Population geography
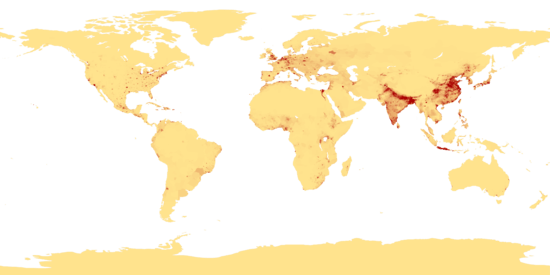
Population geography is a division of human geography. It is the study of the ways in which spatial variations in the distribution, composition, migration, and growth of populations are related to the nature of places. Population geography involves demography in a geographical perspective. It focuses on the characteristics of population distributions that change in a spatial context. Examples can be shown through population density maps. A few types of maps that show the spatial layout of population are choropleth, isoline, and dot maps. Population geography studies:
- Demographic phenomena (natality, mortality, growth rates, etc.) through both space and time
- Increase or decrease in population numbers
- The movements and mobility of populations
- Occupational Structure
- The way in which places in turn react to population phenomena e.g. immigration
Research topics of other geographic sub-disciplines, such as settlement geography, have also a population-geographic dimension:
- Grouping of people in settlements
- The way from the geographical character of places e.g. settlement patterns
All of the above are looked at over space and time.
Notes
N.B. The boundary between population geography and demography is becoming more and more blurred.
| ||||||||||
