10,500 | 16.00 | 11.68 | 0.43% |
| Kurumkansky District | 232 | 129 | 103 | 15,600 | 19.83 | 11.03 | 0.88% |
| Muysky District | 179 | 112 | 67 | 15,600 | 15.30 | 9.57 | 0.57% |
| Okinsky District | 73 | 37 | 36 | 5,100 | 19.08 | 9.67 | 0.94% |
| Severo-Baykalsky District | 196 | 161 | 35 | 15,200 | 17.19 | 14.12 | 0.31% |
| Severobaykalsk | 259 | 174 | 85 | 25,600 | 13.49 | 9.06 | 0.44% |
Ethnic groups
According to the 2010 Census,[6] ethnic Russians make up two thirds of the republic's population, while the ethnic Buryats are only 30%. Other groups include Ukrainians (0.6%), Tatars (0.7%), and a host of smaller groups, each accounting for less than 0.5% of the total population.
| Ethnic group |
1926 Census1 | 1939 Census | 1959 Census | 1970 Census | 1979 Census | 1989 Census | 2002 Census | 2010 Census2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| Buryats | 214,957 | 43.8% | 116,382 | 21.3% | 135,798 | 20.2% | 178,660 | 22.0% | 206,860 | 23.0% | 249,525 | 24.0% | 272,910 | 27.8% | 286,839 | 30.0% |
| Soyots | 161 | 0.0% | 2,739 | 0.3% | 3,579 | 0.4% | ||||||||||
| Russians | 258,796 | 52.7% | 393,057 | 72.0% | 502,568 | 74.6% | 596,960 | 73.5% | 647,785 | 72.0% | 726,165 | 69.9% | 665,512 | 67.8% | 630,783 | 66.1% |
| Tatars | 3,092 | 0.6% | 3,840 | 0.7% | 8,058 | 1.2% | 9,991 | 1.2% | 10,290 | 1.1% | 10,496 | 1.0% | 8,189 | 0.8% | 6,813 | 0.7% |
| Ukrainians | 1,982 | 0.4% | 13,392 | 2.5% | 10,183 | 1.5% | 10,769 | 1.3% | 15,290 | 1.7% | 22,868 | 2.2% | 9,585 | 1.0% | 5,654 | 0.6% |
| Evenks | 2,808 | 0.6% | 1,818 | 0.3% | 1,335 | 0.2% | 1,685 | 0.2% | 1,543 | 0.2% | 1,679 | 0.2% | 2,334 | 0.2% | 2,974 | 0.3% |
| Others | 9,440 | 1.9% | 17,277 | 3.2% | 15,384 | 2.3% | 14,186 | 1.7% | 17,630 | 2.0% | 27,519 | 2.7% | 19,969 | 2.0% | 18,360 | 1.9% |
| 1 In 1926, the Buryat-Mongolian ASSR included Aga-Buryatia, Ust-Orda Buryatia, and Olkhonsky District. These territories were transferred to Chita and Irkutsk Oblasts in 1937. Consequently, the results of the 1926 census cannot be compared to the results of the censuses of 1939 and later.
2 17,019 people were registered from administrative databases, and could not declare an ethnicity. It is estimated that the proportion of ethnicities in this group is the same as that of the declared group.[15] | ||||||||||||||||
History
Slab Grave cultural monuments are found in northern, central and eastern Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, north-western China, southern, central-eastern and southern Baikal territory. The people of Slab Grave culture were Mongols.[16][17]
The Xiongnu Empire (209 BC-93 CE) governed territory of modern Buryat Republic and Mongolian scholars prove that the Xiongnu was Mongolic state but some scholars prove that it was Turkic state.

The Merkits lived in the basins of the Selenge River and lower Orkhon River. After a struggle that took over two decades, they were defeated in 1200 and incorporated into the Mongol Empire formed by Genghis Khan. By the time he had united the other Mongol tribes and was given the title "Chinggis Khan" in 1206, the Merkits seem to have disappeared as a separate ethnic group. Those who survived were most likely absorbed by other Mongol tribes, such as the Oirats and others who fled to Kypchaks mixed with them. After the fall of the Yuan Dynasty, they were a clan of a banner in Northern Yuan. The Merkits were the main inhabitants of southern Buryatia.
At the beginning of the 9th – 13th centuries, the Khori-Tümed Mongols lived near the western side of Lake Baikal.In the 13th century, they were the inhabitants in southern Irkutsk and southwestern Buryatia.[18] In 1207, Genghis Khan, after conquering the Khori-Tumed, decided to move some of these groups south and these people eventually settled in Inner Mongolia.
The Bayad Mongols lived in west of Selenge River (Jida river, Kyakhtinsky District) and they moved to the southwest in 17th century.
