Piet Mondrian
| Piet Mondrian | |
|---|---|
 Piet Mondrian in 1899 | |
| Birth name | Pieter Cornelis Mondriaan |
| Born |
7 March 1872 Amersfoort, Netherlands |
| Died |
1 February 1944 (aged 71) Manhattan, New York, United States |
| Nationality | Dutch |
| Field | Painting |
| Training | Rijksakademie |
| Movement | De Stijl |
Pieter Cornelis "Piet" Mondriaan, after 1906 Mondrian (Dutch pronunciation: [ˈpit ˈmɔndrijaːn], later [ˈmɔndrijɑn]; March 7, 1872 – February 1, 1944) was a Dutch painter.
He was an important contributor to the De Stijl art movement and group, which was founded by Theo van Doesburg. He evolved a non-representational form which he termed neoplasticism. This consisted of white ground, upon which was painted a grid of vertical and horizontal black lines and the three primary colors.[1]
Between his 1905 painting, The River Amstel, and his 1907 Amaryllis, Mondrian changed the spelling of his signature from Mondriaan to Mondrian.[2]
The Netherlands (1872–1911)


Mondrian was born in Amersfoort in the Netherlands, the second of his parents' children.[3] He was descended from Christian Dirkzoon Monderyan who lived in The Hague as early as 1670.[2] The family moved to Winterswijk in the east of the country, when his father, Pieter Cornelius Mondriaan, was appointed Head Teacher at a local primary school.[4] Mondrian was introduced to art from a very early age: his father was a qualified drawing teacher; and, with his uncle, Fritz Mondriaan (a pupil of Willem Maris of the Hague School of artists), the younger Piet often painted and drew along the river Gein.[5]
After a strictly Protestant upbringing, in 1892, Mondrian entered the Academy for Fine Art in Amsterdam.[6] He already was qualified as a teacher.[4] He began his career as a teacher in Primary Education, but he also practiced painting. Most of his work from this period is Naturalistic or Impressionistic, consisting largely of landscapes. These Pastoral images of his native country depict windmills, fields, and rivers, initially in the Dutch Impressionist manner of the Hague School and then in a variety of styles and techniques documenting his search for a personal style. These paintings are most definitely Representational, illustrating the influence various artistic movements had on Mondrian, including Pointillism and the vivid colors of Fauvism.
On display in the Gemeentemuseum in the Hague are a number of paintings from this period, including such Post-Impressionist works as The Red Mill and Trees in Moonrise. Another painting, Evening (Avond) (1908), depicting a tree in a field at dusk, even augurs future developments by using a palette consisting almost entirely of red, yellow, and blue. Although it is in no sense Abstract, Avond is the earliest of Mondrian's works to emphasize the primary colors.
.jpg)
The earliest paintings that show an inkling of the abstraction to come are a series of canvases from 1905 to 1908, which depict dim scenes of indistinct trees and houses with reflections in still water. Although the result leads the viewer to begin emphasizing the forms over the content, these paintings are still firmly rooted in nature; and it is only the knowledge of Mondrian's later achievements that leads one to search for the roots of his future abstraction in these works.
Mondrian's art always was intimately related to his spiritual and philosophical studies. In 1908, he became interested in the theosophical movement launched by Helena Petrovna Blavatsky in the late 19th century; and, in 1909, he joined the Dutch branch of the Theosophical Society. The work of Blavatsky and a parallel spiritual movement, Rudolf Steiner's Anthroposophy, significantly affected the further development of his aesthetic.[7] Blavatsky believed that it was possible to attain a more profound knowledge of nature than that provided by empirical means, and much of Mondrian's work for the rest of his life was inspired by his search for that spiritual knowledge.
Mondrian and his later work were deeply influenced by the 1911 Moderne Kunstkring exhibition of Cubism in Amsterdam. His search for simplification is shown in two versions of Still Life with Ginger Pot (Stilleven met Gemberpot). The 1911 version [8] is Cubist; in, the 1912 version,[9] it is reduced to a round shape with triangles and rectangles.
