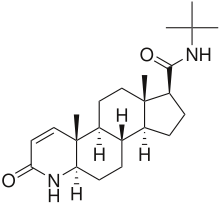
Finasteride
 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| N-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-3-oxo- (5α,17β)-4-azaandrost-1-ene-17-carboxamide | |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Propecia, Proscar |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a698016 |
| Pregnancy cat. | X (will cause birth defects in a fetus) |
| Legal status | POM (UK) ℞-only (US) |
| Routes | Oral |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 63% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Half-life | Elderly: 8 hours Adults: 6 hours |
| Excretion | Feces (57%) and urine (39%) as metabolites |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 98319-26-7 |
| ATC code | G04CB01 D11AX10 |
| PubChem | CID 57363 |
| DrugBank | DB01216 |
| ChemSpider | 51714 |
| UNII | 57GNO57U7G |
| KEGG | D00321 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:5062 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL710 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C23H36N2O2 |
| Mol. mass | 372.549 g/mol |
| SMILES
| |
| |
| | |
Finasteride (brand names Proscar and Propecia by Merck, among other generic names) is a synthetic drug for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and male pattern baldness (MPB). It is a type II 5α-reductase inhibitor. 5α-reductase is an enzyme that converts testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Medical uses
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
Physicians use finasteride for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), informally known as an enlarged prostate. The FDA-approved dose is 5 mg once a day. Six months or more of treatment with finasteride may be required to determine the therapeutic results of treatment. If the drug is discontinued, any therapeutic benefits reverse within about 6–8 months. Finasteride may improve the symptoms associated with BPH such as difficulty urinating, getting up during the night to urinate, hesitation at the start of urination, and decreased urinary flow.[1]
Male pattern baldness
As measured by hair counts, in a 5-year study of men with mild to moderate hair loss, 2 out of 3 of the men who took 1 mg of finasteride daily regrew some hair. In contrast, all of the men in the study who were not taking finasteride lost hair. In the same study, based on photographs that were reviewed by an independent panel of dermatologists, 48% of those treated with finasteride experienced visible regrowth of hair, and a further 42% had no further loss. Average hair count in the treatment group remained above baseline, and showed an increasing difference from hair count in the placebo group, for all five years of the study. Finasteride is effective only for as long as it is taken; the hair gained or maintained is lost within 6–12 months of ceasing therapy.[2] In clinical studies, finasteride, like minoxidil, was shown to work on both the crown area and the hairline,[3] but is most successful in the crown area.
A recent 10-year study of 118 men treated with 1 mg/day finasteride for androgenic alopecia found that 86% of men continued to benefit from treatment over the entire course of 10 years — showing increased or stable rates of hair growth — and only 14% experiencing any further hair loss. Interestingly, it was found that subjects who showed the most hair growth in their first year of treatment were more likely to have better hair growth after 5 years, with nearly 69% of these patients experiencing continued growth; however, many of those who experienced no growth in their first year of treatment were found to improve later on. It was also found that subjects who were older than 30 years of age tended to have better hair growth in the long run, presumably due to having experienced more hair loss by that point in their lives in comparison.
