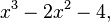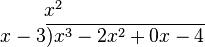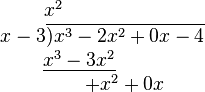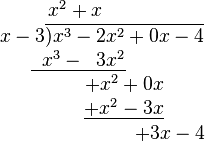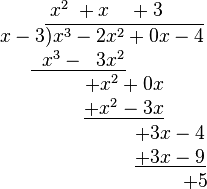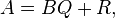Polynomial long division
In algebra, polynomial long division is an algorithm for dividing a polynomial by another polynomial of the same or lower degree, a generalised version of the familiar arithmetic technique called long division. It can be done easily by hand, because it separates an otherwise complex division problem into smaller ones. Sometimes using a shorthand version called synthetic division is faster, with less writing and fewer calculations.
Polynomial long division is an algorithm that implements the Euclidean division of polynomials, which starting from two polynomials A (the dividend) and B (the divisor) produces, if B is not zero, a quotient Q and a remainder R such that
- A = BQ + R,
and either R = 0 or the degree of R is lower than the degree of B. These conditions define uniquely Q and R, which means that Q and R do not depend on the method used to compute them.
Example
Find the quotient and the remainder of the division of
the dividend by
the divisor.
The dividend is first rewritten like this:
The quotient and remainder can then be determined as follows:
- Divide the first term of the dividend by the highest term of the divisor (meaning the one with the highest power of x, which in this case is x). Place the result above the bar (x3 ÷ x = x2).
- Multiply the divisor by the result just obtained (the first term of the eventual quotient). Write the result under the first two terms of the dividend (x2 · (x − 3) = x3 − 3x2).
- Subtract the product just obtained from the appropriate terms of the original dividend (being careful that subtracting something having a minus sign is equivalent to adding something having a plus sign), and write the result underneath ((x3 − 2x2) − (x3 − 3x2) = −2x2 + 3x2 = x2) Then, "bring down" the next term from the dividend.
- Repeat the previous three steps, except this time use the two terms that have just been written as the dividend.
- Repeat step 4. This time, there is nothing to "pull down".
The polynomial above the bar is the quotient q(x), and the number left over ( 5) is the remainder r(x).
The long division algorithm for arithmetic is very similar to the above algorithm, in which the variable x is replaced by the specific number 10.
Pseudo-code
The algorithm can be represented in pseudo-code as follows, where +, -, and × represent polynomial arithmetic, and / represents simple division of two terms:
function n / d:
require d ≠ 0
(q, r) ← (0, n) # At each step n = d × q + r
while r ≠ 0 AND degree(r) ≥ degree(d):
t ← lead(r)/lead(d) # Divide the leading terms
(q, r) ← (q + t, r - (t * d))
return (q, r)
Note that this works equally well when degree(n) < degree(d); in that case the result is just the trivial (0, n).
This algorithm describes exactly above paper and pencil method: d is written on the left of the ")"; q is written, term after term, above the horizontal line, the last term being the value of t; the region under the horizontal line is used to compute and write down the successive values of r.
Euclidean division
Polynomial division allows to prove that for every pair polynomials (A, B) such that B is not the zero polynomial, there exists a quotient Q and a remainder R such that
and either R=0 or degree(R) < degree(B). Moreover (Q, R) is the unique pair of polynomials having this property. written in a divisor–quotient form which is often advantageous. Consider polynomials P(x), D(x) where degree(D) < degree(P). Then, for some quotient polynomial Q(x) and remainder polynomial R(x) with degree(R) < degree(D),
This existence and unicity property is known as Euclidean division and sometimes as division transformation.[1]
Applications
Factoring polynomials
Sometimes one or more roots of a polynomial are known, perhaps having been found using the rational root theorem. If one root r of a polynomial P(x) of degree n is known then polynomial long division can be used to factor P(x) into the form (x - r)(Q(x)) where Q(x) is a polynomial of degree n–1. Q(x) is simply the quotient obtained from the division process; since r is known to be a root of P(x), it is known that the remainder must be zero.
Likewise, if more than one root is known, a linear factor (x – r) in one of them (r) can be divided out to obtain Q(x), and then a linear term in another root, s, can be divided out of Q(x), etc. Alternatively, they can all be divided out at once: for example the linear factors x– r and x – s can be multiplied together to obtain the quadratic factor x2 – (r + s)x + rs, which can then be divided into the original polynomial P(x) to obtain a quotient of degree n – 2.
In this way, sometimes all the roots of a polynomial of degree greater than four can be obtained, even though that is not always possible. For example, if the rational root theorem can be used to obtain a single (rational) root of a quintic polynomial, it can be factored out to obtain a quartic (fourth degree) quotient; the explicit formula for the roots of a quartic polynomial can then be used to find the other four roots of the quintic.
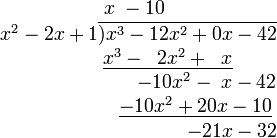
Finding tangents to polynomial functions
Polynomial long division can be used to find the equation of the line that is tangent to the graph of the function defined by the polynomial P(x) at a particular point x = r.[2] If R(x) is the remainder of the division of P(x) divided by (x – r )2, then the equation of the tangent line at x = r to the graph of the function y = P(x) is y = R(x), regardless of whether or not r is a root of the polynomial.

Begin by dividing the equation of the curve by 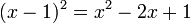
The tangent is 
See also
- Polynomial remainder theorem
- Synthetic division, a more concise method of performing polynomial long division
- Ruffini's rule
- Euclidean domain
- Gröbner basis
- Greatest common divisor of two polynomials
Notes
- ↑ S. Barnard (2008). Higher Algebra. READ BOOKS. p. 24. ISBN 1-4437-3086-6.
- ↑ Strickland-Constable, Charles, "A simple method for finding tangents to polynomial graphs", Mathematical Gazette 89, November 2005: 466-467.