Potato starch

Potato starch is starch extracted from potatoes. The cells of the root tubers of the potato plant contain starch grains (leucoplasts). To extract the starch, the potatoes are crushed; the starch grains are released from the destroyed cells. The starch is then washed out and dried to powder.
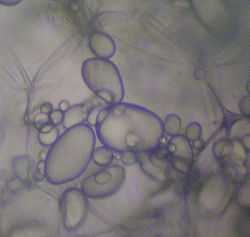
Potato starch contains typical large oval spherical granules; their size ranges between 5 and 100 μm. Potato starch is a very refined starch, containing minimal protein or fat. This gives the powder a clear white colour, and the cooked starch typical characteristics of neutral taste, good clarity, high binding strength, long texture and a minimal tendency to foaming or yellowing of the solution.
Potato starch contains approximately 800 ppm phosphate bound to the starch; this increases the viscosity and gives the solution a slightly anionic character, a low gelatinisation temperature (approximately 140 °F or 60 °C[1]) and high swelling power.
These typical properties are used in food and technical applications.[2]
Use
Starch derivatives are used in many recipes, for example in noodles, wine gums, cocktail nuts, potato chips, hot dog sausages, bakery cream and instant soups and sauces, in gluten-free recipes[3] in kosher foods for Passover[4] and in Asian cuisine.[5] In pastry, e.g. sponge cake, it is used to keep the cake moist and give a soft texture. It is also occasionally used in the preparation of pre-packed grated cheese, to reduce sweating and binding.
Other examples are helmipuuro a porridge made from monodisperse grains of potato starch and milk, papeda, the Moluccan community in the Netherlands use potato starch to make papeda, soul food of the Moluccan Archipelago (East-Indonesia). On the Moluccan islands they use sago flour to make the original papeda. Papeda is also eaten by the Papuan people of New Guinea.
It is also used in technical applications as wallpaper adhesive, for textile finishing and textile sizing, in paper coating and sizing and as an adhesive in paper sacks and gummed tape.
Potato starch was also used in one of the earlier color photography processes, the Lumière brothers' Autochrome Lumière, until the arrival of colour film in the mid-1930s.
Potato varieties
The cultivation of potatoes for starch mainly takes place in Germany, the Netherlands, China, Japan,[6] France, Denmark and Poland, but also in Sweden, Finland, Austria, the Czech Republic, Ukraine, Canada and India.
Some potato starch is also produced as a by-product from the potato processing industry, recovered from the potato cutting circuit during the production of French fries and potato chips.
See also
- Corn starch
- Katakuriko
- Potato starch production
References
- ↑ Shiotsubo, Toshiko (1983). "Starch gelatinization at different temperatures as measured by enzymic digestion method". Agric. Biol. Chem. 47 (11): 2421–2425.
- ↑ BeMiller, James N.; Whistler, Roy Lester (2009). "Potato starch: Production, Modifications and Uses". Starch: Chemistry and Technology (3rd ed.). Academic Press. pp. 511–539. ISBN 978-0-12-746275-2.
- ↑ Fenster, Carol (2006). 1000 Gluten-free Recipes. John Wiley and Sons. ISBN 978-0-470-06780-2.
- ↑ Blech, Zushe Yosef (2004). "Kosher for Passover". Kosher Food Production. Blackwell Publishing. pp. 97–114. ISBN 978-0-8138-2570-0.
- ↑ Shimbo, Hiroko (2000). The Japanese kitchen: 250 recipes in a traditional spirit. The Harvard Common Press. ISBN 1-55832-176-4.
- ↑ In Japan, potato starch is called katakuriko (from katakuri "Erythronium japonicum", and ko "powder"), which refers to the starch from the Erythronium japonicum bulb. Because of its small quantity and high price, starch from Erythorium japonicum is no longer common, potato starch has almost taken its place nowadays and only the name remains.
External links
- Memorandum on potato starch, International Starch Institute
- Potato starch gelatinization film , Youtube