Side effects were seen in only 5.9% of patients, and no patients reported depression or gynecomastia. The authors concluded that the effectiveness of finasteride in treating androgenic alopecia does not reduce over time, even in older patients (including those over 40 years of age), and that it is well-tolerated.[4][5] This study specifically looked at users who continued using the medication. A recent case control evaluated male pattern baldness patients with psychiatric sequellae after discontinuation of finasteride, and reported depressive symptomatology and suicidal ideation for those who also experienced sexual side effects during use of the drug.[6]
Some users, in an effort to save money, buy Proscar (finasteride 5 mg) instead of Propecia, and split the Proscar pills into several parts to approximate the Propecia dosage.[7] The pills are coated to prevent contact with the active ingredient during handling, and the dust or crumbs from broken Proscar tablets should be kept away from pregnant women or women who may become pregnant.[8]
Off-label uses
Finasteride is sometimes used in hormone replacement therapy for male-to-female transsexuals in combination with a form of estrogen due to its antiandrogen properties.[9][10] However, little clinical research of finasteride use for this purpose has been conducted and evidence of efficacy is limited. Indeed, finasteride is a substantially weaker antiandrogen in comparison to conventional antiandrogens like spironolactone and cyproterone acetate. Furthermore, it has been associated with inducing depression and anxiety at a high rate in both male and female patients,[11] symptoms that are very common in transsexuals, who are already at a high risk.[12] As a result, prescription of finasteride for this indication in male-to-female transsexuals may not be particularly useful, and could put them at risk for detrimental emotional side effects. Finasteride has also been found to mitigate the effects of withdrawal after chronic alcohol use.[13]
Adverse effects
Side effects of finasteride include impotence (1.1% to 18.5%), abnormal ejaculation (7.2%), decreased ejaculatory volume (0.9% to 2.8%), abnormal sexual function (2.5%), gynecomastia (2.2%), erectile dysfunction (1.3%), ejaculation disorder (1.2%) and testicular pain. According to the product package insert, resolution occurred in men who discontinued therapy with finasteride due to these side effects and in most men who continued therapy. The PPI also states that patients have reported persisting erectile dysfunction despite discontinuing the drug. In December 2010, Merck added depression as a side effect of finasteride.[14]
In November 1997, an FDA panel refused to recommend approval of the drug Propecia for male pattern baldness. Although it was not disputing its efficacy, the committee members expressed some concerns about the possibility of long-term side effects on sexual function and possibly even fertility, which arose because of some evidence of diminished ejaculate levels.[15]
Prostate cancer
The FDA has added a warning to 5α-reductase inhibitors concerning an increased risk of high-grade prostate cancer.[16] While the effect of finasteride on the risk of developing prostate cancer has not been established, evidence suggests it may temporarily reduce the growth and prevalence of benign prostate tumors, but could also mask the early detection of prostate cancer. The primary concern is patients who develop prostate cancer while taking finasteride for benign prostatic hyperplasia, which in turn could delay diagnosis and early treatment of the prostate cancer, thereby potentially increasing the risk of these patients developing high-grade prostate cancer.[17]
The 2005 Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial (PCPT) showed at a dosage of 5 mg per day, as is commonly prescribed for BPH, participants taking finasteride were 25% less likely to have developed prostate cancer at the end of the trial compared to those taking a placebo.[18] It appeared (incorrectly) that finasteride increased the specificity and selectivity of prostate cancer detection, thus creating an apparently increased rate of high Gleason grade tumor. A 2008 update of this study found that finasteride reduces the incidence of prostate cancer by 30%. In the original study, the smaller prostate caused by finasteride facilitated detection of cancer nests and aggressive-looking cells. Most of the men in the study who had both low and high-grade prostate cancer chose to be treated, and many had their prostates removed. A pathologist then carefully examined each of those 500 prostates and compared the kinds of cancers found at surgery to those initially diagnosed at biopsy. This study concluded that finasteride did not increase the risk of high-grade prostate cancer.[19][20]
Sexual side effects
There are case reports of persistent diminished libido or erectile dysfunction, even after stopping the drug.[21] In December 2008, the Swedish Medical Products agency concluded a safety investigation of finasteride and advised that finasteride may cause irreversible sexual dysfunction. The Agency's updated safety information lists difficulty in obtaining an erection that persists indefinitely, even after the discontinuation of finasteride, as a possible side effect of the drug.[22] The UK's Medical and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) cites reports of erectile dysfunction that persists once use of finasteride has stopped.[23] Similar labeling changes have been made by the Italian government. For a period of time there was a discrepancy between European and North American warning labels regarding the risks of developing persistent sexual side effects from taking Propecia but after two years in April 2011 Merck revised the United States' warning in consumer and medical leaflets to include erectile dysfunction that may persist after stopping finasteride.[24] In April 2012, the FDA chose to approve Merck's proposed labeling from 2011 only after the warning label was further strengthened to include reports of persistent libido disorders, ejaculation disorders, orgasm disorders, and decreased libido.[25][26][27]
Anxiety and depression
Finasteride has been found to robustly induce depressive and anxious behaviors in animals.[28] Accordingly, its clinical use has been associated with depression and anxiety in both men and women in at least several reports in the medical literature.[29] In one study, at a dose of 1 mg per day, finasteride induced moderate to severe depression in 19 of 23 or 83% of participants, notably including all of the female patients.[11] In addition, marked anxiety occurred comorbidly with the depressive symptoms in some cases. Another study with a larger sample size of 128 men, though no women, also at a dose of 1 mg per day, found that finasteride increased both BDI and HADS depression scores significantly.[30] The authors concluded that finasteride should be prescribed cautiously to patients at a high risk of depression.
