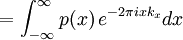Projection-slice theorem
In mathematics, the projection-slice theorem or Fourier slice theorem in two dimensions states that the results of the following two calculations are equal:
- Take a two-dimensional function f(r), project it onto a (one-dimensional) line, and do a Fourier transform of that projection.
- Take that same function, but do a two-dimensional Fourier transform first, and then slice it through its origin, which is parallel to the projection line.
In operator terms, if
- F1 and F2 are the 1- and 2-dimensional Fourier transform operators mentioned above,
- P1 is the projection operator (which projects a 2-D function onto a 1-D line) and
- S1 is a slice operator (which extracts a 1-D central slice from a function),
then:
This idea can be extended to higher dimensions.
This theorem is used, for example, in the analysis of medical CT scans where a "projection" is an x-ray image of an internal organ. The Fourier transforms of these images are seen to be slices through the Fourier transform of the 3-dimensional density of the internal organ, and these slices can be interpolated to build up a complete Fourier transform of that density. The inverse Fourier transform is then used to recover the 3-dimensional density of the object. This technique was first derived by Bracewell (1956) for a radio astronomy problem.
The projection-slice theorem in N dimensions
In N dimensions, the projection-slice theorem states that the Fourier transform of the projection of an N-dimensional function f(r) onto an m-dimensional linear submanifold is equal to an m-dimensional slice of the N-dimensional Fourier transform of that function consisting of an m-dimensional linear submanifold through the origin in the Fourier space which is parallel to the projection submanifold. In operator terms:
Proof in two dimensions

The projection-slice theorem is easily proven for the case of two dimensions. Without loss of generality, we can take the projection line to be the x-axis. There is no loss of generality because using a shifted and rotated line the law still applies. Using a shifted line (in y) gives the same projection and therefore the same 1D Fourier transform. Rotated function is the Fourier pair of the rotated Fourier transform, this completes the explanation.
If f(x, y) is a two-dimensional function, then the projection of f(x, y) onto the x axis is p(x) where
The Fourier transform of  is
is
The slice is then 
which is just the Fourier transform of p(x). The proof for higher dimensions is easily generalized from the above example.
The FHA cycle
If the two-dimensional function f(r) is circularly symmetric, it may be represented as f(r) where r = |r|. In this case the projection onto any projection line will be the Abel transform of f(r). The two-dimensional Fourier transform of f(r) will be a circularly symmetric function given by the zeroth order Hankel transform of f(r), which will therefore also represent any slice through the origin. The projection-slice theorem then states that the Fourier transform of the projection equals the slice or
where A1 represents the Abel transform operator, projecting a two-dimensional circularly symmetric function onto a one-dimensional line, F1 represents the 1-D Fourier transform operator, and H represents the zeroth order Hankel transform operator.
Extension to n-dimension signal
The n-dimensional projection-slice theorem was developed by Ng in 2005 for the application of digital refocusing of light field photographs.
See also
- Relationship with the Fourier Transform
References
- Bracewell, R.N. (1990). "Numerical Transforms". Science 248 (4956): 697–704. doi:10.1126/science.248.4956.697. PMID 17812072.
- Bracewell, R.N. (1956). "Strip Integration in Radio Astronomy". Aust. J. Phys. 9 (2): 198. doi:10.1071/PH560198.
- Gaskill, Jack D. (1978). Linear Systems, Fourier Transforms, and Optics. John Wiley & Sons, New York. ISBN 0-471-29288-5.
- Ng, R. (2005). "Fourier Slice Photography". ACM Transactions on Graphics 24 (3): 735–744. doi:10.1145/1073204.1073256.


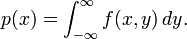
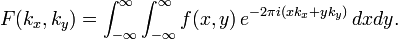

![=\int _{{-\infty }}^{\infty }\left[\int _{{-\infty }}^{\infty }f(x,y)\,dy\right]\,e^{{-2\pi ixk_{x}}}dx](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/8/0/d/b/80db0e3414710b3c0399008918cdc177.png)