Range Minimum Query
Given an array ![A[1,n]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/4/6/6/3/466334ddbb9585cfc7f5dcd9e3e81a37.png) of
of  objects taken from a well-ordered set (such as numbers), a Range Minimum Query (or RMQ) from
objects taken from a well-ordered set (such as numbers), a Range Minimum Query (or RMQ) from  to
to  asks for the position of a minimum element in the sub-array
asks for the position of a minimum element in the sub-array ![A[i,j]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/2/4/e/d/24edb2ea71428b08548c56890a88df9b.png) .
.
For example, when ![A=[0,5,2,5,4,3,1,6,3]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/7/f/d/d/7fddc04800686d0568d254622829962d.png) , then the answer to the range minimum query for the
, then the answer to the range minimum query for the ![A[3,8]=[2,5,4,3,1,6]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/b/a/c/b/bacb83ec4c446910ad6d7658aec8ab78.png) is
is 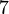 , as
, as ![A[7]=1](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/f/7/f/c/f7fc9ad4ddc3a0730a41a7b7895d5b5c.png) .
.
In a typical setting, the array 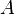 is static, i.e., elements are not inserted or deleted during a series of queries, and the queries to be answered on-line (i.e., the whole set of queries are not known in advance to the algorithm). In this case a suitable preprocessing the array into a data structure (often called a preprocessing scheme) ensures faster query answering.
is static, i.e., elements are not inserted or deleted during a series of queries, and the queries to be answered on-line (i.e., the whole set of queries are not known in advance to the algorithm). In this case a suitable preprocessing the array into a data structure (often called a preprocessing scheme) ensures faster query answering.
It is known that a 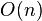 -time preprocessing is sufficient to answer subsequent queries in
-time preprocessing is sufficient to answer subsequent queries in 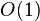 time. The space of the resulting scheme is actually very small, namely
time. The space of the resulting scheme is actually very small, namely 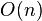 bits (see Fischer & Heun (2007)).
bits (see Fischer & Heun (2007)).
RMQs can be used to solve the lowest common ancestor problem, and is used as a tool for many tasks in exact and approximate string matching.
References
- Berkman, Omer; Vishkin, Uzi (1993), "Recursive Star-Tree Parallel Data Structure", SIAM Journal on Computing 22 (2): 221–242, doi:10.1137/0222017
- Bender, Michael; Farach-Colton, Martin (2000), "The LCA Problem Revisited", Lecture Notes in Computer Science 1776, Springer-Verlag, pp. 88–94, doi:10.1007/10719839_9
- Fischer, Johannes; Heun, Volker (2007), "A New Succinct Representation of RMQ-Information and Improvements in the Enhanced Suffix Array.", Proceedings of the International Symposium on Combinatorics, Algorithms, Probabilistic and Experimental Methodologies, Lecture Notes in Computer Science 4614, Springer-Verlag, pp. 459–470, doi:10.1007/978-3-540-74450-4_41