Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
| Pseudostratified columnar epithelium | |
|---|---|
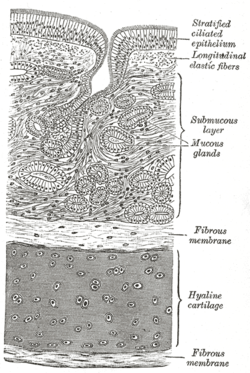 | |
| Transverse section of tracheal tissue. Note that image is incorrectly labeled "ciliated stratified epithelium" at upper right. | |
| Code | TH H2.00.02.0.02021 |
A pseudostratified epithelium is a type of epithelium that, though comprising only a single layer of cells, has its cell nuclei positioned in a manner suggestive of stratified epithelia. As it rarely occurs as squamous or cuboidal epithelia, it is usually considered synonymous with the term pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
The term pseudostratified is derived from the appearance of this epithelium in section which conveys the erroneous (pseudo means false) impression that there is more than one layer of cells, when in fact this is a true simple epithelium since all the cells rest on the basal lamina. The nuclei of these cells, however, are disposed at different levels, thus creating the illusion of cellular stratification. Not all ciliated cells extend to the luminal surface; such cells are capable of cell division providing replacements for cells lost or damaged.
Pseudostratified epithelia function in secretion or absorption. If a specimen looks stratified but has cilia, then it is a pseudostratified ciliated epithelium, since stratified epithelia do not have cilia.
Examples
- Ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelia are found in the lines of the trachea as well as the upper respiratory tract.
- Non-ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelia are located in the membranous part of male vas deferens.
- Pseudostratified columnar epithelia with stereocilia are located in the epididymis. Stereocilia of the epididymis are not cilia because their cytoskeleton is composed of actin filaments, not microtubules.[1] They are structurally and molecularly more similar to microvilli than to true cilia.
Gallery
-
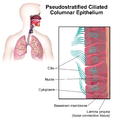
Illustration depicting Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium.
-

Types of epithelia.
-

Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium lining the bronchus (Light Microscope, Hematoxylin and Eosin dye, Magnified 600 times)
References
- ↑ Höfer D, and Drenckhahn D. Cytoskeletal differences between stereocilia of the human sperm passageway and microvilli/stereocilia in other locations. Anatomical Record. 1996 May;245(1):57-64.
External links
- pseudostratified+epithelium at eMedicine Dictionary
- Diagram at uoguelph.ca
- Bioweb at UWLAX Zoolab
- Histology at KUMC epithel-epith08 "Trachea"
- Slide at ohio-state.edu
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||