Quantum point contact
A quantum point contact (QPC) is a narrow constriction between two wide electrically conducting regions, of a width comparable to the electronic wavelength (nano- to micrometer). Quantum point contacts were first reported in 1988 by a Dutch group (Van Wees et al.) and, independently, by a British group (Wharam et al.). They are based on earlier work by the British group which showed how split gates could be used to convert a two-dimensional electron gas into one-dimension, first in silicon (Dean and Pepper) and then in gallium arsenide (Thornton et al., Berggren et al.)
Fabrication
There are several different ways of fabricating a QPC. It can be realized in a break-junction by pulling apart a piece of conductor until it breaks. The breaking point forms the point contact. In a more controlled way, quantum point contacts are formed in a two-dimensional electron gas (2DEG), e.g. in GaAs/AlGaAs heterostructures. By applying a voltage to suitably shaped gate electrodes, the electron gas can be locally depleted and many different types of conducting regions can be created in the plane of the 2DEG, among them quantum dots and quantum point contacts. Another means of creating a QPC is by positioning the tip of a scanning tunneling microscope close to the surface of a conductor.
Properties
Geometrically, a quantum point contact is a constriction in the transverse direction which presents a resistance to the motion of electrons. Applying a voltage  across the point contact induces a current to flow, the magnitude of this current is given by
across the point contact induces a current to flow, the magnitude of this current is given by  , where
, where  is the conductance of the contact. This formula resembles Ohm's law for macroscopic resistors. However there is a fundamental difference here resulting from the small system size which requires a quantum mechanical analysis.
is the conductance of the contact. This formula resembles Ohm's law for macroscopic resistors. However there is a fundamental difference here resulting from the small system size which requires a quantum mechanical analysis.
At low temperatures and voltages, electrons contributing to the current have a certain energy/momentum/wavelength called Fermi energy/momentum/wavelength. Much like in a waveguide, the transverse confinement in the quantum point contact results in a "quantization" of the transverse motion—the transverse motion cannot vary continuously, but has to be one of a series of discrete modes. The electron wave can only pass through the constriction if it interferes constructively, which for a given width of constriction, only happens for a certain number of modes  . The current carried by such a quantum state is the product of the velocity times the electron density. These two quantities by themselves differ from one mode to the other, but their product is mode independent. As a consequence, each state contributes the same amount
. The current carried by such a quantum state is the product of the velocity times the electron density. These two quantities by themselves differ from one mode to the other, but their product is mode independent. As a consequence, each state contributes the same amount 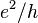 per spin direction to the total conductance
per spin direction to the total conductance
 .
.
This is a fundamental result; the conductance does not take on arbitrary values but is quantized in multiples of the conductance quantum  , which is expressed through the electron charge
, which is expressed through the electron charge  and the Planck constant
and the Planck constant  . The integer number
. The integer number  is determined by the width of the point contact and roughly equals the width divided by half the electron wavelength. As a function of the width of the point contact (or gate voltage in the case of GaAs/AlGaAs heterostructure devices), the conductance shows a staircase behavior as more and more modes (or channels) contribute to the electron transport. The step-height is given by
is determined by the width of the point contact and roughly equals the width divided by half the electron wavelength. As a function of the width of the point contact (or gate voltage in the case of GaAs/AlGaAs heterostructure devices), the conductance shows a staircase behavior as more and more modes (or channels) contribute to the electron transport. The step-height is given by  .
.
An external magnetic field applied to the quantum point contact lifts the spin degeneracy and leads to half-integer steps in the conductance. In addition, the number  of modes that contribute becomes smaller. For large magnetic fields,
of modes that contribute becomes smaller. For large magnetic fields,  is independent of the width of the constriction, given by the theory of the quantum Hall effect. An interesting feature, not yet fully understood, is a plateau at
is independent of the width of the constriction, given by the theory of the quantum Hall effect. An interesting feature, not yet fully understood, is a plateau at 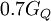 , the so-called 0.7-structure.
, the so-called 0.7-structure.
Applications
Apart from studying fundamentals of charge transport in mesoscopic conductors, quantum point contacts can be used as extremely sensitive charge detectors. Since the conductance through the contact strongly depends on the size of the constriction, any potential fluctuation (for instance, created by other electrons) in the vicinity will influence the current through the QPC. It is possible to detect single electrons with such a scheme. In view of quantum computation in solid-state systems, QPCs may be used as readout devices for the state of a quantum bit (qubit).
References
- H. van Houten and C.W.J. Beenakker (1996). "Quantum point contacts". Physics Today 49 (7): 22–27. arXiv:cond-mat/0512609. Bibcode:1996PhT....49g..22V. doi:10.1063/1.881503.
- C.W.J.Beenakker and H. van Houten (1991). "Quantum Transport in Semiconductor Nanostructures". Solid State Physics 44: 1. arXiv:cond-mat/0412664. Bibcode:2004cond.mat.12664B.
- B.J. van Wees et al. (1988). "Quantized conductance of point contacts in a two-dimensional electron gas". Physical Review Letters 60 (9): 848–850. Bibcode:1988PhRvL..60..848V. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.60.848. PMID 10038668.
- D.A. Wharam et al. (1988). "One-dimensional transport and the quantization of the ballistic resistance". J. Phys. C 21 (8): L209. Bibcode:1988JPhC...21L.209W. doi:10.1088/0022-3719/21/8/002.
- J.M. Elzerman et al. (2003). "Few-electron quantum dot circuit with integrated charge read out". Physical Review B 67 (16): 161308. arXiv:cond-mat/0212489. Bibcode:2003PhRvB..67p1308E. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.67.161308.
- K. J. Thomas et al. (1996). "Possible spin polarization in a one-dimensional electron gas". Physical Review Letters 77 (1): 135. arXiv:cond-mat/9606004. Bibcode:1996PhRvL..77..135T. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.135. PMID 10061790.
- Nicolás Agraït, Alfredo Levy Yeyati, Jan M. van Ruitenbeek (2003). "Quantum properties of atomic-sized conductors". Physics Reports 377 (2–3): 81. arXiv:cond-mat/0208239. Bibcode:2003PhR...377...81A. doi:10.1016/S0370-1573(02)00633-6.
- C.C.Dean and M. Pepper (1982). "The transition from two- to one-dimensional electronic transport in narrow silicon accumulation layers". J. Phys. C 15 (36): L1287. doi:10.1088/0022-3719/15/36/005.
- K-F. Berggren et al (1986). "Magnetic Depopulation of 1D Subbands in a Narrow 2D Electron Gas in a GaAs:AlGaAs Heterojunction". Physical Review Letters 57 (14): 1769. Bibcode:1986PhRvL..57.1769B. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.57.1769. PMID 10033540.
- T. J. Thornton et al. (1986). "One-Dimensional Conduction in the 2D Electron Gas of a GaAs-AlGaAs Heterojunction". Physical Review Letters 56 (11): 1198. Bibcode:1986PhRvL..56.1198T. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.56.1198. PMID 10032595.
- Timp, G. (1992). "Chapter 3: When Does a Wire Become an Electron Waveguide". Semiconductors and Semimetals Volume 35. Semiconductors and Semimetals 35. pp. 113–190. doi:10.1016/S0080-8784(08)62393-5. ISBN 9780127521350.