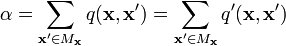Quasireversibility
In queueing theory, a discipline within the mathematical theory of probability, quasireversibility (sometimes QR) is a property of some queues. The concept was first identified by Richard R. Muntz[1] and further developed by Frank Kelly.[2][3] Quasireversibility differs from reversibility in that a stronger condition is imposed on arrival rates and a weaker condition is applied on probability fluxes. For example, an M/M/1 queue with state-dependent arrival rates and state-dependent service times is reversible, but not quasireversible.[4]
A network of queues, such that each individual queue when considered in isolation is quasireversible, always has a product form stationary distribution.[5] Quasireversibility had been conjectured to be a necessary condition for a product form solution in a queueing network, but this was shown not to be the case. Chao et al. exhibited a product form network where quasireversibility was not satisfied.[6]
Definition
A queue with stationary distribution  is quasireversible if its state at time t, x(t) is independent of
is quasireversible if its state at time t, x(t) is independent of
- the arrival times for each class of customer subsequent to time t,
- the departure times for each class of customer prior to time t
for all classes of customer.[7]
Partial balance formulation
Quasireversibility is equivalent to a particular form of partial balance. First, define the reversed rates q'(x,x') by
then considering just customers of a particular class, the arrival and departure processes are the same Poisson process (with parameter  ), so
), so
where Mx is a set such that 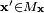 means the state x' represents a single arrival of the particular class of customer to state x.
means the state x' represents a single arrival of the particular class of customer to state x.
Examples
- Burke's theorem shows that an M/M/m queueing system is quasireversible.[8][9][10]
- Kelly showed that each station of a BCMP network is quasireversible when viewed in isolation.[11]
- G-queues in G-networks are quasireversible.[12]
See also
References
- ↑ Muntz, R.R. (1972). Poisson departure process and queueing networks (IBM Research Report RC 4145) (Technical report). Yorktown Heights, N.Y.: IBM Thomas J. Watson Research Center.
- ↑ Kelly, F. P. (1975). "Networks of Queues with Customers of Different Types". Journal of Applied Probability 12 (3): 542–554. doi:10.2307/3212869. JSTOR 3212869.
- ↑ Kelly, F. P. (1976). "Networks of Queues". Advances in Applied Probability 8 (2): 416–432. doi:10.2307/1425912. JSTOR 1425912.
- ↑ Harrison, Peter G.; Patel, Naresh M. (1992). Performance Modelling of Communication Networks and Computer Architectures. Addison-Wesley. p. 288. ISBN 0-201-54419-9.
- ↑ Kelly, F.P. (1982). Networks of quasireversible nodes. In Applied Probability and Computer Science: The Interface (Ralph L. Disney and Teunis J. Ott, editors.) 1 3-29. Birkhäuser, Boston
- ↑ Chao, X.; Miyazawa, M.; Serfozo, R. F.; Takada, H. (1998). Queueing Systems 28 (4): 377. doi:10.1023/A:1019115626557.
- ↑ Kelly, F.P., Reversibility and Stochastic Networks, 1978 pages 66-67
- ↑ Burke, P. J. (1956). "The Output of a Queuing System". Operations Research 4 (6): 699–704. doi:10.1287/opre.4.6.699.
- ↑ Burke, P. J. (1968). "The Output Process of a Stationary M/M/s Queueing System". The Annals of Mathematical Statistics 39 (4): 1144. doi:10.1214/aoms/1177698238.
- ↑ O'Connell, N.; Yor, M. (December 2001). "Brownian analogues of Burke's theorem". Stochastic Processes and their Applications 96 (2): 285–298. doi:10.1016/S0304-4149(01)00119-3.
- ↑ Kelly, F.P. (1979). Reversibility and Stochastic Networks. New York: Wiley.
- ↑ Dao-Thi, T. H.; Mairesse, J. (2005). "Zero-Automatic Queues". Formal Techniques for Computer Systems and Business Processes. Lecture Notes in Computer Science 3670. p. 64. doi:10.1007/11549970_6. ISBN 978-3-540-28701-8.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||