Paris (1911–1914)
In 1911, Mondrian moved to Paris and changed his name (dropping an 'a' from Mondriaan) to emphasize his departure from The Netherlands. This matched the changed signature on his works that is dated to before 1907.[10] While in Paris, the influence of the Cubist style of Picasso and Georges Braque appeared almost immediately in Mondrian's work. Paintings such as The Sea (1912) and his various studies of trees from that year still contain a measure of representation; but increasingly, they are dominated by geometric shapes and interlocking planes. While Mondrian was eager to absorb the Cubist influence into his work, it seems clear that he saw Cubism as a "port of call" on his artistic journey, rather than as a destination.
The Netherlands (1914–1919)
Unlike the Cubists, Mondrian still attempted to reconcile his painting with his spiritual pursuits; and, in 1913, he began to fuse his art and his theosophical studies into a theory that signaled his final break from representational painting. While Mondrian was visiting home in 1914, World War I began, forcing him to remain in The Netherlands for the duration of the conflict. During this period, he stayed at the Laren artist's colony, there meeting Bart van der Leck and Theo van Doesburg, who were both undergoing their own personal journeys toward Abstraction. Van der Leck's use of only primary colors in his art greatly influenced Mondrian. After a meeting with Van der Leck in 1916, Mondrian wrote, "My technique which was more or less Cubist, and therefore more or less pictorial, came under the influence of his precise method."[11] With Van Doesburg, Mondrian founded De Stijl (The Style), a journal of the De Stijl Group, in which he published his first essays defining his theory, for which he adopted the term Neoplasticism.
Mondrian published “De Nieuwe Beelding in de schilderkunst” (“The New Plastic in Painting”)[12] in twelve installments during 1917 and 1918. This was his first major attempt to express his artistic theory in writing. Mondrian's best and most-often quoted expression of this theory, however, comes from a letter he wrote to H.P. Bremmer in 1914:
I construct lines and color combinations on a flat surface, in order to express general beauty with the utmost awareness. Nature (or, that which I see) inspires me, puts me, as with any painter, in an emotional state so that an urge comes about to make something, but I want to come as close as possible to the truth and abstract everything from that, until I reach the foundation (still just an external foundation!) of things…I believe it is possible that, through horizontal and vertical lines constructed with awareness, but not with calculation, led by high intuition, and brought to harmony and rhythm, these basic forms of beauty, supplemented if necessary by other direct lines or curves, can become a work of art, as strong as it is true.[13]
Paris (1919–1938)



When the war ended in 1918, Mondrian returned to France, where he would remain until 1938. Immersed in the crucible of artistic innovation that was post-war Paris, he flourished in an atmosphere of intellectual freedom that enabled him to embrace an art of pure abstraction for the rest of his life. Mondrian began producing grid-based paintings in late 1919, and in 1920, the style for which he came to be renowned began to appear.
In the early paintings of this style the lines delineating the rectangular forms are relatively thin, and they are gray, not black. The lines also tend to fade as they approach the edge of the painting, rather than stopping abruptly. The forms themselves, smaller and more numerous than in later paintings, are filled with primary colors, black, or gray, and nearly all of them are colored; only a few are left white.
During late 1920 and 1921, Mondrian's paintings arrive at what is to casual observers their definitive and mature form. Thick black lines now separate the forms, which are larger and fewer in number, and more of them are left white than was previously the case. This was not the culmination of his artistic evolution, however. Although the refinements became more subtle, Mondrian's work continued to evolve during his years in Paris.
In the 1921 paintings, many of the black lines (but not all of them) stop short at a seemingly arbitrary distance from the edge of the canvas, although the divisions between the rectangular forms remain intact. Here too, the rectangular forms remain mostly colored. As the years passed and Mondrian's work evolved further, he began extending all of the lines to the edges of the canvas and he also began to use fewer and fewer colored forms, favoring white instead.
These tendencies are particularly obvious in the “lozenge” works that Mondrian began producing with regularity in the mid-1920s. The "lozenge" paintings are square canvases tilted 45 degrees, so that they hang in a diamond shape. Typical of these is Schilderij No. 1: Lozenge With Two Lines and Blue (1926), also known as Composition With Blue and Composition in White and Blue, which is currently on display at the Philadelphia Museum of Art. One of the most minimal of Mondrian's canvases, this painting consists only of two black, perpendicular lines and a small triangular form, colored blue. The lines extend all the way to the edges of the canvas, almost giving the impression that the painting is a fragment of a larger work.
