Pydna
| Pydna Πύδνα | |
|---|---|
| Location | |
 Pydna | |
| Coordinates | 40°22′N 22°35′E / 40.367°N 22.583°ECoordinates: 40°22′N 22°35′E / 40.367°N 22.583°E |
Location within the regional unit  | |
| Government | |
| Country: | Greece |
| Administrative region: | Central Macedonia |
| Regional unit: | Pieria |
| Municipality: | Pydna-Kolindros |
| Population statistics (as of 2011)[1] | |
| Municipal unit | |
| - Population: | 3,258 |
| - Area: | 105.59 km2 (41 sq mi) |
| - Density: | 31 /km2 (80 /sq mi) |
| Community | |
| - Population: | 1,206 |
| - Area: | 41.334 km2 (16 sq mi) |
| - Density: | 29 /km2 (76 /sq mi) |
| Other | |
| Time zone: | EET/EEST (UTC+2/3) |
| Elevation (center): | 78 m (256 ft) |
| Postal code: | 600 64 |
| Telephone: | 23510 |
| Auto: | KN |
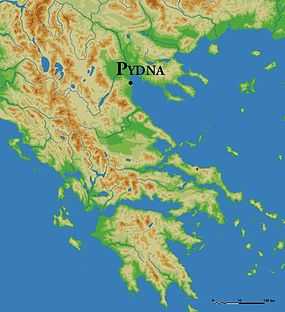
Pydna (in Greek: Πύδνα, older transliteration: Púdna) was a Greek city in ancient Macedon, the most important in Pieria. Modern Pydna is a small town and a former municipality in the northeastern part of Pieria regional unit, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Pydna-Kolindros, of which it is a municipal unit.[2] Pydna is situated in fertile land close to the Thermaic Gulf coast. The main village of the former municipality is Kitros. It lies 6 km north of Korinos, 8 km south of Methoni and 13 km northeast of Katerini. Motorway 1 and the Piraeus–Platy railway (nearest station at Korinos) pass east of the village.
Ancient Pydna
Pydna was already a part of the Macedonian kingdom under Alexander I (Thucydides I.131.1). It was unsuccessfully besieged by the Athenians in 432 BC and again, after seceding from the Macedonian kingdom, in 410 BC by Archelaus I who successfully captured the city and transferred its population further inland, possibly at the site of modern Kitros; however, the old site was re-peopled in the early 4th century. The Athenians, under Timotheus, seized Pydna in 364-363 BC, only to have it retaken in 357 BC by Philip II of Macedon. Pydna would remain part of the kingdom of Macedonia until its Roman conquest. In 317 BC, Alexander III's mother, Olympias took refuge there to escape from Cassander's wrath, incurred by Olympias' scheming against Phillip III and his wife. Cassander besieged the city and managed to capture it during the spring of 316 BC.
The Battle of Pydna (June 22, 168 BC), in which the Roman general Aemilius Paulus defeated King Perseus, ended the reign of the Antigonid dynasty over Macedon.
Population
| Year | Community | Municipal unit |
|---|---|---|
| 1981 | 1,882 | - |
| 1991 | 1,789 | 4,678 |
| 2001 | - | 4,012 |
| 2011[1] | 1,206 | 3,258 |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Detailed census results 2011 (Greek)
- ↑ Kallikratis law Greece Ministry of Interior (Greek)
- Léon Heuzey, Honoré Daumet, Mission archéologique de Macédoine, Paris, 1876, 239-266.
- R. Danoff, RE s. v. "Pydna", Suppl. X (1965), 833-842.
External links
- Livius, Pydna by Jona Lendering (ancient history of Pydna)
- Ancient Pydna
- http://www.factmonster.com/ce6/history/A0840609.html
- The Battle of Pydna
- The Third Macedonian War and the Battle of Pydna (168 BC) by John Foss
- Borza, E., R. Talbert, T. Elliott, S. Gillies. "Places: 491703 (Pydna)". Pleiades. Retrieved March 8, 2012.
See also
| ||||||||||||||