Raton Basin
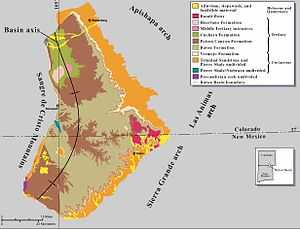
The Raton Basin is a geologic structural basin in southern Colorado and northern New Mexico. It takes its name from Raton Pass and the town of Raton, New Mexico. In extent, the basin is approximately 50 miles (80 km) east-west, and 90 miles (140 km) north-south, in Huerfano and Las Animas Counties, Colorado, and Colfax County, New Mexico.
The basin has long been a source of coal, and more recently of coalbed methane. It is known for its well-preserved exposures of the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary (K–T boundary), which has been intensively studied for evidence of meteorite impact.
Topography
Although structurally a basin, the Raton Basin forms a topographic high dissected by eastward-flowing streams such as the Purgatoire River. The basin forms the foothills of the Rocky Mountains, immediately east of the Sangre de Cristo Range.
Geology
The sedimentary beds that form the basin are of Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Paleogene age. In the eastern part of the basin, the sedimentary section is capped by flows of basalt of Miocene age.[1] The basin is highly asymmetrical, the beds dipping more steeply on the west side than the east.
The sedimentary rocks of the basin are extensively intruded by igneous plugs, dikes and sills of Eocene to Oligocene age. Two large granitic intrusives near the axis of the basin form East Spanish Peak and West Spanish Peak. Dikes of felsic to intermediate composition radiate outward from East and West Spanish Peaks, and on the north side of the peaks have the appearance of large stone walls. Dikes of mafic and ultramafic composition trend east-northeast to west-southwest across the basin.[2] Basaltic sills tend to intrude along the coal beds.
The site of the Raton Basin was a coastal plain at the end of Cretaceous and beginning of Paleogene time, and has a well-preserved sequence of rocks spanning the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary. For this reason, the Raton Basin has been studied for evidence of the iridium anomaly thought to be evidence for a large meteor impact at the end of the Cretaceous that is in turn thought to have caused the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. The boundary is represented in the basin by a 1-cm thick tonstein clay layer which has been found to contain anomalously high concentrations of iridium. The boundary clay layer is accessible to the public at Trinidad Lake State Park, among other places in the basin.[3]
Natural resources
Coal
Bituminous coal mines opened in the Raton Basin in 1873. Walsenburg, Colorado, Trinidad, Colorado and Raton, New Mexico became coal-mining towns. The coal deposits are in the Vermejo Formation (Cretaceous) and overlying Raton Formation (Cretaceous and Paleocene).[4] Most of the mines were underground room-and-pillar, although in later years some mines in New Mexico used longwall mining. Some strip mining was done in New Mexico.
Much of the mining on the Colorado side of the basin supplied the steel mills at Pueblo, Colorado. Production through 1975 was 326 million short tons (295 million tonnes).[5] There are currently no active coal mines in the basin, although the New Elk coal mine, inactive since 1989 and now owned by Cline Mining of Canada, is expected to reopen in 4th quarter 2010.[6][7]
Oil and gas
A number of wells have been drilled over the years seeking conventional oil and natural gas, but none has been produced in economic quantities in the basin. In April 2008, Pioneer Natural Resources announced that they were developing natural gas reserves in the Cretaceous Pierre Shale on their leasehold in the Raton Basin.
Coalbed methane
Coals in the Raton Basin were long known to be "gassy." During development of the Morely mine in the early part of the 20th century, two gas relief wells were drilled into the coal, as a safety measure to drain off gas ahead of mining.[8]
The first wells seeking to produce coalbed methane were drilled in the Raton Basin in 1982.[9] Thousands of wells have successfully extracted coalbed methane from the Vermejo Formation and Raton Formation coals. The productive coalbed methane area now covers the central part of the basin, and straddles the Colorado-New Mexico state line. The two major producing companies are Pioneer Natural Resources (on the Colorado side) and El Paso Corporation (on the New Mexico side).
In 2007, the coalbed methane field of the Raton Basin produced 124 billion cubic feet of gas, making it the 17th largest source of natural gas in the United States.[10]
References
Johnson, Ronald C., and Thomas M. Finn (2001) Potential for a Basin-Centered Gas Accumulation in the Raton Basin, Colorado and New Mexico, US Geological Survey, Bulletin 2184-B.
- ↑ Charles L. Pillmore (1991) Geology and Coal Resources of the Raton Coalfield, US Geological Survey, Bulletin 1972(D).
- ↑ Ross B. Johnson (1969) Geologic Map of the Trinidad Quadrangle, South-Central Colorado, US Geological Survey, Miscellaneous Geologic Investigations Map I-558.
- ↑ "Online guide to the continental Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary in the Raton basin, Colorado and New Mexico". USGS. Retrieved 2010-03-30.
- ↑ Ross B. Johnson (1961) Coal Resources of the Trinidad Coal Field in Huerfano and Las Animas Counties, Colorado, US Geological Survey, Bulletin 1112-E.
- ↑ R.M Flores and L.R. Bader (1999) A Summary of Tertiary Coal resources of the Raton Basin, Colorado and New Mexico, US Geological Survey, Professional paper 1625-A, p.13.
- ↑ "New Elk Coal Mine expects production in 2013," Mining Engineering, November 2010, p.44.
- ↑ Cline Mining, New Elk Coal, Colorado, accessed 19 November 2010.
- ↑ R.M Flores and L.R. Bader (1999) A Summary of Tertiary Coal resources of the Raton Basin, Colorado and New Mexico, US Geological Survey, Professional paper 1625-A, p.13.
- ↑ H. Thomas Hemborg (1998) Spanish Peak Field, Las Animas County, Colorado, Colorado Geological Survey, Resource Series 33.
- ↑ US Energy Information Administration, Top 100 oil and gas fields, PDF file, retrieved 18 February 2009.
Coordinates: 37°00′N 105°00′W / 37.0°N 105.0°W