Projective cone
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A projective cone (or just cone) in projective geometry is the union of all lines that intersect a projective subspace R (the apex of the cone) and an arbitrary subset A (the basis) of some other subspace S, disjoint from R.
In the special case that R is a single point, S is a plane, and A is a conic section on S, the projective cone is a conical surface; hence the name.
Definition
Let X be a projective space over some field K, and R, S be disjoint subspaces of X. Let A be an arbitrary subset of S. Then we define RA, the cone with top R and basis A, as follows :
- When A is empty, RA = A.
- When A is not empty, RA consists of all those points on a line connecting a point on R and a point on A.
Properties
- As R and S are disjoint, one may deduce from linear algebra and the definition of a projective space that every point on RA not in R or A is on exactly one line connecting a point in R and a point in A.
- (RA)
 S = A
S = A - When K = GF(q),
 =
= 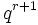
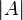 +
+ 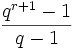 .
.
See also
- Cone (geometry)
- Cone (topology)
- Cone (linear algebra)
- Conic section
- Ruled surface
- Hyperboloid
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.