Quartier Mazarin
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
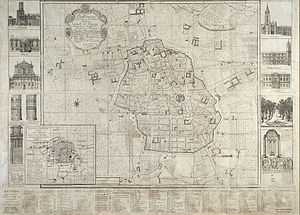
Esprit Devoux: Map of Aix-en-Provence in 1753, showing the extension of the city ramparts to the south, the tree-lined cours Mirabeau and the quartier Mazarin, newly constructed in the second half of the seventeenth century (please click for detail)
The quartier Mazarin is a district in the centre of Aix-en-Provence, directly to the south of the cours Mirabeau, the principal boulevard in Aix. On the initiative of Archbishop Michel Mazarin, brother of the Cardinal Jules Mazarin and Archbishop of Aix from 1645-8 and later himself a cardinal, city plans were devised in 1646 by Jean Lombard, director of public works, to extend the city ramparts to the south, incorporating land owned by the Archbishopric of Aix and by the Order of Saint-Jean-de-Malte. Following a grid plan of streets, the quartier contains a large number of hôtels particuliers originally built for the nobility and wealthy merchant class.
History
Notable monuments, buildings and residents
- The descriptions below are taken from Bouyala d'Arnaud (1964) and Castaldo (2011).
Cours Mirabeau (south side)
Main article: Cours Mirabeau
- Hôtel d'Esmivy de Moussac
- Maison de Vacon
- Hôtel d'Isoard-Vauvenargues
- Former Benedictine monastery
- Hôtel de Fauris-de-Vincens
- Hôtel de Mougins-Roquefort
- Hôtel de Meryronnet Saint-Marc
- Hôtel de Forbin
- Hôtel d'Entrechaux
- Hôtel Courtès
- Hôtel d'Espagnet
- Hôtel de Suffren
- Hôtel Saint-Ferréol
- Hôtel Gassendi
- Hôtel de Perrin
Rue Mazarine
- Hôtel de Ribbe
- Hôtel de Marignane
- Hôtel de Guillebert de la Lauzière
Rue Goyrand
- Hôtel de Lagoy
- Hôtel de Tressemanes
- Hôtel de Félix du Muy
- Hôtel de Gallifet
- Hôtel de Simiane
Rue Fernand-Dol
- Hôtel de Bonnet de la Baume
Place Saint-Jean-de-Malte
- Church of Saint-Jean-de-Malte
- Musée Granet
Rue Cardinale
- Hôtel d'Agay
- Hôtel de Joursanvault
- Former Convent of the Pères de la Merci
- Chapelle des Andrettes
- Lycée Mignet
- Émile Zola was a boarder at the Lycée Mignet (then the Collège Bourbon) from 1852 until 1858. There as an adolescent he formed a close friendship with Baptistin Baille and Paul Cézanne. Following the death of his father François Zola in 1847 and the subsequent collapse of his canal company in 1853, reduced means forced his mother to seek more modest accommodation in Aix. They lodged twice in the quartier Mazarin: briefly in 1853-1854 at 8 rue Roux-Alphéran (at the time rue Longue-Saint-Jean); and in 1857-1859 at 2 rue Mazarine, where Zola spent the summers of 1858 and 1859 in the small set of attic rooms.[1][2]
Rue Roux-Alphéran
- Former home of Ambroise Roux-Alphéran
- Hôtel de Boisseulh
- Hôtel de Castillon
- Hôtel Ripert de Monclar
- Hôtel Sallier
Rue Sallier
Rue Peysonnel
Rue Laroque
Rue Joseph-Cabassol
Rue du Quatre-Septembre
- Academy of Science, Agriculture, Arts and Letters of Aix
- Hôtel de Saizieu
- Hôtel de Villeneuve d'Ansouis
- Hôtel d'Olivary
- Hôtel de Boisgelin
- Hôtel de Pigenat
- Hôtel de Valori
Place des Quatre-Dauphins
- Fontaine des Quatre-Dauphins
Rue Frédéric-Mistral
- Former home of Frédéric Mistral
Rue d'Italie
- Hôtel de Garidel-Thoron
- Outbuildings of Church of Saint-Jean-de-Malte
- Former site of Church of Nôtre-Dame-de-la-Pitié and Hospital of St John of Jerusalem
Rues Maréchal-Joffre, Pavillon, Clovis-Hugues, Petit-Saint-Esprit, Saint-Joseph
Notes
References
- Bouyala d'Arnaud, André (1964), Évocation du vieil Aix-en-Provence, éditions de Minuit, ISBN 978-2-7073-0271-7
- Castaldo, Inès (2011), Le Quartier Mazarin. Habiter noblement à Aix-en-Provence, Le Temps de l'Histoire, Presses universitaires de Provence, ISBN 978-2-85399-789-8
- Pagès, Alain; Morgan, Owen (2002), Guide Émile Zola, Ellipse, pp. 109–110, ISBN 9782729808853
- Becker, Colette; Gourdin-Servenière, Gina; Lavielle, Véronique (1993), Dictionnaire d'Émile Zola, Robert Laffont, p. 22, ISBN 2-221-07612-5
- Roux, Jean-Marie (1987), Saint-Jean-de-Malte. Une église de l'ordre de Malte à Aix-en-Provence, Édisud
External links
- « Aix-en-Provence - Le quartier Mazarin », office de tourisme.
- « Le quartier Mazarin ou l'Aix du XVIIe siecle », GénéProvence.
Coordinates: 43°31′31″N 5°27′00″E / 43.52528°N 5.45000°E
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.