Pi3 Orionis
|
Observation data
Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 |
| Constellation |
Orion |
| Right ascension |
04h 49m 50.41091s[1] |
| Declination |
+06° 57′ 40.5883″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 3.16[2] |
| Characteristics |
|---|
| Spectral type | F6 V[2] |
| U−B color index | +0.00[2] |
| B−V color index | +0.46[2] |
| Variable type | Suspected[3] |
| Astrometry |
|---|
|
|---|
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 24.1[4] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 464.06[1] mas/yr
Dec.: 11.21[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 123.94 ± 0.17[1] mas |
| Distance | 26.32 ± 0.04 ly
(8.07 ± 0.01 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 3.65[5] |
|
|---|
| Details |
|---|
|
|---|
| Mass | 1.236[6] M☉ |
| Radius | 1.323 ± 0.004[7] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 2.822 ± 0.030[7] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.4[8] cgs |
| Temperature | 6,516 ± 19[7] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | 0.02[8] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 17[9] km/s |
| Age | 1.4[5] Gyr |
|
|---|
| Other designations |
|---|
Tabit, π3 Ori, 1 Ori, BD+06°762, FK5 1134, GCTP 1077.00, Gliese 178, HD 30652, HIP 22449, HR 1543, LTT 11517, SAO 112106. [10] |
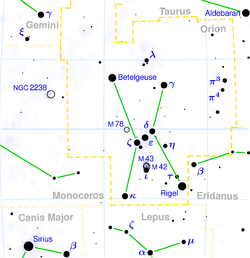
Pi3 Orionis (π3 Ori, π3 Orionis) is the Bayer designation for a star in the equatorial constellation of Orion. It has the traditional name of Tabit[11] and the Flamsteed designation 1 Orionis. At an apparent visual magnitude of 3.16,[2] it is readily visible to the naked eye. Pi3 Orionis is the brightest star in the lion's hide (or shield) that Orion is holding. The distance to this star, as measured using the parallax technique, is 26.32 light-years (8.07 parsecs).[1] Though no extrasolar planets have been observed around Pi3 Orionis, the star is considered a prime location for planets as small as the Earth.
Pi3 Orionis is a main-sequence star of spectral type F6 V. Since 1943, the spectrum of this star has served as one of the stable anchor points by which other stars are classified.[12] Compared to the Sun, it has about 124%[6] of the mass, 132% of the radius, and nearly 3 times the luminosity.[7] This energy is being radiated from the star's outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of 6,516 K,[7] giving it the yellow-white glow of an F-type star. Pi3 Orionis is most likely single; a nearby star is probably an optical companion.[13]
Although a periodicity of 73.26 days has been observed in the star's radial velocity, it seems likely to be bound more to stellar activity than to a planetary object in close orbit. No substellar companion has been detected so far around Pi3 Orionis and the McDonald Observatory team has set limits to the presence of one or more planets[14] with masses between 0.84 and 46.7 Jupiter masses and average separations spanning between 0.05 and 5.2 astronomical units. Thus, so far it appears that an Earth-like planet could easily orbit the star without any complications caused by a gravitationally perturbing body.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 van Leeuwen, F. (November 2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv:0708.1752, Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Johnson, H. L.; Morgan, W. W. (1953), "Fundamental stellar photometry for standards of spectral type on the revised system of the Yerkes spectral atlas", Astrophysical Journal 117: 313–352, Bibcode:1953ApJ...117..313J, doi:10.1086/145697.
- ↑ Kukarkin, B. V.; et al. (1981), Nachrichtenblatt der Vereinigung der Sternfreunde e.V. (Catalogue of suspected variable stars), Moscow: Academy of Sciences USSR Shternberg, Bibcode:1981NVS...C......0K.
- ↑ Evans, D. S. (June 20–24, 1966), "The Revision of the General Catalogue of Radial Velocities", in Batten, Alan Henry; Heard, John Frederick, Determination of Radial Velocities and their Applications, Proceedings from IAU Symposium no. 30, University of Toronto: International Astronomical Union, Bibcode:1967IAUS...30...57E.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Holmberg, J.; Nordström, B.; Andersen, J. (July 2009), "The Geneva-Copenhagen survey of the solar neighbourhood. III. Improved distances, ages, and kinematics", Astronomy and Astrophysics, Supplement Series 501 (3): 941−947, arXiv:0811.3982, Bibcode:2009A&A...501..941H, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200811191. Note: see VizieR catalogue V/130.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Takeda, G.; et al. (2007), "Stellar parameters of nearby cool stars. II. Physical properties of ~1000 cool stars from the SPOCS catalog", Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 168: 297–318, Bibcode:2008yCat..21680297T Note: see VizieR catalogue J/ApJS/168/297.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 Boyajian, Tabetha S. et al. (February 2012), "Stellar Diameters and Temperatures. I. Main-sequence A, F, and G Stars", The Astrophysical Journal 746 (1): 101, arXiv:1112.3316, Bibcode:2012ApJ...746..101B, doi:10.1088/0004-637X/746/1/101. See Table 10.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Kuroczkin, D.; Wiszniewski, A. (1997), "The problem of iron abundance in the SMR stars.", Acta Astronomica 27: 145–150, Bibcode:1977AcA....27..145K.
