Racer goby
| Racer goby | |
|---|---|
 | |
| The Racer Goby from the Bug River, Poland | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Perciformes |
| Suborder: | Gobioidei |
| Family: | Gobiidae |
| Subfamily: | Benthophilinae |
| Genus: | Babka Iljin, 1927 |
| Species: | B. gymnotrachelus |
| Binomial name | |
| Babka gymnotrachelus (Kessler, 1857) | |
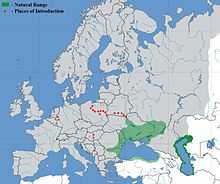 | |
| The range of the racer goby | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Babka gymnotrachelus, the Racer goby, is a species of goby native to fresh, sometimes brackish, waters, of the Black Sea basin.[2] It is a Ponto-Caspian relict species. The species is related to a monotypic genus Babka, which was considered as subgenus of Neogobius genus earlier, but now it is erected based on the molecular analysis.[3][4]
Characteristics

It has 7–8 dorsal spines, 14–18 dorsal soft rays, a single anal spine and 12–16 anal soft rays. This species is distinguished from its congeners by the multiple characteristics. It has diagonal bars of irregular position and shape. The first branched ray of second dorsal is about as long as its penultimate ray. It lacks scales on midline of nape, anterior to its preoperculum. It has a pelvic-disc fraenum with small rounded lobes and length less than 1/6 of width at base. It has 54-62 + 2-3 scales in midlateral series. The posterior part of first dorsal has no black spot.
Ecology
Range
This goby inhabits the coasts of Turkey, the rivers of the Caucasus, including Inguri, Rioni and the rivers of Kolkhida, including Lake Paliastomi, Lake Suzha. In the north-western Black Sea it inhabits the Dnieper-Bug Estuary, Dniester Estuary, near the Tendra sandbar and Berezan Island. In the Danube River it is widspread up to Vidin, and lives in tributaries and lakes of Danube delta, including Brateş, Kahul, Yalpug, Katlabuh, Kitay, Razelm, etc. It inhabits the Dniester River and its tributaries, including Zbruch, Zhvanchik, Smotrych, Răut, Bîc, Dubăsari Reservoir. It is common in the Southern Bug River and in the Dnieper River as far as Kiev. It lives in the Kamchiya River and Lake Shablensko in Bulgaria. In the Sea of Azov it is in Taganrog Bay and the Don, Aksay, Seversky Donets rivers. Also inhabits the Caspian Sea, where presented by the subspecies Babka gymnotrachelus macrophthalmus.
The racer goby inhabits but is non-indigenous in the rivers of the Baltic basin, including the Bug and Vistula.[5][6][7] It was also introduced in the Middle Danube, in Hungary.[8] Through the Danube River this fish species was introduced to the Rhine River, were it is occurred since 2010.[9]
Feeding
In the Dniester Estuary half of its diet consists of fish. The rest is a mix of crustaceans (Corophiidae) (29.6%), molluscs (Dreissena, Adacna, Monodacna) (12,5%) and polychaetes (Hypania invalida).[10] In the Dnieper River near Kiev the diet consists of molluscs Dreissena sp., amphipods and sewage worms Tubifex tubifex.
Look also
References
| External identifiers for Racer goby | |
|---|---|
| Encyclopedia of Life | 224378 |
| ITIS | 172070 |
| NCBI | 320567 |
| WoRMS | 126914 |
| Also found in: FishBase | |
- ↑ Freyhof, J. & Kottelat, M. 2008. Babka gymnotrachelus. In: IUCN 2013. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.1. <www.iucnredlist.org>. Downloaded on 31 July 2013.
- ↑ Smirnov A.I. (1986) Perch-likes (gobiids), scorpionfishes, flatfishes, clingfishes, anglerfishes [in:] Fauna of Ukraine, Vol. 8, No 5, Kiev: Naukova Dumka, 320 pp. (in Russian)
- ↑ Stepien C.A., Tumeo M.A. (2006): Invasion genetics of Ponto-Caspian gobies in the Great Lakes: a "cryptic" species, absence of founder effects, and comparative risk analysis. Biological Invasions, 8: 61–78.
- ↑ Neilson M.E., Stepien C.A. (2009) Escape from the Ponto-Caspian: Evolution and biogeography of an endemic goby species flock (Benthophilinae: Gobiidae: Teleostei). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 52(1): 84-102. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2008.12.023
- ↑ Danilkiewicz Z. (1996): Babka łysa (gołogłowa), Neogobius gymnotrachelus (Kessler, 1857) (Perciformes, Gobiidae) - nowy, gatunek w ichtiofaunie zlewiska Morza Bałtyckiego. Komunikaty Rybackie, 2: 27–29.
- ↑ Kostrzewa J., Grabowski M., Zięba G. 2004. Nowe inwazyjne gatunki ryb w wodach Polski. Archives of Polish Fisheries 12 (suppl. 2): 21-34.
- ↑ Jaroszewska M., Dabrowski K., Wilczynska B., Kakareko T. (2008) Structure of the gut of the racer goby Neogobius gymnotrachelus (Kessler, 1857). Journal of Fish Biology, Volume 72, Issue 7, Page 1773-1786, doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.2008.01870.x
- ↑ Guti G. (2004) First record of Racer Goby Neogobius gymnotrachelus (Pallas, 1811) in the Hungarian section of the Danube. Opusc. Zool. Budapest, 35: 83-84.
- ↑ Borcherding, J., Gertzen, S., Staas, S. (2011). First record of Pontian racer goby, Babka gymnotrachelus (Gobiidae: Teleostei), in the River Rhine, Germany. Journal of Applied Ichtyology in press.
- ↑ Strautman I.F. (1972) Pitaniye i pishchevyje vzaimootnoshenija bychkov (sem. Gobiidae) Dnestrovskogo limana. Vestnik Zoologii, 4: 35-38. (in Russian)
External links
- Racer Goby Phylogeography
- Neogobius gymnotrachelus (Kessler, 1857) - Alien species in Poland
- Fishes of the waters of Ukraine
- Ponto-Caspian gobiid fishes invaded the Lower Rhine. Research Topic on Fish Ecology, University of Cologne
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