Although one is hampered by the glass protecting the painting, and by the toll that age and handling have obviously taken on the canvas, a close examination of this painting begins to reveal something of the artist's method. Mondrian's paintings are not composed of perfectly flat planes of color, as one might expect. Brush strokes are evident throughout, although they are subtle, and the artist appears to have used different techniques for the various elements.
The black lines are the flattest elements, with the least amount of depth. The colored forms have the most obvious brush strokes, all running in one direction. Most interesting, however, are the white forms, which clearly have been painted in layers, using brush strokes running in different directions. This generates a greater sense of depth in the white forms, as though they are overwhelming the lines and the colors, which indeed they were, as Mondrian's paintings of this period came to be increasingly dominated by white space.
Schilderij No. 1 may be the most extreme extent of Mondrian's minimalism. As the years progressed, lines began to take precedence over forms in his painting. In the 1930s, he began to use thinner lines and double lines more frequently, punctuated with a few small colored forms, if any at all. Double lines particularly excited Mondrian, for he believed they offered his paintings a new dynamism which he was eager to explore.
London and New York (1938–1944)
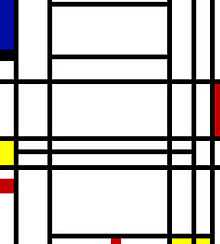
In September 1938, Mondrian left Paris in the face of advancing fascism and moved to London. After the Netherlands were invaded and Paris fell in 1940, he left London for Manhattan, where he would remain until his death. Some of Mondrian's later works are difficult to place in terms of his artistic development, because there were quite a few canvases that he began in Paris or London which he only completed months or years later in Manhattan. The finished works from this later period demonstrate an unprecedented business, however, with more lines than any of his work since the 1920s, placed in an overlapping arrangement that is almost cartographical in appearance. He spent many long hours painting on his own until his hands blistered and he sometimes cried or made himself sick.
Mondrian produced Lozenge Composition With Four Yellow Lines (1933), a simple painting that introduced what for him was a shocking innovation: thick, colored lines instead of black ones. After that one painting, this practice remained dormant in Mondrian's work until he arrived in Manhattan, at which time he began to embrace it with abandon. In some examples of this new direction, such as Composition (1938) / Place de la Concorde (1943), he appears to have taken unfinished black-line paintings from Paris and completed them in New York by adding short perpendicular lines of different colors, running between the longer black lines, or from a black line to the edge of the canvas. The newly colored areas are thick, almost bridging the gap between lines and forms, and it is startling to see color in a Mondrian painting that is unbounded by black. Other works mix long lines of red amidst the familiar black lines, creating a new sense of depth by the addition of a colored layer on top of the black one.
The new canvases that Mondrian began in Manhattan are even more startling, and indicate the beginning of a new idiom that was cut short by the artist's death. New York City (1942) is a complex lattice of red, blue, and yellow lines, occasionally interlacing to create a greater sense of depth than his previous works. An unfinished 1941 version of this work uses strips of painted paper tape, which the artist could rearrange at will to experiment with different designs.
His painting Broadway Boogie-Woogie (1942–43) at The Museum of Modern Art in Manhattan was highly influential in the school of abstract geometric painting. The piece is made up of a number of shimmering squares of bright color that leap from the canvas, then appear to shimmer, drawing the viewer into those neon lights. In this painting and the unfinished Victory Boogie Woogie (1942–44), Mondrian replaced former solid lines with lines created from small adjoining rectangles of color, created in part by using small pieces of paper tape in various colors. Larger unbounded rectangles of color punctuate the design, some with smaller concentric rectangles inside them. While Mondrian's works of the 1920s and 1930s tend to have an almost scientific austerity about them, these are bright, lively paintings, reflecting the upbeat music that inspired them and the city in which they were made.
