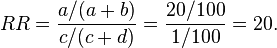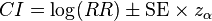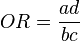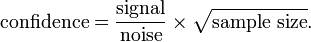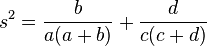Relative risk
In statistics and mathematical epidemiology, relative risk (RR) is the ratio of the probability of an event occurring (for example, developing a disease, being injured) in an exposed group to the probability of the event occurring in a comparison, non-exposed group. Relative risk includes two important features. One, a comparison of risk between two "exposures" puts risks in context, and, two, "exposure" is ensured by having proper denominators for each group representing the exposure [1][2]
| Risk | Disease status | |
|---|---|---|
| Present | Absent | |
| Smoker |  |
 |
| Non-smoker |  |
 |
Consider an example where the probability of developing lung cancer among smokers was 20% and among non-smokers 1%. This situation is expressed in the 2 × 2 table to the right.
Here, a = 20, b = 80, c = 1, and d = 99. Then the relative risk of cancer associated with smoking would be
Smokers would be twenty times as likely as non-smokers to develop lung cancer.
Another term for the relative risk is the risk ratio because it is the ratio of the risk in the exposed divided by the risk in the unexposed.
Statistical use and meaning
Relative risk is used frequently in the statistical analysis of binary outcomes where the outcome of interest has relatively low probability. It is thus often suited to clinical trial data, where it is used to compare the risk of developing a disease, in people not receiving the new medical treatment (or receiving a placebo) versus people who are receiving an established (standard of care) treatment. Alternatively, it is used to compare the risk of developing a side effect in people receiving a drug as compared to the people who are not receiving the treatment (or receiving a placebo). It is particularly attractive because it can be calculated by hand in the simple case, but is also amenable to regression modelling, typically in a Poisson regression framework.
In a simple comparison between an experimental group and a control group:
- A relative risk of 1 means there is no difference in risk between the two groups.
- An RR of < 1 means the event is less likely to occur in the experimental group than in the control group.
- An RR of > 1 means the event is more likely to occur in the experimental group than in the control group.
As a consequence of the Delta method, the log of the relative risk has a sampling distribution that is approximately normal with variance that can be estimated by a formula involving the number of subjects in each group and the event rates in each group (see Delta method).[3] This permits the construction of a confidence interval (CI) which is symmetric around log(RR), i.e.,
where 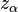 is the standard score for the chosen level of significance and SE the standard error. The antilog can be taken of the two bounds of the log-CI, giving the high and low bounds for an asymmetric confidence interval around the relative risk.
is the standard score for the chosen level of significance and SE the standard error. The antilog can be taken of the two bounds of the log-CI, giving the high and low bounds for an asymmetric confidence interval around the relative risk.
In regression models, the treatment is typically included as a dummy variable along with other factors that may affect risk. The relative risk is normally reported as calculated for the mean of the sample values of the explanatory variables.
Comparison to the odds ratio
Relative risk is different from the odds ratio, although it asymptotically approaches it for small probabilities. In the example of association of smoking to lung cancer considered above, if a is substantially smaller than b, then a/(a + b)  a/b. And if similarly c is much smaller than d, then c/(c + d)
a/b. And if similarly c is much smaller than d, then c/(c + d)  c/d. Thus
c/d. Thus
This is the odds ratio.
In fact, the odds ratio has much wider use in statistics, since logistic regression, often associated with clinical trials, works with the log of the odds ratio, not relative risk. Because the log of the odds ratio is estimated as a linear function of the explanatory variables, the estimated odds ratio for 70-year-olds and 60-year-olds associated with type of treatment would be the same in a logistic regression models where the outcome is associated with drug and age, although the relative risk might be significantly different. In cases like this, statistical models of the odds ratio often reflect the underlying mechanisms more effectively.
Since relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effectiveness, the distinction is important especially in cases of medium to high probabilities. If action A carries a risk of 99.9% and action B a risk of 99.0% then the relative risk is just over 1, while the odds associated with action A are more than 10 times higher than the odds with B.
In medical research, the odds ratio is commonly used for case-control studies, as odds, but not probabilities, are usually estimated.[4] Relative risk is used in randomized controlled trials and cohort studies.[5]
In statistical modelling, approaches like poisson regression (for counts of events per unit exposure) have relative risk interpretations: the estimated effect of an explanatory variable is multiplicative on the rate, and thus leads to a risk ratio or relative risk. Logistic regression (for binary outcomes, or counts of successes out of a number of trials) must be interpreted in odds-ratio terms: the effect of an explanatory variable is multiplicative on the odds and thus leads to an odds ratio.
Statistical significance (confidence) and relative risk
Whether a given relative risk can be considered statistically significant is dependent on the relative difference between the conditions compared, the amount of measurement and the noise associated with the measurement (of the events considered). In other words, the confidence one has, in a given relative risk being non-random (i.e. it is not a consequence of chance), depends on the signal-to-noise ratio and the sample size.
Expressed mathematically, the confidence that a result is not by random chance is given by the following formula by Sackett:[6]
For clarity, the above formula is presented in tabular form below.
Dependence of confidence with noise, signal and sample size (tabular form)
| Parameter | Parameter increases | Parameter decreases |
|---|---|---|
| Noise | Confidence decreases | Confidence increases |
| Signal | Confidence increases | Confidence decreases |
| Sample size | Confidence increases | Confidence decreases |
In words, the confidence is higher if the noise is lower and/or the sample size is larger and/or the effect size (signal) is increased. The confidence of a relative risk value (and its associated confidence interval) is not dependent on effect size alone. If the sample size is large and the noise is low a small effect size can be measured with great confidence. Whether a small effect size is considered important is dependent on the context of the events compared.
