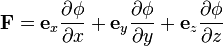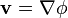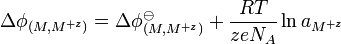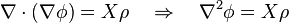Potential gradient
In physics, chemistry and biology, a potential gradient is the local rate of change of the potential with respect to displacement, i.e. spatial derivative, or gradient. This quantity frequently occurs in equations of physical processes because it leads to some form of flux. In electrical engineering it refers specifically to electric potential gradient, which is equal to the electric field.
Definition
One dimension
The simplest definitions for a potential gradient F, in one dimension, is the following:[1]
where ϕ(x) is some type of scalar potential and x is displacement (not distance), in the x direction, the subscripts label two different positions x1, x2, and potentials at those points, ϕ1 = ϕ(x1), ϕ2 = ϕ(x2). In the limit of infinitesimal displacements, the ratio of differences becomes a ratio of differentials:
Three dimensions
In three dimensions, Cartesian coordinates make it clear that the resultant potential gradient is the sum of the potential gradients in each direction:
where ex, ey, ez are unit vectors in the x, y, z directions. This can be compactly written in terms of the gradient operator ∇,
although this final form holds in any curvilinear coordinate system, not just Cartesian.
This expression represents the significant feature of any conservative vector field F, namely F has a corresponding potential ϕ.[2]
Using Stoke's theorem, this is equivalently stated as
meaning the curl, denoted ∇×, of the vector field vanishes.
In physics, conservative force fields have corresponding potentials.
Physics
Newtonian gravitation
In the case of the gravitational field g, which can be shown to be conservative[citation needed], it is equal to the gradient in gravitational potential Φ:
There are opposite signs between gravitational field and potential, because as the potential gradient and field are opposite in direction, as the potential increases, the gravitational field strength decreases and vice versa.
Electromagnetism
In electrostatics, the electric field E is independent of time t, so there is no induction of a time-dependent magnetic field B by Faraday's law of induction:
which implies E is the gradient of the electric potential ϕ, identical to the classical gravitational field:[3]
In electrodynamics, the E field is time dependent and induces a time-dependent B field also (again by Faraday's law), so the curl of E is not zero like before, which implies the electric field is no longer the gradient of electric potential, a time-dependent term must be added;[4]
where A is the electromagnetic vector potential. This last potential expression in fact reduces Faraday's law to an identity.
Fluid mechanics
In fluid mechanics, the velocity field v describes the fluid motion. An irrotational flow means the velocity field is conservative, or equivalently the vorticity pseudovector field ω is zero:
This allows the velocity potential to be defined simply as:
Chemistry
In an Electrochemical half-cell, at the interface between the electrolyte (an ionic solution) and the metal electrode, the standard electric potential difference is;[5]
where R = gas constant, T = temperature of solution, z = valency of the metal, e = elementary charge, NA = Avogadro's constant, and aM+z is the activity of the ions in solution. Quantities with superscript o denote the measurement is taken under standard conditions. The potential gradient is relatively abrupt, since there is an almost definite boundary between the metal and solution, hence the interface term.
Biology
In biology, potential gradients is the net difference in electric charge across a cell membrane.
Non-uniqueness of potentials
Since gradients in potentials correspond to physical fields, it makes no difference if a constant is added on (it is erased by the gradient operator ∇ which includes partial differentiation). This means there is no way to tell what the "absolute value" of the potential "is" - the zero value of potential is completely arbitrary and can be chosen anywhere by convenience (even "at infinity"). This idea also applies to vector potentials, and is exploited in classical field theory and also gauge field theory.
Absolute values of potentials are not physically observable, only gradients are. However, the Aharonov–Bohm effect is a quantum mechanical effect which illustrates that non-zero electromagnetic potentials (even when the E and B fields are zero) lead to changes in the phase of the wavefunction of an electrically charged particle, so the potentials appear to have measurable significance.
Potential theory
Field equations, such as Gauss's laws for electricity, for magnetism, and for gravity, can be written in the form:
where ρ is the electric charge density, monopole density (should they exist), or mass density and X is a constant (in terms of physical constants G, ε0, μ0 and other numerical factors).
Scalar potential gradients lead to Poisson's equation:
A general theory of potentials has been developed to solve this equation for the potential, the gradient of that solution gives the physical field, solving the field equation.
See also
References
- ↑ Essential Principles of Physics, P.M. Whelan, M.J. Hodgeson, 2nd Edition, 1978, John Murray, ISBN 0-7195-3382-1
- ↑ Vector Analysis (2nd Edition), M.R. Spiegel, S. Lipcshutz, D. Spellman, Schaum’s Outlines, McGraw Hill (USA), 2009, ISBN 978-0-07-161545-7
- ↑ Electromagnetism (2nd Edition), I.S. Grant, W.R. Phillips, Manchester Physics, John Wiley & Sons, 2008, ISBN 978-0-471-92712-9
- ↑ Introduction to Electrodynamics (3rd Edition), D.J. Griffiths, Pearson Education, Dorling Kindersley, 2007, ISBN 81-7758-293-3
- ↑ Physical chemistry, P.W. Atkins, Oxford University Press, 1978, ISBN 0-19-855148-7