In these final works, the forms have indeed usurped the role of the lines, opening another new door for Mondrian's development as an abstractionist. The Boogie-Woogie paintings were clearly more of a revolutionary change than an evolutionary one, representing the most profound development in Mondrian's work since his abandonment of representational art in 1913.
In 2008 the Dutch television program Andere Tijden found the only known movie footage with Mondrian.[14] The discovery of the film footage was announced at the end of a two-year research program on the Victory Boogie Woogie. The research found that the painting was in very good condition and that Mondrian painted the composition in one session. It also was found that the composition was changed radically by Mondrian shortly before his death by using small pieces of colored tape.
Wall works
When the 47-year-old Piet Mondrian left the Netherlands for unfettered Paris for the second and last time in 1919, he set about at once to make his studio a nurturing environment for paintings he had in mind that would increasingly express the principles of Neo-Plasticism about which he had been writing for two years. To hide the studio's structural flaws quickly and inexpensively, he tacked up large rectangular placards, each in a single color or neutral hue. Smaller colored paper squares and rectangles, composed together, accented the walls. Then came an intense period of painting. Then again he addressed the walls, repositioning the colored cutouts, adding to their number, altering the dynamics of color and space, producing new tensions and equilibrium. Before long, he had established a creative schedule in which a period of painting took turns with a period of experimentally regrouping the smaller papers on the walls, a process that directly fed the next period of painting. It was a pattern he followed for the rest of his life, through wartime moves from Paris to London’s Hampstead in 1938 and 1940, across the Atlantic to Manhattan.
At the age of 71 in the fall of 1943, Mondrian moved into his second and final Manhattan studio at 15 East 59th Street, and set about to recreate the environment he had learned over the years was most congenial to his modest way of life and most stimulating to his art. He painted the high walls the same off-white he used on his easel and on the seats, tables and storage cases he designed and fashioned meticulously from discarded orange and apple-crates. He glossed the top of a white metal stool in the same brilliant primary red he applied to the cardboard sheath he made for the radio-phonograph that spilled forth his beloved jazz from well-traveled records. Visitors to this last studio seldom saw more than one or two new canvases, but found, often to their astonishment, that eight large compositions of colored bits of paper he had tacked and re-tacked to the walls in ever-changing relationships constituted together an environment that, paradoxically and simultaneously, was both kinetic and serene, stimulating and restful. It was the best space, Mondrian said, that he had ever inhabited. Tragically, he was there for only a few months, as he died in February 1944.
After his death, Mondrian’s friend and sponsor in Manhattan, artist Harry Holtzman, and another painter friend, Fritz Glarner, carefully documented the studio on film and in still photographs before opening it to the public for a six-week exhibition. Before dismantling the studio, Holtzman (who was also Mondrian’s heir) traced the wall compositions precisely, prepared exact portable facsimiles of the space each had occupied, and affixed to each the original surviving cut-out components. These portable Mondrian compositions have become known as "The Wall Works". They have been exhibited twice since Mondrian’s death at Manhattan’s Museum of Modern Art (1983/1995-96), once in SoHo at The Carpenter + Hochman Gallery (1984), once each at Galerie Tokoro in Tokyo, Japan (1993), the XXII Biennial of Sao Paulo (1994), The University of Michigan (1995) and, the first time to be shown in Europe, at the Akademie der Künste (Academy of The Arts), in Berlin (February 22 – April 22, 2007).
