PikeOS
| Company / developer | SYSGO AG |
|---|---|
| OS family | Real-time |
| Latest stable release | 3.4 / October 2013 |
| Marketing target | Safety and security critical embedded systems |
| Kernel type | Microkernel |
| Official website | http://www.sysgo.com/products/pikeos-rtos-and-virtualization-concept/ |
PikeOS is a microkernel-based real-time operating system made by SYSGO AG. It is targeted at safety and security critical embedded systems. It provides a partitioned environment for multiple operating systems with different design goals, safety requirements, or security requirements to coexist in a single machine.
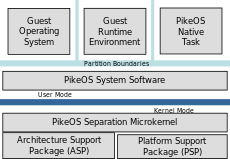
If several programs having different criticality levels are to coexist in one machine, the underlying OS must ensure that they remain independent. Resource partitioning is a widely accepted technique to achieve this. PikeOS combines resource partitioning and virtualisation: Its virtual machine environments (VMs) are able to host entire operating systems, along with their applications. Since PikeOS uses paravirtualisation, operating systems need to be adapted in order to run in one of its VMs. Application programs, however, can run unmodified.
Since each VM has its own, separate set of resources, programs hosted by one VM are independent of those hosted by another. This allows for legacy (e.g. Linux) programs to coexist with safety-critical programs in one machine. Unlike other popular virtualisation systems, PikeOS features not only separation of spatial resources, but also strictly separates temporal resources of its client OSes. This allows for hard real-time systems to be virtualised, while still retaining their timing properties. The PikeOS scheduling method is patented.[1]
Spatial and temporal resources are assigned statically to the individual VMs by the PikeOS System Software. Together with the PikeOS microkernel, this system software forms a minimal layer of globally trusted code. Due to the small amount of trusted code and the modular design PikeOS is suited for safety-critical projects requiring certification according to industrial standards. Known examples are the development of the Airbus A350 Integrated Modular Avionics devices and the Airbus A400M loadmaster workstation.[2][3][4]
Certification standards
PikeOS is certified according to the following standards:[5]
PikeOS is the only operating system that achieved a SIL4 certification for SMP usage on multi-core platforms.[6]
Certifications in progress:
- ISO 26262
- EN 62304
Programming interfaces and environments
Currently the following application programming interfaces, run-time environments and guest operating systems are available:
- PikeOS native interface
- ARINC 653 APEX
- POSIX PSE51 and PSE52
- Linux
- Android[7][8]
- COQOS[9] including AUTOSAR
- Real-time Java
- Ada
- RTEMS
- OSEK
- ITRON
Supported hardware
PikeOS supports processors with PowerPC, x86, ARM, MIPS, SPARC and SuperH architectures. The strict separation of system resources requires that the processor has a memory management unit or a memory protection unit.
Since version 3.1 PikeOS supports multi-core systems.[10]
References
- ↑ SYSGO’s Patent for scheduling mixed real-time and non-real-time applications www.wipo.int/pctdb/en/wo.jsp?IA=WO2006%2F050967
- ↑ Airbus selects SYSGO PikeOS for A350 XWB aircraft Article on EDA Geek(18/11/2008)
- ↑ Rheinmetall selects DO178B certifiable PikeOS from SYSGO for A400M project Article from Military Embedded Systems (10/12/2008)
- ↑ In-Flight Equipment for Airbus A400M www.menmicro.com/applications/avionics-in-flight,30AP011.html
- ↑ SIL 3-4 certificate
- ↑ World premiere with SIL4 certification on a multi-core platform
- ↑ SYSGO’s Embedded Virtualization RTOS PikeOS Offers Android Personality Article from ElectronicSpecifier (April 2011)
- ↑ Android & Autosar running concurrently on PikeOS Video from Embedded World 2011
- ↑ OpenSynergy brings security to infotainment EETimes Automotive (01/11/2011)
- ↑ PikeOS adds multicore Article from EE-Times (02/03/2010)