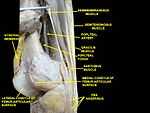
Popliteal artery
| Artery: Popliteal artery | |
|---|---|
 | |
| The arteries of the gluteal and posterior femoral regions. (Popliteal labeled at bottom center.) | |
 | |
| Lymph glands of popliteal fossa. | |
| Latin | arteria poplitea |
| Gray's | p.632 |
| Source | femoral artery |
| Branches | anterior tibial, posterior tibial artery, sural, superior genicular (medial, lateral), middle genicular, inferior genicular (medial, lateral) |
| Vein | popliteal vein |
| MeSH | Popliteal+Artery |
In human anatomy, the popliteal artery is defined as the extension of the "superficial" femoral artery after passing through the adductor canal and adductor hiatus above the knee. The termination of the popliteal artery is its bifurcation into the anterior tibial artery and posterior tibial artery.
The popliteal artery, through numerous smaller branches, supplies blood to the knee joint and muscles in the thigh and calf. It is accompanied, along its length, by the popliteal vein.
Branches
The branches of the popliteal artery are:
- anterior tibial artery
- posterior tibial artery
- sural artery
- medial superior genicular artery
- lateral superior genicular artery
- middle genicular artery
- lateral inferior genicular artery
- medial inferior genicular artery
Tibial-fibular trunk
The fibular artery typically arises from the posterior tibial artery.[1] Therefore, the posterior tibial artery proximal to the fibular artery origin is sometimes called the tibial-peroneal trunk or tibial-fibular trunk and it could be said that the popliteal artery bifurates into the tibial-fibular trunk and anterior tibial artery.
Pulse
Its pulse can be palpated behind the knee when it is semi-flexed, but is generally more challenging to find than other arteries of the leg; thus, a readily-detectable and easy-to-find popliteal pulse may actually suggest some pathology.
Additional images
-
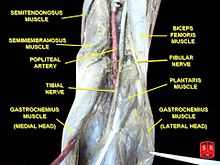
Popliteal artery
-

The popliteal, posterior tibial, and peroneal arteries.
-
Muscles of thigh. Lateral view.
See also
References
- ↑ Day C, Orme R (2006). "Popliteal artery branching patterns -- an angiographic study". Clin Radiol 61 (8): 696–9. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2006.03.014. PMID 16843754.
External links
- SUNY Figs 12:04-10 - "Arteries of the lower extremity shown in association with major landmarks."
- Popliteal+artery at eMedicine Dictionary
- Image at umich.edu - pulse
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||