The Barga Mongols share the same 11 clans into which the Khori-Buryats were divided and they were the main inhabitants of Bargujin Töhöm (modern northern Buryatia).[18] They first apppeared in Buryatia under the name Bairgu in the 6th-7th centuries. The main body of Khori-Barga moved to the area between Ergune river and the Greater Khingan Range where they became subject to the Daurs and Solon Ewenkis. A large body of Barga Khoris fled back east to the Onon river in 1594. When the Manchu-Qing Dynasty attacked the Cossacks in the Ergune and Shilka rivers in 1685-89, those Barga Mongols east of the Ergune River were deported to Inner Mongolia. The Barga, Merkit, Tümed and Bayads were major tribes of Baikal Lake region and specially the Merkit and Tumed were warlike tribes of the 13th century.
Territory of modern Buryat Republic was part of Mongolic Xianbei state (93-234), Rouran Khaganate (330-555), Mongol Empire (1206-1368) and Northern Yuan (1368-1691) until 1691.
The area of the present-day Buryatia was first colonized in the 17th century by Russians in search of wealth, furs, and gold.
In 1923, the Buryat-Mongolian Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic (Buryat: Буряадай Автономито Совет Социалис Республика; Russian: Бурятская Автономная Советская Социалистическая Республика) was created as a result of the merger of State of Buryat-Mongolia and Mongol-Buryat Oblasts. In 1937, Aga Buryatia and Ust-Orda Buryatia were detached from the Buryat-Mongolian ASSR and merged with Chita and Irkutsk Oblasts, respectively. In 1958, the name "Mongol" was removed from the name of the republic. The Buryat ASSR declared its sovereignty in 1990 and adopted the name Republic of Buryatia in 1992. However, it remained an autonomous republic within the Russian Federation.
The Buryat Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic was an Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic in the former Soviet Union.
Politics

The head of the Republic is the Head (formerly President), who is appointed by the President of Russia for a four-year term. Between 1991-2007, the President was Leonid Vasilyevich Potapov, who was elected on July 1, 1994, re-elected in 1998 (with 63.25% of votes), and then re-elected again on June 23, 2002 (with over 67% of votes). Prior to the elections, Potapov was the Chairman of the Supreme Soviet of the Republic—the highest post at that time.
The current Head of the Republic is Vyacheslav Nagovitsyn, who was appointed by Vladimir Putin in 2007.[19]
The Republic's parliament is the People's Khural, popularly elected every four years. The People's Khural has 65 deputies. Alexander Lubsanov is the current Chairman of the People's Khural since 2002.
The Republic's Constitution was adopted on February 22, 1994.
Economy
The republic's economy is composed of important agricultural and commercial products including wheat, vegetables, potatoes, timber, leather, graphite, and textiles. Fishing, hunting, fur farming, sheep and cattle farming, mining, stock raising, engineering, and food processing are also important economic generators.
Education
The higher education institutions of the republic include Buryat State University, Buryat State Academy of Agriculture, East Siberian State Academy of Arts and Culture, and East Siberia State University of Technology and Management.
Religion
As of a 2012 official survey[20] 27.4% of the population adheres to the Russian Orthodox Church, 19.8% to Buddhism, 2% to Rodnovery, Tengrism or Buryat shamanism, 4% declares to be generically unaffiliated Christian (excluding Catholic and Protestant), 1% follows other Orthodox Churches, 1% Protestantism. In addition, 25% of the population declares to be "spiritual but not religious", 13% to be atheist, and 10.8% follows other religion or did not give an answer to the survey.[20]
Tibetan Buddhism and Orthodox Christianity are the most widespread religions in the republic. Many Slavs, who constitute around 67% of the population, are Russian Orthodox. Since the breakup of the USSR in 1991, a small number have converted to various Protestant denominations or to Rodnovery, Slavic Paganism. There are also some Catholics among the Slavs. Most of the Germans (0.11% of the population) are also Orthodox, so are some other non-European groups like Armene (0.23%), Georgian (0.03%), and Soyot (0.37%). Buryats constitute 30.04% of the total population.
Most urban Buryats are either Buddhist or Orthodox, while those in the rural areas often adhere to Yellow shamanism, a mixture of shamanism and Buddhism, or to Black shamanism. There are also Tengrist movements. Siberian Tatars are around 0.7% of the population. However due to isolation from the main body of Tatars, many of them now are either non-religious or Orthodox. Islam is followed by immigrant groups like Azeris and Uzbeks, who constitute another 0.7% of the population.

Tourism
Lake Baikal is a popular tourist destination, especially in summer.
See also
- Music of Buryatia
- Sport in Buryatia
References
- ↑ Президент Российской Федерации. Указ №849 от 13 мая 2000 г. «О полномочном представителе Президента Российской Федерации в федеральном округе». Вступил в силу 13 мая 2000 г. Опубликован: "Собрание законодательства РФ", №20, ст. 2112, 15 мая 2000 г. (President of the Russian Federation. Decree #849 of May 13, 2000 On the Plenipotentiary Representative of the President of the Russian Federation in a Federal District. Effective as of May 13, 2000.).