In medicine, small effect sizes (reflected by small relative risk values) are usually considered clinically relevant (if there is great confidence in them) and are frequently used to guide treatment decisions. A relative risk of 1.10 may seem very small, but over a large number of patients will make a noticeable difference. Whether a given treatment is considered a worthy endeavour is dependent on the risks, benefits and costs.
Tests
The distribution of the log Relative Risk is approximately normal with:
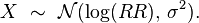
The standard error for the log (Relative Risk) is approximately[citation needed]:
![SE(log(RR))={\sqrt {[1/a+1/c]-[1/(a+b)+1/(c+d)]}}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/2/7/6/a/276a196327be5dbdf78e32141ca67fac.png)
This is an asymptotic approximation.
The risk ratio confidence intervals are based on the sampling distribution of
This is considered to be (approximately) normal with
and
where m is the mean and s2 is the variance. The 95% confidence intervals (CI) for the relative risk are
In applications using this estimator the sample size should be at least 25.
Worked example
| Example 1: risk reduction | Example 2: risk increase | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental group (E) | Control group (C) | Total | (E) | (C) | Total | |
| Events (E) | EE = 15 | CE = 100 | 115 | EE = 75 | CE = 100 | 175 |
| Non-events (N) | EN = 135 | CN = 150 | 285 | EN = 75 | CN = 150 | 225 |
| Total subjects (S) | ES = EE + EN = 150 | CS = CE + CN = 250 | 400 | ES = 150 | CS = 250 | 400 |
| Event rate (ER) | EER = EE / ES = 0.1, or 10% | CER = CE / CS = 0.4, or 40% | EER = 0.5 (50%) | CER = 0.4 (40%) | ||
| Equation | Variable | Abbr. | Example 1 | Example 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CER − EER | < 0: absolute risk reduction | ARR | (−)0.3, or (−)30% | N/A |
| > 0: absolute risk increase | ARI | N/A | 0.1, or 10% | |
| (CER − EER) / CER | < 0: relative risk reduction | RRR | (−)0.75, or (−)75% | N/A |
| > 0: relative risk increase | RRI | N/A | 0.25, or 25% | |
| 1 / (CER − EER) | < 0: number needed to treat | NNT | (−)3.33 | N/A |
| > 0: number needed to harm | NNH | N/A | 10 | |
| EER / CER | relative risk | RR | 0.25 | 1.25 |
| (EE / EN) / (CE / CN) | odds ratio | OR | 0.167 | 1.5 |
| EER − CER | attributable risk | AR | (−)0.30, or (−)30% | 0.1, or 10% |
| (RR − 1) / RR | attributable risk percent | ARP | N/A | 20% |
| 1 − RR (or 1 − OR) | preventive fraction | PF | 0.75, or 75% | N/A |
- Example 3: Ratios are presented for each of experimental and control groups. In the disease-risk 2 × 2 table above, suppose a + c = 1 and b + d = 1 and the total number of patients and healthy people be m and n, respectively. Then prevalence ratio becomes p = m/(m + n). We can put q = m/n = p/(1 − p). Thus
- If p is small enough, then q would be small enough and either of (b/d)q and (a/c)q would be small enough to be regarded as 0 compared with 1. RR would be reduced to the odd ratio as above.
- Among Japanese, not a small fraction of patients of Behçet's disease are bestowed with a specific HLA type, namely HLA-B51 gene.[7] In a survey, the proportion is 63% of the patients with this gene, while in healthy people the ratio is 21%.[7] If the figures are considered to be representative for most Japanese, using the values of 12,700 patients in Japan in 1984 and the Japanese population about 120 million in 1982, then RR = 6.40. Compare with the odd ratio 6.41.
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Statistics for relative risk. |
- Absolute risk reduction
- (Population) attributable risk
- Confidence interval
- Number needed to treat (NNT)
- Number needed to harm (NNH)
- OpenEpi
- Epi Info
- The rare disease assumption
Statistical ratios
References
- ↑ Sistrom CL, Garvan CW (January 2004). "Proportions, odds, and risk". Radiology 230 (1): 12–9. doi:10.1148/radiol.2301031028. PMID 14695382.
- ↑ Weddell, Angie. "Evidence from Safety Research to Update Cycling Training Materials in Canada". University of British Columbia. Retrieved 30 September 2013.
- ↑ See e.g. Stata FAQ on CIs for odds ratios, hazard ratios, IRRs and RRRs at http://www.stata.com/support/faqs/stat/2deltameth.html
- ↑ Deeks J (1998). "When can odds ratios mislead? Odds ratios should be used only in case-control studies and logistic regression analyses". BMJ 317 (7166): 1155–6. PMC 1114127. PMID 9784470.
- ↑ Medical University of South Carolina. Odds ratio versus relative risk. Accessed on: September 8, 2005.
- ↑ Sackett DL. Why randomized controlled trials fail but needn't: 2. Failure to employ physiological statistics, or the only formula a clinician-trialist is ever likely to need (or understand!). CMAJ. 2001 Oct 30;165(9):1226-37. PMID 11706914. Free Full Text.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Ohno S, Ohguchi M, Hirose S, Matsuda H, Wakisaka A, Aizawa M (1982). "Close association of HLA-BW51, MT2 and Behçet's disease," In Inaba, G, ed. (1982). Behçet's Disease : Pathogenetic Mechanism and Clinical Future: Proceedings of the International Conference on Behçet's Disease, held October 23–24, 1981, pp. 73–79, Tokyo: University of Tokyo Press, ISBN 0-86008-322-5.
External links
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||