Protein efficiency ratio
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Protein efficiency ratio (PER) is based on the weight gain of a test subject divided by its intake of a particular food protein during the test period.
From 1919 until very recently, the PER had been a widely used method for evaluating the quality of protein in food.
In the United States, the food industry used to use the PER as the standard for evaluating the protein quality of food proteins. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration now uses the PDCAAS as the basis for the percent of the U.S. recommended daily allowance (USRDA) for protein shown on food labels.
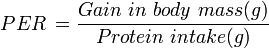
See also
- Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDCAAS)
- Net protein utilization
- Nitrogen balance
- Protein digestibility
- Protein : Amino Acids
- Whey protein
- Soy protein
- Casein
- Biological value
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.