- ↑ Госстандарт Российской Федерации. №ОК 024-95 27 декабря 1995 г. «Общероссийский классификатор экономических регионов. 2. Экономические районы», в ред. Изменения №5/2001 ОКЭР. (Gosstandart of the Russian Federation. #OK 024-95 December 27, 1995 Russian Classification of Economic Regions. 2. Economic Regions, as amended by the Amendment #5/2001 OKER. ).
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Constitution, Article 5.3
- ↑ Official website of the Head of the Republic of Buryatia. Biography of Vyacheslav Vladimirovich Nagovitsyn
- ↑ Федеральная служба государственной статистики (Federal State Statistics Service) (2004-05-21). "Территория, число районов, населённых пунктов и сельских администраций по субъектам Российской Федерации (Territory, Number of Districts, Inhabited Localities, and Rural Administration by Federal Subjects of the Russian Federation)". Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года (All-Russia Population Census of 2002) (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved 2011-11-01.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 "Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года. Том 1" [2010 All-Russian Population Census, vol. 1]. Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года (2010 All-Russia Population Census) (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service. 2011. Retrieved June 29, 2012.
- ↑ The density value was calculated by dividing the population reported by the 2010 Census by the area shown in the "Area" field. Please note that this value may not be accurate as the area specified in the infobox is not necessarily reported for the same year as the population.
- ↑ Правительство Российской Федерации. Постановление №725 от 31 августа 2011 г. «О составе территорий, образующих каждую часовую зону, и порядке исчисления времени в часовых зонах, а также о признании утратившими силу отдельных Постановлений Правительства Российской Федерации». Вступил в силу по истечении 7 дней после дня официального опубликования. Опубликован: "Российская Газета", №197, 6 сентября 2011 г. (Government of the Russian Federation. Resolution #725 of August 31, 2011 On the Composition of the Territories Included into Each Time Zone and on the Procedures of Timekeeping in the Time Zones, as Well as on Abrogation of Several Resolutions of the Government of the Russian Federation. Effective as of after 7 days following the day of the official publication.).
- ↑ Official the whole territory of Russia according to Article 68.1 of the Constitution of Russia.
- ↑ Constitution, Article 67
- ↑ "Численность населения России, субъектов Российской Федерации в составе федеральных округов, районов, городских поселений, сельских населённых пунктов – районных центров и сельских населённых пунктов с населением 3 тысячи и более человек" [Population of Russia, its federal districts, federal subjects, districts, urban localities, rural localities—administrative centers, and rural localities with population of over 3,000]. Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года (All-Russia Population Census of 2002) (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service. May 21, 2004. Retrieved February 9, 2012.
- ↑ Demoscope Weekly (1989). "Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 г. Численность наличного населения союзных и автономных республик, автономных областей и округов, краёв, областей, районов, городских поселений и сёл-райцентров." [All Union Population Census of 1989. Present population of union and autonomous republics, autonomous oblasts and okrugs, krais, oblasts, districts, urban settlements, and villages serving as district administrative centers]. Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 года (All-Union Population Census of 1989) (in Russian). Institute of Demographics of the State University—Higher School of Economics. Retrieved February 9, 2012.
- ↑ http://www.gks.ru/wps/wcm/connect/rosstat_main/rosstat/ru/statistics/publications/catalog/doc_1137674209312
- ↑
- ↑ http://www.perepis-2010.ru/news/detail.php?ID=6936
- ↑ N.Navaan, Bronze Age of Eastern Mongolia
- ↑ History of Mongolia, Volume I, 2003
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 History of Mongolia, Volume II, 2003
- ↑ "Биография (in Russian)". Retrieved 19 November 2012.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 Arena - Atlas of Religions and Nationalities in Russia. Sreda.org
- ↑ 2012 Survey Maps. "Ogonek", № 34 (5243), 27/08/2012. Retrieved 24-09-2012.
Sources
- Верховный Совет Республики Бурятия. 22 февраля 1994 г. «Республика Бурятия. Конституция», в ред. Закона №332-IV от 7 июля 2008 г. (Supreme Council of the Republic of Buryatia. February 22, 1994 Republic of Buryatia. Constitution, as amended by the Law #332-IV of July 7, 2008. ).
Further reading
- Leisse, Olaf; Utta-Kristin Leisse (September 2007). "A Siberian Challenge: Dealing with Multiethnicity in the Republic of Buryatia". Nationalities Papers 35 (4): 773–788. doi:10.1080/00905990701475178.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Buryatia. |
- Official website of the Republic of Buryatia
- (Russian) Official website of the Republic of Buryatia
- Official website of the Republic of Buryatia (in Buryat)
- (Russian) Buryatia.org, site about life in the Republic of Buryatia
- Article on Buddhism in Buryatia and Mongolia
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||


