Plicatic acid
| Plicatic acid | |
|---|---|
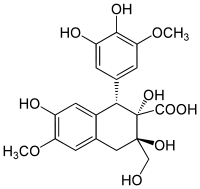 | |
| IUPAC name (1S,2S,3R)-1-(3,4-Dihydroxy-5-methoxyphenyl)-2,3,7-trihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)-6-methoxy-1,4-dihydronaphthalene-2-carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 16462-65-0 |
| PubChem | 104836 |
| ChemSpider | 94630 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:O=C(O)[C@]2(O)[C@H](c1c(cc(OC)c(O)c1)C[C@@]2(O)CO)c3cc(O)c(O)c(OC)c3|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C20H22O10 |
| Molar mass | 422.38 g mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Plicatic acid is a carboxylic acid from the resin acid group. It is naturally found in Thuja and cypress resin. It is the main irritant and contact allergen present in thuja wood. (Cf. pine, where the primary irritant is abietic acid.)
The highest concentrations of plicatic acid can be found in Thuja plicata (Western Redcedar), but Thuja occidentalis (Eastern Arborvitae) and Cryptomeria japonica (Sugi) contain it in significant proportions as well.
Exposure to plicatic acid or thuja wood dust can worsen asthma and provoke allergic reactions.[1]