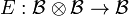Quantum Markov chain
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In mathematics, the quantum Markov chain is a reformulation of the ideas of a classical Markov chain, replacing the classical definitions of probability with quantum probability. Very roughly, the theory of a quantum Markov chain resembles that of a measure-many automata, with some important substitutions: the initial state is to be replaced by a density matrix, and the projection operators are to be replaced by positive operator valued measures.
More precisely, a quantum Markov chain is a pair 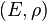 with
with  a density matrix and
a density matrix and  a quantum channel such that
a quantum channel such that
is a completely positive trace-preserving map, and 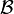 a C*-algebra of bounded operators. The pair must obey the quantum Markov condition, that
a C*-algebra of bounded operators. The pair must obey the quantum Markov condition, that
for all 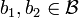 .
.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.