In late 2010, Merck revised the label of its Propecia formulation of finasteride in the United States and Canada to add depression to the list of possible side effects.[31]
In August 2012, a study of 61 former users of finasteride with persistent sexual side effects found that 75% of them showed significantly higher rates of depressive symptoms relative to a control group. Of the treated men, 36% had severe symptoms, 28% had moderate symptoms, and 11% had mild symptoms. In addition, 44% of these men reported suicidal ideation. In the control group of 29 men, 10% showed depressive symptoms, with all of these cases being mild, and 3% reported thoughts of suicide. It was concluded that finasteride may cause symptoms of depression and suicidal ideation in some persons which can persist even after discontinuation of treatment.[32][33]
Male breast cancer
In December 2009, the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency in the UK announced new drug safety advice on finasteride and the potential risk of male breast cancer. The agency concluded that, although overall incidence of male breast cancer in clinical trials for finasteride 5 mg was not significantly increased, a higher risk of male breast cancer with finasteride use cannot be excluded. A warning on this risk will be included in the product information.[34] Merck revised the United States' warning in consumer and medical leaflets to include the risk of male breast cancer.[24]
Teratogenicity
Finasteride is in the FDA pregnancy category X. This means that it is known to cause birth defects in a fetus. Women who are or who may become pregnant must not handle crushed or broken finasteride tablets, because the medication could be absorbed through the skin. Finasteride is known to cause birth defects in a developing male baby. Exposure to whole tablets should be avoided whenever possible, however exposure to whole tablets is not expected to be harmful as long as the tablets are not swallowed. It is not known whether finasteride passes into breast milk, and thus should not be taken by breastfeeding women. Finasteride may pass into the semen of men, but Merck states that a pregnant woman's contact with the semen of a man taking finasteride is not an issue for concern. Finasteride is known to affect blood donations, and potential donors are typically restricted for at least a month after their most recent dose.[35]
Interference with doping assays
Many sports organizations have banned finasteride because it can be used to mask steroid abuse.[36] Since 2005, finasteride has been on the World Anti-Doping Agency's list of banned substances. However, it was removed from the list in 2009.[37] Notable athletes who used finasteride for hair loss and were banned from international competition include skeleton racer Zach Lund, bobsledder Sebastien Gattuso, footballer Romário and ice hockey goaltender José Théodore.[38]
Mechanism of action
Testosterone in males is produced primarily in the testicles, but also in the adrenal glands. The majority of testosterone in the body is bound to sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), a protein produced in the liver that transports testosterone through the bloodstream, prevents its metabolism, and prolongs its half-life. Once it becomes unbound from SHBG, free testosterone can enter cells throughout the body. In certain tissues, notably the scalp, skin, and prostate, testosterone is converted into 5α-dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by the enzyme 5α-reductase. DHT is a more powerful androgen than testosterone (as it has approximately 3-10x the potency at the androgen receptor, the site of action of the androgen hormones), so 5α-reductase can be thought to amplify the androgenic effect of testosterone in the tissues in which it's found.
