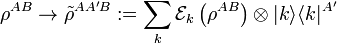Quantum instrument
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In physics, a quantum instrument is a mathematical abstraction of a quantum measurement, capturing both the classical and quantum outputs. It combines the concepts of measurement and quantum operation.
Definition
Quantum instruments are usually defined as a weighted collection of completely positive maps, the sum of which is trace preserving. That is, it is a collection 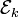 of operators that act as
of operators that act as
A quantum instrument is more general than a quantum operation because it records the outcome k of which operator acted on the state. An expanded development of quanum instruments is given in quantum channel.
References
- E. Davies, J. Lewis. An operational approach to quantum probability, Comm. Math. Phys., vol. 17, pp. 239-260, 1970.
- Distillation of secret key paper
- Another paper which uses the concept
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.