Reduction
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Look up reduce, reduced, or reduction in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Reduction, reduced, or reduce may refer to:
Science
Chemistry
- Reduction, part of a reduction-oxidation (redox) reaction in which atoms have their oxidation state changed.
- Organic redox reaction, a redox reaction that takes place with organic compounds
- Reduced gas, a gas with a low oxidation number
- Reducing agent, element or compound in a redox reaction that donates an electron to another species
- Reducing atmosphere, an oxygen-poor gaseous environment that inhibits oxidation
- Reductase, an enzyme that catalyzes a reduction reaction
- Reduction potential, a measure of the tendency of a chemical species to acquire electrons
- Ore reduction: see smelting
Computing and algorithms
- Reduction (complexity), a transformation of one problem into another problem
- Graph reduction, an efficient version of non-strict evaluation
- Strength reduction, a compiler optimization where a function of some systematically changing variable is calculated more efficiently by using previous values of the function
- Reduction (recursion theory), given sets A and B of natural numbers, is it possible to effectively convert a method for deciding membership in B into a method for deciding membership in A?
- L-reduction, a transformation of optimization problems which keeps the approximability features
- Variance reduction, a procedure used to increase the precision of the estimates that can be obtained for a given number of iterations
- Partial order reduction, a technique for reducing the size of the state-space to be searched by a model checking algorithm
- Bit Rate Reduction, an audio compression method
- Reduce (computer algebra system), a general-purpose computer algebra system geared towards applications in physics
- Reduce (higher-order function), in functional programming, a family of higher-order functions that process a data structure in some order and build up a return value
- Reduced instruction set computing, a CPU design philosophy that favors an instruction set reduced both in size and complexity of addressing modes, in order to enable easier implementation, greater instruction level parallelism, and more efficient compilers
Pure mathematics and statistics
- Reducible may be the opposite of irreducible (mathematics)
- Reduction (mathematics), the rewriting of an expression into a simpler form
- Beta reduction, the rewriting of an expression from lambda calculus into a simpler form
- Subject reduction or preservation, a rewrite of an expression that does not change its type
- Reduction system, reduction strategy, the application of rewriting systems to eliminate reducible expressions
- Dimension reduction, the process of reducing the number of random variables under consideration
- Lattice reduction, given an integer lattice basis as input, to find a basis with short, nearly orthogonal vectors
- Reduction of order, a technique for solving second-order ordinary differential equations
- Relation reduction, the extent to which a given relation is determined by an indexed family or a sequence of other relations, called the relation dataset
- Reduction of the structure group, for a
 -bundle
-bundle  and a map
and a map 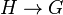 an
an 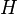 -bundle
-bundle 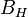 such that the pushout
such that the pushout  is isomorphic to
is isomorphic to 
- Reduced form, in statistics, an equation which relates the endogenous variable X to all the available exogenous variables, both those included in the regression of interest (W) and the instruments (Z)
- Reduced ring, a ring with no non-zero nilpotent elements
- Reduced residue system, a set of φ(n) integers such that each integer is relatively prime to n and no two are congruent modulo n
- Reduced product, a construction that generalizes both direct product and ultraproduct
- Reduced word, in a free group, a word with no adjacent generator-inverse pairs
- Reduced homology, a minor modification made to homology theory in algebraic topology, designed to make a point have all its homology groups zero
- Reduced row echelon form, a certain reduced row echelon form of a matrix which completely and uniquely determines its row space
Physics
- Dimensional reduction, the limit of a compactified theory where the size of the compact dimension goes to zero
- Reduction criterion, in quantum information theory, a necessary condition a mixed state must satisfy in order for it to be separable
- Reduced properties of a fluid, defined based on the fluid's critical point:
- Reduced pressure
- Reduced temperature
- Reduced volume
- Reduced mass, the "effective" inertial mass appearing in the two-body problem of Newtonian mechanics
Technology
- Noise reduction, acoustic or signal processing
- Reduction drive, a mechanical device to shift rotational speed
Philosophy
- Eidetic reduction, a technique in the study of essences in phenomenology whose goal is to identify the basic components of phenomena
- Intertheoretic reduction, in philosophy of science, one theory makes predictions that perfectly or almost perfectly match the predictions of a second theory
- Reduction (philosophy), the process by which one object, property, concept, theory, etc., is shown to be entirely dispensable in favor of another
- Reductionism, a range of philosophical systems
Medicine
- Weight loss
- Selective reduction (or fetal reduction), the practice of reducing the number of fetuses in a multifetal pregnancy
- Reduction (orthopedic surgery), a medical procedure to restore a fracture or dislocation to the correct alignment
- Ventricular reduction, a type of operation in cardiac surgery
- Urea reduction ratio (URR), a dimensionless number used to quantify hemodialysis treatment adequacy
Cosmetic surgery
Epidemiology
- Relative risk reduction, the absolute risk reduction by the control event rate
- Absolute risk reduction, the decrease in risk of a given activity or treatment in relation to a control activity or treatment
Linguistics
- Accent reduction, modifying one's foreign accent towards that of a native speaker
- Vowel reduction, any change in vowel quality perceived as "weakening"
- Relaxed pronunciation, slurring of syllables of common words
- Definite article reduction, use of vowel-less forms of the English definite article in Northern England
Politics and social policy
- Demand reduction, efforts aimed at reducing public desire for illegal and illicit drugs
- Harm reduction, policies designed to reduce the harmful consequences associated with recreational drug use and other high risk activities
- Immigration reduction
- Paperwork reduction, reducing red tape
- Poverty reduction
- Reduced price meal, a reimbursable meal (or snack) served in the USA to a child who qualifies because of low family’s income.
- Risk reduction (disambiguation), risk management by reducing the severity of an eventuated risk
- Reuse
- Supply reduction, efforts aimed at disrupting the manufacturing and distribution supply chains for illegal and illicit drugs
History
- Lithic reduction, in Stone Age toolmaking, to detach lithic flakes from a lump of tool stone
- Reduction can refer to the siege and capture of a fortified place
- Reduction (Sweden), return to the Crown of fiefs that had been granted to the Swedish nobility
- Indian Reductions, settlements in Spanish America intended to assimilate Indians
Other
- Ego reduction, predicated on the use of Sigmund Freud's concept of the ego
- Piano reduction, sheet music for the piano that was once music for other instruments that was reduced to its most basic components within a two line staff for piano
- Reduction (cooking), the process of thickening or intensifying the flavor of a liquid mixture such as a soup, sauce, wine, or juice by evaporation
- Reductio ad absurdum, a form of argument in which a proposition is disproven by following its implications to an absurd consequence
- Reduction in rank, military law
- Reduction to practice, in United States patent law, the embodiment of the concept of an invention
- Reduce (waste), minimizing waste
See also
- Prevention (disambiguation)
| |
This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the same title. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.