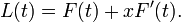Pursuit curve
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
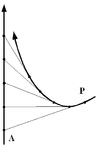
Simple pursuit curve

Curves of pursuit with different parameters
A curve of pursuit is a curve constructed by analogy to having a point or points representing pursuers and pursuees; the curve of pursuit is the curve traced by the pursuers.
With the paths of the pursuer and pursuee parameterized in time, the pursuee is always on the pursuer's tangent. That is, given F(t) the pursuer (follower) and L(t) the pursuee (leader), there is for every t with F′(t) ≠ 0 an x such that
Multiple pursuers

Curve of pursuit of vertices of a square (the mice problem for n=4).
Typical drawings of curves of pursuit have each point acting as both pursuer and pursuee, inside a polygon, and having each pursuer pursue the adjacent point on the polygon. An example of this is the mice problem.
See also
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Curve of pursuit. |
- Mathworld, with a slightly narrower definition that |L′(t)| and |F′(t)| are constant
- MacTutor Pursuit curve
| |||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.