Finasteride, a 4-azasteroid and analogue of testosterone, works by acting as a potent and specific, competitive inhibitor of one of the two subtypes of 5α-reductase, specifically the type II isoenzyme.[39] In other words, it binds to the enzyme and prevents endogenous substrates such as testosterone from being metabolized. 5α-reductase type I and type II are responsible for approximately one-third and two-thirds of systemic DHT production, respectively.[40]
Other 5a-reductase substrates include progesterone, androstenedione, epi-testosterone, cortisol, aldosterone, and deoxycorticosterone. The entire physiologic effect of their reduction is unknown, but likely related to their excretion or is itself physiologic. Beyond being a catalyst in the rate-limiting step in testosterone reduction, 5alpha-reductase enzyme isoforms I and II reduce progesterone to dihydroprogesterone (DHP) and deoxycorticosterone to dihydrodeoxycorticosterone (DHDOC). In vitro and animal models suggest subsequent 3alpha-reduction of DHT, DHP and DHDOC lead to steroid metabolites with effect on cerebral function by enhancing gamma-aminobutyric acid GABAergic inhibition. These neuroactive steroid derivatives enhance GABA at GABA(A) receptors and have anticonvulsant, antidepressant and anxiolytic effects, and also alter sexual and alcohol related behavior.[41] 5α-dihydrocortisol is present in the aqueous humor of the eye, is synthesized in the lens, and might help make the aqueous humor itself.[42] Allopregnanolone and THDOC are neurosteroids, with the latter having effects on the susceptibility of animals to seizures. 5α-dihydroaldosterone is a potent antidiuretic agent, although different from aldosterone. Its formation in the kidney is enhanced by restriction of dietary salt, suggesting it may help retain sodium as follows:[43]
- Substrate + NADPH + H+ → 5α-substrate + NADP+
5α-DHP is a major hormone in circulation of normal cycling and pregnant women.[44]
By inhibiting 5a-reductase, finasteride prevents conversion of testosterone to DHT by the type II isoenzyme, resulting in a decrease in serum DHT levels by about 65–70% and in prostate DHT levels by up to 85–90%,[45] where expression of the type II isoenzyme dominates. Unlike dual inhibitors of both isoenzymes of 5α-reductase which can reduce DHT levels in the entire body by more than 99%, finasteride does not completely suppress DHT production because it lacks significant inhibitory effects on the 5α-reductase type I isoenzyme, with 100-fold less affinity for I as compared to II.[40] In addition to blocking the type II isoenzyme, finasteride competitively inhibits the 5β-reductase type II isoenzyme,[46] though this is not believed to affect androgen metabolism.
By blocking DHT production, finasteride reduces androgen activity in the scalp. In the prostate, inhibition of 5α-reductase reduces prostate volume, which improves benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and reduces risk of prostate cancer. 5α-reductase inhibition also reduces epididymal weight, and decreases motility and normal morphology of spermatozoa in the epididymis.[47]
Cause of mood-related and sexual side effects
DHT, and neuroactive steroids (NAs) such as allopregnanolone (ALLO) and tetrahydrodeoxycorticosterone (THDOC)—potent positive allosteric modulators of the GABAA receptor (the same site of action of euphoriant and anxiolytic drugs like benzodiazepines and alcohol)—are important endogenous neuroregulators that have been shown to possess powerful antidepressant and anxiolytic effects as well as to play a positive role in sexual function.[28][29][48] Their biosynthesis is dependent on both isoforms of 5α-reductase, and accordingly, finasteride has been shown to reduce their formation in the body.[49][50][51] As such, this effect of finasteride is a likely cause of the emotional and sexual side effects associated with the drug.[28][29] Additionally, due to the fact that the NAs and not just DHT are involved, the fact that the mood and anxiety-related side effects occur not only in men but in women as well[30] can also potentially be explained.
Vehicle
Drug trade names include Propecia and Proscar, the former marketed for male pattern baldness (MPB) and the latter for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), both are products of Merck & Co. There is 1 mg of finasteride in Propecia and 5 mg in Proscar. Merck's patent on finasteride for the treatment of BPH expired on June 19, 2006.[52] Merck was awarded a separate patent for the use of finasteride to treat MPB. This patent is set to expire in November 2013.[53]
Some studies have shown that the dose of finasteride needed to treat male pattern baldness may be smaller than 1 mg.[54] Petitions to the FDA to re-examine the approved dosage in light of the statistical evidence and possible long-term risks,[55] were met with the response that a study had shown increased effect of a 1 mg dose compared to 0.2 mg without added risks; the same study also concluded that doses of 0.01 mg per day were found to be ineffective in treating hair loss.[55]
Finasteride is lipophilic,[56] and development of a liposomal system of finasteride for topical application has been a subject of recent study.[57] Topical formulations show some effect in reversal of androgenic effects on hair follicles,[58] as well as in hirsutism.[59] More recent studies have looked at microemulsions[56] and liquid crystalline nanoparticles for topical finasteride delivery. In the latter, addition of glycerol, propylene glycol, and polyethylene glycol 400, increased finasteride permeation, while addition of oleic acid made it decrease.[60] Topical finasteride in combination with topical minoxidil is more effective than topical minoxidil alone.[61] Small studies of topical finasteride formulations in combination with other drugs have also been found effective.[62] Surfactants have been shown to aid topical absorption.[63] Topical finasteride gel has been shown an effective route of administration.[64]
Chemical synthesis


Finasteride is synthesized from progesterone:[65][66]

History
In 1974, Julianne Imperato-McGinley of Cornell Medical College in New York attended a conference on birth defects. She reported on a group of intersex children in the Caribbean who appeared sexually ambiguous at birth, and were initially raised as girls, but then grew external male genitalia and other masculine characteristic post-onset of puberty. Her research group found that these children shared a genetic mutation, causing deficiency of the 5α-reductase enzyme and male hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which was found to have been the etiology behind abnormalities in male sexual development. Upon maturation, these individuals were observed to have smaller prostates which were underdeveloped, and were also observed to lack incidence of male pattern baldness.[67][68]
In 1975, copies of Imperato-McGinley's presentation were seen by P. Roy Vagelos, who was then serving as Merck's basic-research chief. He was intrigued by the notion that decreased levels of DHT led to the development of smaller prostates. Dr. Vagelos then sought to create a drug which could mimic the condition found in these children in order to treat older men who were suffering from benign prostatic hyperplasia.[69]
In 1992, finasteride (5 mg) was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), which Merck marketed under the brand name Proscar.
