Radiant energy density
In radiometry, radiant energy density is the measure of the amount of radiant energy per unit volume at a given location and time.[1] Its SI unit is joule per cubic metre (J/m3).
It is defined by
where
Relation to other radiometric quantities
Because radiation always transmits the energy,[2] it is useful to wonder what the speed of the transmission is. If all the radiation at given location propagates in the same direction, then the radiant flux through a unit area perpendicular to the propagation direction is expressed by radiant flux density, whose value is
where
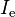 is the radiant flux density (i.e. radiant flux per unit area),
is the radiant flux density (i.e. radiant flux per unit area), is the speed of light (generally radiation propagation speed),
is the speed of light (generally radiation propagation speed), is the radiant energy density.
is the radiant energy density.
Contrarily if the radiation intensity is equal in all directions, like in a cavity in a thermodynamic equilibrium, then the energy transmition is best described by radiance (i.e. radiant flux per unit area and unit solid angle), whose value is
Radiant exitance through a small opening from such cavity is 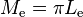 .[4] These relations can be used for example in the black body radiation equations derivation.
.[4] These relations can be used for example in the black body radiation equations derivation.
References
- ↑ IUPAC. Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book"). Radiant energy density. Compiled by A. D. McNaught and A. Wilkinson. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford (1997). XML on-line corrected version (2006-) created by M. Nic, J. Jirat, B. Kosata; updates compiled by A. Jenkins. ISBN 0-9678550-9-8. doi:10.1351/goldbook.R05040. Last update: 2012-08-19; version: 2.3.2. Visited 2013-10-07.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Karel Rusňák. Přenos energie elektromagnetickým vlněním. Department of Physics, Faculty of Applied Sciences, University of West Bohemia. 2005-11. Visited 2013-10-06
- ↑ Max Plack. The Theory of Heat Radiation. Equation 21. 1914.
- ↑ Max Plack. The Theory of Heat Radiation. Equation 7. 1914.
| Quantity | Unit | Dimension | Notes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Symbol[nb 1] | Name | Symbol | Symbol | ||||
| Radiant energy | Qe[nb 2] | joule | J | M⋅L2⋅T−2 | energy | |||
| Radiant flux | Φe[nb 2] | watt | W or J/s | M⋅L2⋅T−3 | radiant energy per unit time, also called radiant power. | |||
| Spectral power | Φeλ[nb 2][nb 3] | watt per metre | W⋅m−1 | M⋅L⋅T−3 | radiant power per wavelength. | |||
| Radiant intensity | Ie | watt per steradian | W⋅sr−1 | M⋅L2⋅T−3 | power per unit solid angle. | |||
| Spectral intensity | Ieλ[nb 3] | watt per steradian per metre | W⋅sr−1⋅m−1 | M⋅L⋅T−3 | radiant intensity per wavelength. | |||
| Radiance | Le | watt per steradian per square metre | W⋅sr−1⋅m−2 | M⋅T−3 | power per unit solid angle per unit projected source area. confusingly called "intensity" in some other fields of study. | |||
| Spectral radiance | Leλ[nb 3] or Leν[nb 4] |
watt per steradian per metre3 or watt per steradian per square |
W⋅sr−1⋅m−3 or W⋅sr−1⋅m−2⋅Hz−1 |
M⋅L−1⋅T−3 or M⋅T−2 |
commonly measured in W⋅sr−1⋅m−2⋅nm−1 with surface area and either wavelength or frequency. | |||
| Irradiance | Ee[nb 2] | watt per square metre | W⋅m−2 | M⋅T−3 | power incident on a surface, also called radiant flux density. sometimes confusingly called "intensity" as well. | |||
| Spectral irradiance | Eeλ[nb 3] or Eeν[nb 4] |
watt per metre3 or watt per square metre per hertz |
W⋅m−3 or W⋅m−2⋅Hz−1 |
M⋅L−1⋅T−3 or M⋅T−2 |
commonly measured in W⋅m−2⋅nm−1 or 10−22 W⋅m−2⋅Hz−1, known as solar flux unit.[nb 5] | |||
| Radiant exitance / Radiant emittance |
Me[nb 2] | watt per square metre | W⋅m−2 | M⋅T−3 | power emitted from a surface. | |||
| Spectral radiant exitance / Spectral radiant emittance |
Meλ[nb 3] or Meν[nb 4] |
watt per metre3 or watt per square |
W⋅m−3 or W⋅m−2⋅Hz−1 |
M⋅L−1⋅T−3 or M⋅T−2 |
power emitted from a surface per unit wavelength or frequency. | |||
| Radiosity | Je | watt per square metre | W⋅m−2 | M⋅T−3 | emitted plus reflected power leaving a surface. | |||
| Spectral radiosity | Jeλ[nb 3] | watt per metre3 | W⋅m−3 | M⋅L−1⋅T−3 | emitted plus reflected power leaving a surface per unit wavelength | |||
| Radiant exposure | He | joule per square metre | J⋅m−2 | M⋅T−2 | also referred to as fluence | |||
| Radiant energy density | ωe | joule per metre3 | J⋅m−3 | M⋅L−1⋅T−2 | ||||
| See also: SI · Radiometry · Photometry | ||||||||
- ↑ Standards organizations recommend that radiometric quantities should be denoted with a suffix "e" (for "energetic") to avoid confusion with photometric or photon quantities.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Alternative symbols sometimes seen: W or E for radiant energy, P or F for radiant flux, I for irradiance, W for radiant emittance.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 Spectral quantities given per unit wavelength are denoted with suffix "λ" (Greek) to indicate a spectral concentration. Spectral functions of wavelength are indicated by "(λ)" in parentheses instead, for example in spectral transmittance, reflectance and responsivity.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Spectral quantities given per unit frequency are denoted with suffix "ν" (Greek)—not to be confused with the suffix "v" (for "visual") indicating a photometric quantity.
- ↑ NOAA / Space Weather Prediction Center includes a definition of the solar flux unit (SFU).

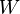 is the amount of radiant energy in some
is the amount of radiant energy in some  is the
is the 