Death
Piet Mondrian died of pneumonia on February 1, 1944 and was interred in the Cypress Hills Cemetery in Brooklyn, New York.[15]
On February 3, 1944, a memorial, attended by nearly 200 people including Alexander Archipenko, Marc Chagall, Marcel Duchamp, Fernand Léger, Alexander Calder, and Robert Motherwell, was held for Mondrian at the Universal Chapel on Lexington Avenue and 52nd Street in Manhattan.[16]
The Mondrian / Holtzman Trust functions as Mondrian's official estate, and "aims to promote awareness of Mondrian's artwork and to ensure the integrity of his work".[17]
References in culture
- The National Museum of Serbia was the first museum to include one of Mondrian's paintings in its permanent exhibition.[18]
- Along with Klee and Kandinsky, Mondrian was one of the main inspirations to the early pointillist musical aesthetic of serialist composer Pierre Boulez,[19] although his interest in Mondrian was restricted to the works of 1914–15.[20] By May 1949 Boulez said he was "suspicious of Mondrian," and by December 1951 expressed a dislike for his paintings (regarding them as "the most denuded of mystery that have ever been in the world"), and a strong preference for Klee.[21]
- In the 1930s, the French fashion designer Lola Prusac, who worked at that time for Hermès in Paris, designed a range of luggage and bags inspired by the latest works of Mondrian: inlays of red, blue, and yellow leather squares.[22]
- In 2001–2003 British artist Keith Milow made a series of paintings based on the so-called Transatlantic Paintings (1935–1940) by Mondrian.[23]
- Fashion designer Yves Saint Laurent's Fall 1965 Mondrian collection featured shift dresses in blocks of primary color with black bordering, inspired by Mondrian.[24] The collection proved so popular that it inspired a range of imitations that encompassed garments from coats to boots.
- In the 1970s the television show The Partridge Family painted a 1957 Chevrolet school bus in Mondrian style.
- The La Vie Claire cycling team's bicycles and clothing designs were inspired by Mondrian's work throughout the 1980s. The French ski and bicycle equipment manufacturer LOOK, which also sponsored the team, used a Mondrian-inspired logo for a while. The style was revived in 2008 for a limited edition frame.[25]
- 1980s R&B sensation Force MDs created a popular music video for their hit "Love is a House", superimposing themselves performing inside of digitally drawn squares inspired by Composition II.[26]
- Piet is an esoteric programming language named after Piet Mondrian.[27]
- Mondrian (programming language) is a programming language named after him.[28]
- The Mondrian is a 20-story high-rise in the Cityplace neighborhood of Oak Lawn, Dallas, Texas (US). Construction started on the structure in 2003 and the building was completed in 2005.
- In 2008, Nike released a pair of Dunk Low SB shoes inspired by Mondrian's iconic neo-plastic paintings.[29]
Partial list of works
- The Factory (1900)
- Field with Young Trees in the Foreground (1907), Cleveland Museum of Art
- Molen Mill; Mill in Sunlight (1908) External link.
- Avond Evening; Red Tree (1908) External link.
- Chrysanthemum (1908) External link.
- Windmill by the Water (1908)
- View from the Dunes with Beach and Piers, Domburg, (1909)
- The Red Tree (1909–10)
- Amaryllis (1910)
- Evolution (1910–11)
- The Red Mill (1910–11) External link.
- Horizontal Tree (1911)
- Gray Tree (1911) Gemeentemuseum Den Haag.
- Still Life with Ginger Pot I (Cubist) (1911) Guggenheim Collection.
- Still Life with Ginger Pot II (Simplified) (1912) Guggenheim Collection.
- Apple Tree in Bloom (1912)
- Eucaliptus (1912)
- Trees (1912–1913)
- Scaffoldings (1912–1914)
- Composition No. II; Composition in Line and Color (1913)
- Ocean 5 (1915)
- Composition III with Color Planes (1917)
- Composition with Color Planes and Gray Lines 1 (1918)
- Composition with Gray and Light Brown (1918)
- Composition with Grid VII (1919)
- Composition: Checkerboard, Dark Colors (1919)
- Composition A: Composition with Black, Red, Gray, Yellow, and Blue (1920)
- Composition with Black, Red, Gray, Yellow, and Blue (1920) External link.
- Tableau I (1921)
- Lozenge Composition with Yellow, Black, Blue, Red, and Gray (1921)
- Composition with Large Blue Plane, Red, Black, Yellow, and Gray (1921)
- Composition with Blue, Yellow, Black, and Red (1922)
- Composition #2 (1922)
- Composition with Yellow, Black, Blue, and Grey (1923) Berardo Collection.
- Lozenge Composition with Red, Black, Blue, and Yellow (1925)
- Lozenge Composition with Red, Gray, Blue, Yellow, and Black (1925) External link.