In 1997, Merck was successful in obtaining FDA approval for a second indication of finasteride (1 mg) for treatment of male pattern baldness (MPB), which was marketed under the brand name Propecia.
See also
- Dutasteride, related 5α-reductase inhibitor.
References
- ↑ Edwards JE, Moore RA (December 2002). "Finasteride in the treatment of clinical benign prostatic hyperplasia: a systematic review of randomised trials". BMC Urol 2: 14. doi:10.1186/1471-2490-2-14. PMC 140032. PMID 12477383.
- ↑ Rossi S (Ed.) (2004). Australian Medicines Handbook 2004. Adelaide: Australian Medicines Handbook. ISBN 0-9578521-4-2.
- ↑ Leyden J, Dunlap F, Miller B, Winters P, Lebwohl M, Hecker D, Kraus S, Baldwin H, Shalita A, Draelos Z, Markou M, Thiboutot D, Rapaport M, Kang S, Kelly T, Pariser D, Webster G, Hordinsky M, Rietschel R, Katz HI, Terranella L, Best S, Round E, Waldstreicher J (June 1999). "Finasteride in the treatment of men with frontal male pattern hair loss". J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 40 (6 Pt 1): 930–7. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(99)70081-2. PMID 10365924.
- ↑ Rossi, A.; Cantisani, C.; Scarnò, M.; Trucchia, A.; Fortuna, M. C.; Calvieri, S. (2011). "Finasteride, 1 mg daily administration on male androgenetic alopecia in different age groups: 10-year follow-up". Dermatologic Therapy 24 (4): 455–461. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8019.2011.01441.x. PMID 21910805.
- ↑ Banka, N.; Bunagan, K.; Shapiro, J. (2012). "Pattern Hair Loss in Men". Dermatologic Clinics 31 (1): 129–140. doi:10.1016/j.det.2012.08.003. PMID 23159182.
- ↑ Irwig, M. S. (2012). "Depressive Symptoms and Suicidal Thoughts Among Former Users of Finasteride with Persistent Sexual Side Effects". The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 73 (9): 1220–1223. doi:10.4088/JCP.12m07887. PMID 22939118.
- ↑ Morrow, David J. (March 19, 1999). "New Profits in Old Bottles; Companies Find Bonus in Drugs That Cure Several Ills". The New York Times. Retrieved June 6, 2010.
- ↑ "Patient Information About Proscar". Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.
- ↑ Gooren L (2005). "Hormone treatment of the adult transsexual patient". Hormone Research. 64 Suppl 2: 31–6. doi:10.1159/000087751. PMID 16286768.
- ↑ Knezevich EL, Viereck LK, Drincic AT (January 2012). "Medical management of adult transsexual persons". Pharmacotherapy 32 (1): 54–66. doi:10.1002/PHAR.1006. PMID 22392828.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Altomare G, Capella GL (October 2002). "Depression circumstantially related to the administration of finasteride for androgenetic alopecia". The Journal of Dermatology 29 (10): 665–9. PMID 12433001.
