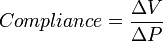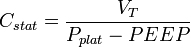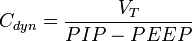Pulmonary compliance
Pulmonary compliance (or lung compliance) can refer to either dynamic or static lung compliance. Static lung compliance is the change in volume for any given applied pressure.[1] Dynamic lung compliance is the compliance of the lung at any given time during actual movement of air.
The compliance of the lungs demonstrate hysteresis, that is the compliance is different on inspiration and expiration for identical volumes.
Compliance is greatest at moderate lung volumes, and much lower at volumes which are very low or very high.
Calculation
Pulmonary compliance is calculated using the following equation, where ΔV is the change in volume, and ΔP is the change in pleural pressure:
For example if a patient inhales 500 mL of air from a spirometer with an intrapleural pressure before inspiration of – 5 cm H2O and -10 cm H2O at the end of inspiration. Then:
Static Compliance (Cstat)
Static compliance represents pulmonary compliance during periods without gas flow, such as during an inspiratory pause. It can be calculated with the formula:
where Pplat = plateau pressure. Pplat is measured at the end of inhalation and prior to exhalation using an inspiratory hold maneuver. During this maneuver, airflow is transiently (~0.5 sec) discontinued, which eliminates the effects of airway resistance. Pplat is never > PIP and is typically < 3-5 cmH2O lower than PIP when airway resistance is not elevated.
Dynamic Compliance (Cdyn)
Dynamic compliance represents pulmonary compliance during periods of gas flow, such as during active inspiration. Dynamic compliance is always less than or equal to static lung compliance. It can be calculated using the following equation, where Cdyn = Dynamic compliance; VT = tidal volume; PIP = Peak inspiratory pressure; PEEP = Positive End Expiratory Pressure:
where PIP = peak inspiratory pressure (the maximum pressure during inspiration). Alterations in airway resistance, lung compliance and chest wall compliance influence Cdyn.
Clinical significance
It is in fact an important measurement in respiratory physiology.[2][3][4]
- fibrosis is associated with a decrease in pulmonary compliance.
- emphysema/COPD may be associated with an increase in pulmonary compliance due to the loss of alveolar and elastic tissue.
Pulmonary surfactant increases compliance by decreasing the surface tension of water. The internal surface of the alveolus is covered with a thin coat of fluid. The water in this fluid has a high surface tension, and provides a force that could collapse the alveolus. The presence of surfactant in this fluid breaks up the surface tension of water, making it less likely that the alveolus can collapse inward. If the alveolus were to collapse, a great force would be required to open it, meaning that compliance would decrease drastically.
Functional significance of abnormally high or low compliance
Low compliance indicates a stiff lung and means extra work is required to bring in a normal volume of air. This occurs as the lungs in this case become fibrotic, lose their distensibility and become stiffer.
In a highly compliant lung, as in emphysema, the elastic tissue is damaged by enzymes. These enzymes are secreted by leukocytes (white blood cells) in response to a variety of inhaled irritants, such as cigarette smoke. Patients with emphysema have a very high lung compliance due to the poor elastic recoil, they have no problem inflating the lungs but have extreme difficulty exhaling air. In this condition extra work is required to get air out of the lungs. Compliance also increases with increasing age.
Compliance decreases in the following cases:
- Supine position
- Laparoscopic surgical interventions
- Severe restrictive pathologies
- Chronic restrictive pathologies
- Hydrothorax
- Pneumothorax
- High standing of a diaphragm
- Acute asthma attacks
References
- ↑ Lung compliance at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- ↑ Compliance
- ↑ Nikischin W, Gerhardt T, Everett R, Bancalari E (1998). "A new method to analyze lung compliance when pressure-volume relationship is nonlinear.". Am J Respir Crit Care Med 158 (4): 1052–60. PMID 9769260. article
- ↑ Physiology at MCG 4/4ch2/s4ch2_21