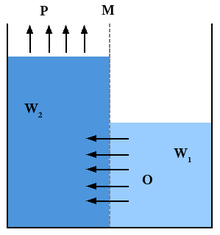
Pressure retarded osmosis (PRO) is the salinity gradient energy retrieved from the difference in the salt concentration between seawater and river water.
In PRO, the water potential between fresh water and sea water corresponds to a pressure of 26 bars. This pressure is equivalent to a column of water (hydraulic head) 270 meters high.
[1]
However, the optimal working pressure is only half of this, 11 to 15 bar.
[2] This method of generating power was invented by Prof. Sidney Loeb in 1973 at the Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beersheba, Israel.[3]
Testing
The world's first osmotic plant with capacity of 4 kW was opened by Statkraft on 24 November 2009 in Tofte, Norway.[4]
It is estimated that each year 1600 TWh could be generated world wide, and 12 TWh in Norway, sufficient to meet 10% of Norway's total demand for electricity.[5]
See also
References
Further reading
- Loeb S., Norman R. S. (1975). "Osmotic Power Plants". Science 189 (4203): 654–655. doi:10.1126/science.189.4203.654. PMID 17838753.
- Loeb S. (1998). "Energy Production at the Dead Sea by Pressure-Retarded Osmosis: Challenge or Chimera?". Desalination 120: 247–262. doi:10.1016/S0011-9164(98)00222-7.
- Norman R. S. (1974). "Water Salination: A Source of Energy". Science 186 (4161): 350. doi:10.1126/science.186.4161.350. PMID 17839865.
- Cath T. Y., Childress A. E., Elimelech M. (2006). "Forward osmosis: Principles, applications, and recent developments (Review)". Journal of Membrane Science 281: 70–87. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2006.05.048.
- Loeb S. (1988). "Comments on the suitability of reverse osmosis membranes for energy recover by submarine osmotic power plants Desalination (Review)". Journal of Membrane Science 68: 75–76. doi:10.1016/0011-9164(88)80044-4.
- Loeb S. (2002). "Large-scale power production by pressure-retarded osmosis, using river water and sea water passing through spiral modules desalination (Review)". Journal of Membrane Science 143: 115–122. doi:10.1016/S0011-9164(02)00233-3.
- Achilli A., Cath T. Y., Childress A. E. (2009). "Power generation with pressure retarded osmosis: an experimental and theoretical investigation". Journal of Membrane Science 343: 42–52. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2009.07.006.
|
|---|
| | By electrolyte | |
|---|
| | By fuel | |
|---|
| | Biofuel cells | |
|---|
| | Others | |
|---|
| | Hydrogen | |
|---|
|