Polysorbate 80
| Polysorbate 80[1] | ||
|---|---|---|
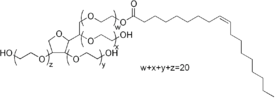 | ||
| IUPAC name Polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan monooleate | ||
| Other names Alkest TW 80 | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| CAS number | 9005-65-6 | |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1697847 | |
| RTECS number | WG2932500 | |
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C64H124O26 | |
| Molar mass | 1310 g/mol | |
| Appearance | Amber colored viscous liquid | |
| Density | 1.06–1.09 g/mL, oily liquid | |
| Boiling point | > 100°C | |
| Solubility in water | Very soluble | |
| Solubility in other solvents | soluble in ethanol, cottonseed oil, corn oil, ethyl acetate, methanol, toluene | |
| Viscosity | 300–500 centistokes (@25°C) | |
| Hazards | ||
| Main hazards | Irritant | |
| NFPA 704 |
 0
1
0
| |
| Flash point | 113 °C; 235 °F; 386 K | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Polysorbate 80 (brand names include Alkest, Canarcel and Tween, which is a registered trademark of ICI Americas, Inc.)[2] is a nonionic surfactant and emulsifier derived from polyethoxylated sorbitan and oleic acid, and is often used in foods. Polysorbate 80 is a viscous, water-soluble yellow liquid. The hydrophilic groups in this compound are polyethers also known as polyoxyethylene groups which are polymers of ethylene oxide. In the nomenclature of polysorbates, the numeric designation following polysorbate refers to the lipophilic group, in this case the oleic acid (see polysorbate for more detail). Polysorbate 80 is often used in food and other products as an emulsifier.
Other names
- Polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan monooleate
- (x)-sorbitan mono-9-octadecenoate poly(oxy-1,2-ethanediyl)
- Alkest TW 80
- Poegasorb 80
- Tween 80
- POE (20) sorbitan monooleate
- E433
Polysorbate 80 is also used in some eye drops (e.g., ROHTO cool redness reliever/lubricant eye drops).
Data
The critical micelle concentration of polysorbate 80 in pure water is reported as 0.012 mM.[3]
Food use
Polysorbate 80 is used as an emulsifier in foods, particularly in ice cream. Here, polysorbate is added to up to 0.5% (v/v) concentration and makes the ice cream smoother and easier to handle, as well as increasing its resistance to melting.[4] Adding this substance prevents milk proteins from completely coating the fat droplets. This allows them to join together in chains and nets, which hold air in the mixture, and provide a firmer texture that holds its shape as the ice cream melts.
Medical use
Polysorbate 80 is an excipient that is used to stabilize aqueous formulations of medications for parenteral administration, and used as an emulsifier in the manufacture of the popular anti-arrhythmic amiodarone.[5] It is also used as an excipient in some European and Canadian influenza vaccines.[6] It is also used in the culture of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Middlebrook 7H9 broth.It is also used as an emulsifier in Estrogen regulating drug Estrasorb.[7]
Laboratory use
Some mycobacteria contain a type of lipase (enzyme that breaks up lipid molecules). When added to a mixture of Tween 80 and phenol red, they cause the solution to change colour, so this is used as a test to identify the phenotype of a strain or isolate.
Consumption and potential effects
In Europe and America people eat about 100 mg of polysorbate 80 in foods per day.[8] Influenza vaccines contain 25 μg of polysorbate 80 per dose.[6]
In general, polysorbate 80 is safe and well tolerated, although a small number of people may be sensitive to this substance,[9] and it may be harmful to people with Crohn's disease.[10] Polysorbate 80 is not carcinogenic.[11]
Rats fed with diets containing up to 5% polysorbate 80 by volume for 12 weeks showed no toxic effects. However, the levels of polysorbate 80 used in the study were determined based on an assumed maximum human consumption of 750 mg per day, and the study did find statistically significant differences in efficiency of caloric utilization. [12] A 1956 study saw no effect on reproduction in rats at up to 5% of their diet being polysorbate 80, although reproduction decreased at 20% of the diet (duration of study?).[13] A 1993 study raised concerns that polysorbate 80 might decrease fertility in rats.[14] A 1997 study on two rats looked at the effect of consuming three doses by body weight of 0.5%/day on the sex organs of female rats and saw no abnormal changes in uterine weight, note that this does not take into account myriad possible epigenetic, or even physically observable differences in structure and function. (duration of study?); this is equivalent to a 70 kg person consuming about 350 g per day for three days. [15] A 2008 study concluded that there was no observable adverse effects at doses per body weight of up to 1.85 ml/kg·day, which is equivalent to a 70 kg person consuming about 140 g of this substance per day for 21 days. However, administration of 16.783 ml/kg·day to pregnant rats lowered body weight in male and female offspring.[8] This is equivalent to a person consuming about 1.3 kg of polysorbate 80 per day for 21 days.
