Poly(p-phenylene oxide)
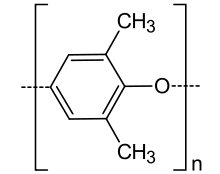
Poly(p-phenylene oxide) (PPO) or poly(p-phenylene ether) (PPE) is a high-temperature thermoplastic. It is rarely used in its pure form due to difficulties in processing. It is mainly used as blend with polystyrene, high impact styrene-butadiene copolymer or polyamide.
History
Polyphenylene ether was discovered in 1956 by Allan Hay, and was commercialized by General Electric in 1960.
While it was one of the cheapest high-temperature resistant plastics, processing was difficult and the impact and heat resistance decreased with time. Mixing it with polystyrene in any ratio could compensate for the disadvantages. In the 1960s, modified PPE came into the market under the trade name Noryl.[1]
Properties
PPE is an amorphous high-performance plastic. The glass transition temperature is 215 °C, but it can be varied by mixing with polystyrene. Through modification and the incorporation of fillers such as glass fibers, the properties can be extensively modified.
Applications

PPE blends are used for structural parts, electronics, household and automotive items that depend on high heat resistance, dimensional stability and accuracy. They are also used in medicine for sterilizable instruments made of plastic.[2]
This plastic is processed by injection molding or extrusion; depending on the type, the processing temperature is 260-300 °C. The surface can be printed, hot-stamped, painted or metallized. Welds are possible by means of heating element, friction or ultrasonic welding. It can be glued with halogenated solvents or various adhesives.
Production from natural products
Natural phenols can be enzymatically polymerised. Laccase and peroxidase induced the polymerization of syringic acid to give a poly(1,4-phenylene oxide) bearing a carboxylic acid at one end and a phenolic hydroxyl group at the other.[3]
References
Translated from the article Polyphenylenether on the German Wikipedia.
- ↑ D. Alberti "Modifizierte aromatische Polyether" in Kunststoffe 10/87, S. 1001
- ↑ A. Hohmann, W. Hielscher: Lexikon der Zahntechnik: Das grundlegende Werk: 12,000 Begriffe aus Zahntechnik und Zahnheilkunde in einem Band. Verlag Neuer Merkur, 1998, ISBN 978-3-929360-28-8 - they are used. [6] The PPE blends are characterized by hot water resistance with low water absorption, high impact strength, halogen-free fire protection and low density.
- ↑ Uyama, Hiroshi; Ikeda, Ryohei; Yaguchi, Shigeru; Kobayashi, Shiro (2001). "Enzymatic Polymerization of Natural Phenol Derivatives and Enzymatic Synthesis of Polyesters from Vinyl Esters". Polymers from Renewable Resources. ACS Symposium Series 764. p. 113. doi:10.1021/bk-2000-0764.ch009. ISBN 0-8412-3646-1.
External links
- Douglas Robello. "Poly(phenylene oxide)". University of Rochester.