- ↑ Hepp U, Kraemer B, Schnyder U, Miller N, Delsignore A (March 2005). "Psychiatric comorbidity in gender identity disorder". Journal of Psychosomatic Research 58 (3): 259–61. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychores.2004.08.010. PMID 15865950.
- ↑ Finn, D. A.; Long, S. L.; Tanchuck, M. A.; Crabbe, J. C. (2004). "Interaction of chronic ethanol exposure and finasteride: Sex and strain differences". Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior 78 (3): 435–443. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2004.04.016. PMID 15251252.
- ↑ Drugs.com | Propecia Side Effects
- ↑ <http://www.thepharmaletter.com/file/68682/propecia-approved-in-usa-for-male-pattern-baldness.html>
- ↑ 5α-reductase inhibitors (5-ARIs): Label Change – Increased Risk of Prostate Cancer | U.S. Department of Health & Human Services
- ↑ Walsh PC (April 2010). "Chemoprevention of prostate cancer". N. Engl. J. Med. 362 (13): 1237–8. doi:10.1056/NEJMe1001045. PMID 20357287.
- ↑ "Can Prostate Cancer Be Prevented?" American Cancer Society, May 25, 2005.
- ↑ Gina Kolata (June 15, 2008). "New Take on a Prostate Drug, and a New Debate". NY Times. Retrieved 2008-06-15.
- ↑ Redman MW, Tangen CM, Goodman PJ, Lucia MS, Coltman CA, Thompson IM (August 2008). "Finasteride does not increase the risk of high-grade prostate cancer: a bias-adjusted modeling approach". Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 1 (3): 174–81. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-08-0092. PMC 2844801. PMID 19138953.
- ↑ Traish AM, Hassani J, Guay AT, Zitzmann M, Hansen ML (March 2011). "Adverse side effects of 5α-reductase inhibitors therapy: persistent diminished libido and erectile dysfunction and depression in a subset of patients". The Journal of Sexual Medicine 8 (3): 872–84. doi:10.1111/j.1743-6109.2010.02157.x. PMID 21176115.
- ↑ Package Leaflet Information for the User, Swedish package insert for Propecia 1mg.
- ↑ MHRA PUBLIC ASSESSMENT REPORT | The risk of male breast cancer with finasteride
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 PROPECIA® (finasteride) | Merck & Co., Inc.
- ↑ <http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/InformationbyDrugClass/ucm299754.htm?utm_source=fdaSearch&utm_medium=website&utm_term=finasteride&utm_content=2>
- ↑ <http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2011/020180s039ltr.pdf>
- ↑ <http://www.businessweek.com/ap/2012-04/D9U3HR3G0.htm>
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 28.2 Römer B, Gass P (December 2010). "Finasteride-induced depression: new insights into possible pathomechanisms". Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology 9 (4): 331–2. doi:10.1111/j.1473-2165.2010.00533.x. PMID 21122055.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 29.2 Finn DA, Beadles-Bohling AS, Beckley EH, et al. (2006). "A new look at the 5alpha-reductase inhibitor finasteride". CNS Drug Reviews 12 (1): 53–76. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2006.00053.x. PMID 16834758.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 Rahimi-Ardabili B, Pourandarjani R, Habibollahi P, Mualeki A (2006). "Finasteride induced depression: a prospective study". BMC Clinical Pharmacology 6: 7. doi:10.1186/1472-6904-6-7. PMC 1622749. PMID 17026771.
- ↑ Allen, Jane E (3 May 2012). "Pursuit of Better Hairline Costs Some Men Their Sex Lives". ABC News. pp. 1–3. Retrieved 2012-05-10.
- ↑ Irwig MS (September 2012). "Depressive symptoms and suicidal thoughts among former users of finasteride with persistent sexual side effects". J Clin Psychiatry 73 (9): 1220–3. doi:10.4088/JCP.12m07887. PMID 22939118.
- ↑ George Washington University (7 August 2012). /releases/2012/08/120807101330.htm "Depressive symptoms and suicidal thoughts found in former finasteride users". ScienceDaily. Retrieved 5 October 2012.
- ↑ "MHRA drug safety advice: Finasteride and potential risk of male breast cancer". 4 December 2009. Retrieved 4 December 2009.
- ↑ "FDA guidance on blood donors and medications" (pdf). U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Archived from the original on October 31, 2005. Retrieved 01-02-2009.