- Composition with Red, Yellow, and Blue (1927), Cleveland Museum of Art
- Fox Trot; Lozenge Composition with Three Black Lines (1929)
- Composition No. III/ Fox Trot B with Black, Red, Blue and Yellow (1929), Yale University Art Gallery
- Composition with Yellow Patch (1930)
- Composition with Yellow (1930)
- Composition with Blue and Yellow (1932)
- Composition No. III Blanc-Jaune (1935–42)
- Rhythm of Straight Lines (1935–42) Harvard University.
- Rhythm of Black Lines painting (1935–42)
- Composition blanc, rouge et noir or Composition in White, Black and Red (1936)
- Vertical Composition with Blue and White (1936)
- Abstraction (1937–42)
- Composition with Red, Yellow, and Blue (1937–42)
- Composition No. 8 (1939–42)
- Painting #9 (1939–42)
- Composition No. 10 (1939–1942)
- New York City I (1942)
- Chrysanthemum (1942), Cleveland Museum of Art
- Trafalgar Square (1939–1943)
- Broadway Boogie-Woogie (1942–43) Museum of Modern Art.
- Place de la Concorde (1943)
- Victory Boogie-Woogie (1943–44) Gemeentemuseum Den Haag.
See also
Footnotes
- ↑ "Piet Mondrian", Tate gallery, published in Ronald Alley, Catalogue of the Tate Gallery's Collection of Modern Art other than Works by British Artists, Tate Gallery and Sotheby Parke-Bernet, London 1981, pp.532–3. Retrieved 18 December 2007.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Michel Seuphor, Piet Mondrian: Life and Work (New York: Harry N. Abrams), pp. 44 and 407.
- ↑ Deicher (1995), p. 93
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Milner (1992), p. 9
- ↑ Milner (1995), pp. 9–10
- ↑ Deicher (1995), pp. 7–8
- ↑ Sellon, Emily B.; Weber, Renee (1992). "Theosophy and the Theosophical Society". In Faivre, Antoine. Modern Esoteric Spirituality. World Spirituality 21. Crossroad. p. 327. ISBN 0824514440.
- ↑ Guggenheim Collection – Artist – Mondrian – Still Life with Gingerpot I at www.guggenheimcollection.org
- ↑ Guggenheim Collection – Artist – Mondrian – Still Life with Gingerpot II at www.guggenheimcollection.org
- ↑ Mondriaan, Pieter Cornelis (1872–1944) at www.inghist.nl
- ↑ The Dictionary of Painters. New York, NY: Larousse and Co., Inc. 1976. p. 285.
- ↑ Mondrian 1986, 18–74.
- ↑ Van Doesburg at Tate Modern By Jackie Wullschlager, Published 2010/6/2
- ↑ (Dutch) "Eerste filmbeelden Mondriaan" (NOS Journaal, 28-08-2008, visited: idem)
- ↑ October 21, 2010 at Find a Grave
- ↑ "Piet Mondrian [1872-1944]". New Netherland Institute. Retrieved 28 October 2013.
- ↑ Mission Statement page of The Mondrian / Holtzman Trust website
- ↑
- ↑ Peter F. Stacy (1987). Boulez and the Modern Concept. Scholar Press. ISBN 0-8032-4183-6.
- ↑ Strauss 1989, 133.
- ↑ Boulez and Cage 1995, 103, 116–17.
- ↑ Guerrand 1988, 57.
- ↑ "Keith Milow – Paintings II". Keith Milow. Retrieved 18 Feb 2010.
- ↑ "Yves Saint Laurent: 'Mondrian' day dress (C.I.69.23)". Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History (Metropolitan Museum of Art). October 2006.
- ↑ "Look! It’s 1986! The French frame maker offers a limited edition Mondrian paint scheme". velonews.com. 8 May 2008.
- ↑ "Force M.D.s video "Love Is A House" made available on youtube". 10 June 2010.
- ↑ David Morgan-Mar (25 January 2008). "Piet". Retrieved 18 Feb 2010.
- ↑ "Mondrian". Retrieved 18 Nov 2012.
- ↑ Khan, Furqan (26 April 2008). "Piet Mondrian - Nike Dunk Low SB - Available!", KicksOnFire.com. Retrieved 30 May 2013.