See also
- Polysorbate 20: Used as a wetting agent in mouth drops.
- Polysorbate 40
- Polysorbate 60: Used as an emulsifier in powdered drink preparations such as hot cocoa mix.
- Polysorbate 65
References
- ↑ Merck Index, 13th Edition, 7664.
- ↑ US PTO TESS Registry Number 2885675
- ↑ Chou DK, Krishnamurthy R, Randolph TW, Carpenter JF, Manning MC (June 2005). "Effects of Tween 20 and Tween 80 on the stability of Albutropin during agitation". J Pharm Sci 94 (6): 1368–81. doi:10.1002/jps.20365. PMID 15858848.
- ↑ Goff, H. Douglas (1997). "Colloidal aspects of ice cream—A review". International Dairy Journal 7 (6–7): 363–373. doi:10.1016/S0958-6946(97)00040-X. ISSN 0958-6946.
- ↑ Gautier & Bellamy. "Pharmaceutical amiodarone composition for parenteral delivery". Retrieved 2008-04-06.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Pandemic H1N1 (pH1N1) Influenza Vaccine Quick Reference Guide Winnipeg Regional Health Authority 2009
- ↑ http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2003/21371_estrasorb_lbl.pdf
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Ema, M.; Hara, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Hirata-Koizumi, M.; Hirose, A.; Kamata, E. (2008). "Evaluation of developmental neurotoxicity of polysorbate 80 in rats". Reproductive Toxicology 25 (1): 89–52. doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2007.08.003. PMID 17961976.
- ↑ Steele RH, Limaye S, Cleland B, Chow J, Suranyi MG (2005). "Hypersensitivity reactions to the polysorbate contained in recombinant erythropoietin and darbepoietin". Nephrology (Carlton) 10 (3): 317–20. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1797.2005.00389.x. PMID 15958049.
- ↑ Roberts, Carol L; Keita, A. V.; Duncan, S. H.; O'Kennedy, N.; Soderholm, J. D.; Rhodes, J. M.; Campbell, B. J. (2010-09-01). "Translocation of Crohn's disease Escherichia coli across M-cells: contrasting effects of soluble plant fibres and emulsifiers". Gut 59 (10): 1331–1339. doi:10.1136/gut.2009.195370. PMC 2976079. PMID 20813719. Retrieved 2010-12-20. Lay summary (2010-08-30).
- ↑ Polysorbate 80 (CAS 9005-65-6) The Carcinogenic Potency Database (CPDB)
- ↑ OSER BL, OSER M (November 1956). "Nutritional studies on rats on diets containing high levels of partial ester emulsifiers. I. General plan and procedures; growth and food utilization". J. Nutr. 60 (3): 367–90. PMID 13377228.
- ↑ OSER BL, OSER M (December 1956). "Nutritional studies on rats of diets containing high levels of partial ester emulsifiers. II. Reproduction and lactation". J. Nutr. 60 (4): 489–505. PMID 13385715.
- ↑ Gajdová M, Jakubovsky J, Války J (March 1993). "Delayed effects of neonatal exposure to Tween 80 on female reproductive organs in rats". Food Chem. Toxicol. 31 (3): 183–90. doi:10.1016/0278-6915(93)90092-D. PMID 8473002.
- ↑ Williams J, Odum J, Lewis RW, Brady AM (March 1997). "The oral administration of polysorbate 80 to the immature female rat does not increase uterine weight". Toxicol. Lett. 91 (1): 19–24. doi:10.1016/S0378-4274(96)03863-5. PMID 9096282.