- ↑ Sandomir, Richard (2006-01-19). "Skin Deep; Fighting Baldness, and Now an Olympic Ban". The New York Times. Retrieved 2010-05-02.
- ↑ World Anti-Doping Agency Q&A: Status of Finasteride
- ↑ "Theodore's hair tonic causes positive test". TSN. 2006-02-10. Retrieved 2006-07-22.
- ↑ Aggarwal S, Thareja S, Verma A, Bhardwaj TR, Kumar M (February 2010). "An overview on 5alpha-reductase inhibitors". Steroids 75 (2): 109–53. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2009.10.005. PMID 19879888.
- ↑ 40.0 40.1 "PROPECIA® (finasteride) Tablets, 1 mg [US/FDA label]" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-05-22.
- ↑ Finn, D. A.; Beadles-Bohling, A. S.; Beckley, E. H.; Ford, M. M.; Gililland, K. R.; Gorin-Meyer, R. E.; Wiren, K. M. (2006). "A New Look at the 5?-Reductase Inhibitor Finasteride". CNS Drug Reviews 12 (1): 53–76. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2006.00053.x. PMID 16834758.
- ↑ Weinstein BI, Kandalaft N, Ritch R, Camras CB, Morris DJ, Latif SA, Vecsei P, Vittek J, Gordon GG, Southren AL (June 1991). "5 alpha-dihydrocortisol in human aqueous humor and metabolism of cortisol by human lenses in vitro". Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 32 (7): 2130–5. PMID 2055703.
- ↑ Kenyon CJ, Brem AS, McDermott MJ, Deconti GA, Latif SA, Morris DJ (May 1983). "Antinatriuretic and kaliuretic activities of the reduced derivatives of aldosterone". Endocrinology 112 (5): 1852–6. doi:10.1210/endo-112-5-1852. PMID 6403339.
- ↑ Milewich L, Gomez-Sanchez C, Crowley G, Porter JC, Madden JD, MacDonald PC (October 1977). "Progesterone and 5alpha-pregnane-3,20-dione in peripheral blood of normal young women: Daily measurements throughout the menstrual cycle". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 45 (4): 617–22. doi:10.1210/jcem-45-4-617. PMID 914969.
- ↑ Bartsch, G.; Rittmaster, R. S.; Klocker, H. (2000). "Dihydrotestosterone and the concept of 5alpha-reductase inhibition in human benign prostatic hyperplasia". European Urology 37 (4): 367–380. doi:10.1159/000020181. PMID 10765065.
- ↑ Drury, J. E.; Di Costanzo, L.; Penning, T. M.; Christianson, D. W. (2009). "Inhibition of Human Steroid 5 -Reductase (AKR1D1) by Finasteride and Structure of the Enzyme-Inhibitor Complex". Journal of Biological Chemistry 284 (30): 19786–19790. doi:10.1074/jbc.C109.016931. PMC 2740403. PMID 19515843.
- ↑ Robaire B, Henderson NA (May 2006). "Actions of 5alpha-reductase inhibitors on the epididymis". Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 250 (1–2): 190–5. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2005.12.044. PMID 16476520.
- ↑ Gunn BG, Brown AR, Lambert JJ, Belelli D (2011). "Neurosteroids and GABA(A) Receptor Interactions: A Focus on Stress". Frontiers in Neuroscience 5: 131. doi:10.3389/fnins.2011.00131. PMC 3230140. PMID 22164129.
- ↑ Vermeulen A, Giagulli VA, De Schepper P, Buntinx A, Stoner E (1989). "Hormonal effects of an orally active 4-azasteroid inhibitor of 5 alpha-reductase in humans". The Prostate 14 (1): 45–53. PMID 2538808.
- ↑ Kokate TG, Banks MK, Magee T, Yamaguchi S, Rogawski MA (February 1999). "Finasteride, a 5alpha-reductase inhibitor, blocks the anticonvulsant activity of progesterone in mice". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 288 (2): 679–84. PMID 9918575.
- ↑ Dusková M, Hill M, Hanus M, Matousková M, Stárka L (2009). "Finasteride treatment and neuroactive steroid formation". Prague Medical Report 110 (3): 222–30. PMID 19655698.
