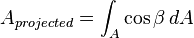Projected area
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia

Example of a projected area from a hardness indentation.
Projected area is two-dimensional area measurement of a three-dimensional object by projecting its shape on to an arbitrary plane. This is often used in mechanical engineering related fields, specifically hardness testing, axial stress and terminal velocity.
The geometrical definition of a projected area is: "the rectilinear parallel projection of a surface of any shape onto a plane". This translates into the equation:
where A is the original area, and 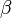 is the angle between the normal to the surface A and the normal to the arbitrary plane onto which we project. For basic shapes the results are listed in the table below.[1]
is the angle between the normal to the surface A and the normal to the arbitrary plane onto which we project. For basic shapes the results are listed in the table below.[1]
| Shape | Area | Projected area |
|---|---|---|
| Flat rectangle |  | 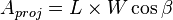 |
| Circular disc |  |  |
| Sphere |  | 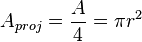 |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Palmer, James M. (1999-07-08), Radiometry and photometry FAQ, retrieved 2011-04-02.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.