References
- Bax, Marty (2001). Complete Mondrian. Aldershot (Hampshire) and Burlington (Vermont): Lund Humphries. ISBN 0-85331-803-4 (cloth) ISBN 0-85331-822-0 (pbk).
- Boulez, Pierre, and John Cage (1995). The Boulez-Cage Correspondence, new edition, edited by Jean-Jacques Nattiez; translated from the French by Robert Samuels. Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-48558-4.
- Cooper, Harry A. (1997). "Dialectics of Painting: Mondrian's Diamond Series, 1918–1944". PhD diss. Cambridge: Harvard University.
- Deicher, Susanne (1995). Piet Mondrian, 1872–1944: Structures in Space. Cologne: Benedikt Taschen. ISBN 3-8228-8885-0.
- Faerna, José María (ed.) (1997). Mondrian Great Modern Masters. New York: Cameo/Abrams. ISBN 0-8109-4687-4.
- Guerrand, Jean R. (1988). Souvenirs cousus sellier: un demi-siècle chez Hermès. Paris: Oliver Orban. ISBN 2-85565-377-0.
- Janssen, Hans (2008). Mondriaan in het Gemeentemuseum Den Haag. [The Hague]: Gemeentemuseum Den Haag. ISBN 978-90-400-8443-0
- Locher, Hans (1994) Piet Mondrian: Colour, Structure, and Symbolism: An Essay. Bern: Verlag Gachnang & Springer. ISBN 978-3-906127-44-6
- Milner, John (1992). Mondrian. London: Phaidon. ISBN 0-7148-2659-6.
- Mondrian, Piet (1986). The New Art – The New Life: The Collected Writings of Piet Mondrian, edited by Harry Holtzman and Martin S. James. Documents of 20th-Century Art. Boston: G. K. Hall and Co. ISBN 0-8057-9957-5. Reprinted 1987, London: Thames and Hudson. ISBN 0-500-60011-2. Reprinted 1993, New York: Da Capo Press. ISBN 0-306-80508-1.
- Schapiro, Meyer (1995). Mondrian: On the Humanity of Abstract Painting. New York: George Braziller. ISBN 0-8076-1369-X (cloth) ISBN 0-8076-1370-3 (pbk).
- Strauss Walter A. (1989). "Stacey Peter F. Boulez and the Modern Concept. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, 1987". SubStance 18, no. 2, issue 59:131–34.
- Welsh, Robert P., Joop J. Joosten, and Henk Scheepmaker (1998). Piet Mondrian: Catalogue Raisonné, translated by Jacques Bosser. Blaricum: V+K Publishing/Inmerc.
- Larousse and Co., Inc. (1976). Mondrian, Piet. In Dictionary of Painters (p. 285). New York: Larousse and Co., Inc.
Further reading
- Busignani, Alberto (1968). Mondrian: The Life and Work of the Artist, Illustrated by 80 Colour Plates, translated from the Italian by Caroline Beamish. A Dolphin Art Book. London: Thames and Hudson.
- Gooding, Mel (2001). Abstract Art. Movements in Modern Art. London: Tate Publishing; Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 1-85437-302-1 (Tate); ISBN 0-521-80928-2 (Cambridge, cloth); ISBN 0-521-00631-7 (Cambridge, pbk).
- Hajdu, István (1987). Piet Mondrian. Pantheon. Budapest: Corvina Kiadó. ISBN 963-13-2265-3. (Hungarian)
- Apollonio, Umbro (1970). Piet Mondrian, Milano: Fabri 1976. (Italian)
- Wiegand, Charmion (1943). "The Meaning of Mondrian". The Journal of Aesthetics and Art Criticism (Blackwell Publishing on behalf of The American Society for Aesthetics) 2 (8 (Autumn, 1943)): 62–70. doi:10.2307/425946.
External links
- Mondrian Trust, the official holder of reproduction rights to Mondrian's works.
- Piet Mondrian at the Museum of Modern Art
- Piet Mondrian: The Transatlantic Paintings
- Guggenheim NY Mondrian collection
- Mondrian's daily behavior and his paintings
- Piet Mondrian in London by Barbara Hepworth, Herbert Read, Ben Nicholson, Naum Gabo and others
| ||||||||
|