- ↑ Primary Patent Expirations for Selected High Revenue Drugs
- ↑ fda.gov | Patent Expiration for Propecia
- ↑ "Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, Application Number NDA 20–788" (PDF). U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
- ↑ 55.0 55.1 "Letter to Dr. Sherman Frankel, University of Pennsylvania" (PDF). U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
- ↑ 56.0 56.1 Azeem, A.; Khan, Z. I.; Aqil, M.; Ahmad, F. J.; Khar, R. K.; Talegaonkar, S. (2009). "Microemulsions as a Surrogate Carrier for Dermal Drug Delivery". Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy 35 (5): 525–547. doi:10.1080/03639040802448646. PMID 19016057.
- ↑ Kumar, R.; Singh, B.; Bakshi, G.; Katare, O. P. (2007). "Development of Liposomal Systems of Finasteride for Topical Applications: Design, Characterization, and in Vitro Evaluation". Pharmaceutical Development and Technology 12 (6): 591–601. doi:10.1080/10837450701481181. PMID 18161632.
- ↑ Ye, F.; Imamura, K.; Imanishi, N.; Rhodes, L.; Uno, H. (1997). "Effects of topical antiandrogen and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors on sebaceous glands in male fuzzy rats". Skin pharmacology : the official journal of the Skin Pharmacology Society 10 (5–6): 288–297. PMID 9449168.
- ↑ Póltorak, J. L. (1976). "Bile duct calculosis". Polski tygodnik lekarski (Warsaw, Poland : 1960) 31 (4): 145–148. PMID 1250761.
- ↑ Madheswaran, T.; Baskaran, R.; Thapa, R. K.; Rhyu, J. Y.; Choi, H. Y.; Kim, J. O.; Yong, C. S.; Yoo, B. K. (2012). "Design and in Vitro Evaluation of Finasteride-Loaded Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles for Topical Delivery". AAPS PharmSciTech. doi:10.1208/s12249-012-9888-y. PMID 23207960.
- ↑ Tanglertsampan, C. (2012). "Efficacy and safety of 3% minoxidil versus combined 3% minoxidil / 0.1% finasteride in male pattern hair loss: A randomized, double-blind, comparative study". Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand = Chotmaihet thangphaet 95 (10): 1312–1316. PMID 23193746.
- ↑ Rafi, A. W.; Katz, R. M. (2011). "Pilot Study of 15 Patients Receiving a New Treatment Regimen for Androgenic Alopecia: The Effects of Atopy on AGA". ISRN Dermatology 2011: 1. doi:10.5402/2011/241953. PMC 3262531. PMID 22363845.
- ↑ Javadzadeh, Y.; Shokri, J.; Hallaj-Nezhadi, S.; Hamishehkar, H.; Nokhodchi, A. (2010). "Enhancement of percutaneous absorption of Finasteride by cosolvents, cosurfactant and surfactants". Pharmaceutical Development and Technology 15 (6): 619–625. doi:10.3109/10837450903397610. PMID 19929166.
- ↑ Hajheydari, Z.; Akbari, J.; Saeedi, M.; Shokoohi, L. (2009). "Comparing the therapeutic effects of finasteride gel and tablet in treatment of the androgenetic alopecia". Indian journal of dermatology, venereology and leprology 75 (1): 47–51. PMID 19172031.
- ↑ Rasmusson GH, Reynolds GF, Steinberg NG, Walton E, Patel GF, Liang T, Cascieri MA, Cheung AH, Brooks JR, Berman C (November 1986). "Azasteroids: structure-activity relationships for inhibition of 5 alpha-reductase and of androgen receptor binding". J. Med. Chem. 29 (11): 2298–315. doi:10.1021/jm00161a028. PMID 3783591.
- ↑ Bhattacharya A, Dimichele LM, Dolling U, Douglas AW, Grabowski EJJ (May 1988). "Silylation-mediated oxidation of 4-aza-3-ketosteroids with DDQ proceeds via DDQ-substrate adducts". Journal of the American Chemical Society 110: 3318–9. doi:10.1021/ja00218a062.
- ↑ 5-Alpha-Reductase Deficiency | WebMD
- ↑ Dutasteride | Clinical Trials | International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery
- ↑ Freudenheim, Milt (February 16, 1992). "Keeping the Pipeline Filled at Merck". The New York Times.
External links
| |||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||