Raphanin
| Raphanin | |
|---|---|
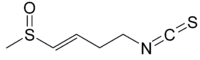 | |
| IUPAC name 4-Isothiocyanato-1-(methylsulfinyl)but-1-ene | |
| Other names Sulforaphen; Sulforaphene; Sativin | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 592-95-0 |
| PubChem | 6433206 |
| ChemSpider | 16736047 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C6H9NOS2 |
| Molar mass | 175.27 g mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Raphanin is the main sulfur component found in radish seeds of Raphanus sativus and is also found in broccoli and red cabbage.[1][2] It was first described by G. Ivanovics and S. Horvath in 1947.[3][4] Raphanin inhibits activity of viruses, some fungi and various bacteria including Staphylococus, Streptococus, Pneumococcus and Escherichia coli (see table). The effect is stronger against Gram-positive than Gram-negative bacteria and against DNA than RNA viruses; it is suppressed by serum and by sulfur compounds such as hydrogen sulfide, mercaptoacetic acid, cystine and glutathione.[5][6][3][7][8] The antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral effects from consuming radishes were recognized in Traditional Chinese medicine.[9]Given that Raphanin can be chiefly responsible for keeping the production of thyroxine and calcitonin in normal balance, in Russia, radishes have long been used for treating both types of thyroid problems.[10]However, in the abstract to his 1947 paper, Ivanovics noted that because raphanin is highly toxic, it did not "hold the promise of a useful therapeutic agent." [11]
| Bacteria | MIC (mg/mL) |
|---|---|
| Staphylococus | 0.04 |
| Shigella dysenteriae | 0.125 |
| Salmonella typhi | 0.125 |
| Escherichia coli | 0.2 |
See also
References
- ↑ Sinha, Nirmal K.; Hui, Y. H.; Muhammad Siddiq, Jasim Ahmed (21 December 2010). Handbook of Vegetables and Vegetable Processing. John Wiley and Sons. p. 156. ISBN 978-0-8138-1541-1. Retrieved 28 August 2011.
- ↑ Michael Meyer and Sieghard T. Adam. "Comparison of glucosinolate levels in commercial broccoli and red cabbage from conventional and ecological farming". European Food Research and Technology 226 (6): 1429–1437. doi:10.1007/s00217-007-0674-0.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Baron, Abraham Louis (1950). Handbook of antibiotics. Reinhold. p. 215. Retrieved 28 August 2011.
- ↑ Ivãnovics, G. & S. Horvãth (1947). "Raphanin, an Antibacterial Principle of the Radish (Raphanus sativus)". Nature 160 (4061): 297–298. doi:10.1038/160297a0. PMID 20261763.
- ↑ Florey, Howard (1949). Antibiotics: a survey of penicillin, streptomycin, and other antimicrobial substances from fungi, actinomycetes, bacteria, and plants. Oxford University Press. pp. 625–6. Retrieved 28 August 2011.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Chang, Hson-Mou; Pui-Hay, Paul; Yao, Sih-Cheng (1 October 2001). Pharmacology and Applications of Chinese Material Medical. World Scientific. p. 969. ISBN 978-981-02-3694-6. Retrieved 28 August 2011.
- ↑ Acta microbiologica Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae. Magyar Tudományos Akadémia. 1968. pp. 311–3. Retrieved 28 August 2011.
- ↑ Summers, Sean (30 September 2007). World History on Satan's Diet. Wheatmark, Inc. p. 4. ISBN 978-1-58736-806-6. Retrieved 28 August 2011.
- ↑ Hu, Shiu-ying (2005). Food plants of China. Chinese University Press. p. 132. ISBN 978-962-996-229-6. Retrieved 28 August 2011.
- ↑ "Radishes". Natural Pedia. Retrieved 4 September 2011.
- ↑ Ivànovics, G. and S. Horvath (1947). "Isolation and Properties of Raphanin, an Antibacterial Substance from Radish Seed". Experimental Biology and Medicine 66 (3): 625–630. PMID 18900045.
External links
- A patent for: Poisonless sulfur free of noxious ingredients and method for manufacturing the same , includes discussion of raphanin
- Rawsome!: maximizing health, energy, and culinary delight with the raw foods diet