- ↑ Bernacca, P. L.; Perinotto, M. (1970), "A catalogue of stellar rotational velocities", Contributi Osservatorio Astronomico di Padova in Asiago 239 (1), Bibcode:1970CoAsi.239....1B.
- ↑ "1 Ori -- Variable Star", SIMBAD Astronomical Object Database (Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg), retrieved 2011-01-07
- ↑ Moore, Patrick; Rees, Robin (2011), Patrick Moore's Data Book of Astronomy (2nd ed.), Cambridge University Press, p. 460, ISBN 0521899354
- ↑ Garrison, R. F. (December 1993), "Anchor Points for the MK System of Spectral Classification", Bulletin of the American Astronomical Society 25: 1319, Bibcode:1993AAS...183.1710G, retrieved 2012-02-04
- ↑ Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (September 2008), "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 389 (2): 869–879, arXiv:0806.2878, Bibcode:2008MNRAS.389..869E, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x.
- ↑ Wittenmyer, Robert A.; et al. (July 2006), "Detection Limits from the McDonald Observatory Planet Search Program", The Astronomical Journal 132 (1): 177–188, arXiv:astro-ph/0604171, Bibcode:2006AJ....132..177W, doi:10.1086/504942.
External links
|
|---|
| | |
| |
|
|---|
|
|
- Sirius (8.60 ± 0.04 ly; 2 stars)
|
|---|
| |
| |
|
| |
|
|---|
|
| |
|
- Tau Ceti (11.905 ± 0.007 ly; 1 star, 5? planets: b
- c
- d
- e
- f)
|
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
| |
|
|---|
|
|
- Altair (16.73 ± 0.05 ly; 1 star)
|
|---|
| |
| |
| |
|
- Gliese 876 (15.21 ± 0.04 ly; 1 star, 4 planets: d
- c
- b
- e)
- GJ 1002 (15.31 ± 0.26 ly; 1 star)
- LHS 288 (15.55 ± 0.20 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 412 (15.81 ± 0.08 ly; 2 stars)
- AD Leonis (15.94 ± 0.22 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 832 (16.16 ± 0.08 ly; 1 star, 1 planet: b)
- EV Lacertae (16.46 ± 0.07 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 682 (16.60 ± 0.20 ly; 1 star)
- GJ 1116 (17.06 ± 0.23 ly; 2 stars)
- GJ 3379 (17.10 ± 0.17 ly; 1 star)
- LHS 1723 (17.36 ± 0.12 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 445 (17.42 ± 0.15 ly; 1 star)
- Wolf 498 (17.66 ± 0.07 ly; 1 star)
- Stein 2051 (18.07 ± 0.08 ly; 2 stars)
- Gliese 251 (18.31 ± 0.15 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 205 (18.53 ± 0.11 ly; 1 star)
- L 449-1 (18.6 ± 3.9 ly; 1 star)
- LP 816-060 (18.63 ± 0.37 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 229 (18.77 ± 0.11 ly; 1 star, 1 brown dwarf)
- Ross 47 (19.02 ± 0.11 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 693 (19.06 ± 0.25 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 752 (19.08 ± 0.06 ly; 2 stars: A
- B (vB 10))
- Gliese 754 (19.28 ± 0.18 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 588 (19.35 ± 0.15 ly; 1 star)
- GJ 1005 (19.37 ± 0.10 ly; 2 stars)
- Gliese 908 (19.41 ± 0.14 ly; 1 star)
- YZ Canis Minoris (19.51 ± 0.24 ly; 1 star)
- 2MASS J05332802-4257205 (~19.6 ly; 1 star)
- 2MASS J18450079-1409036 (~19.6 ly; 2 stars)
- Gliese 338 (19.92 ± 0.31 ly; 2 stars)
- Gliese 268 (19.96 ± 0.22 ly; 2 stars)
|
|---|
| |
| |
|
| |
|
|---|
|
| |
| |
|
- Gliese 784 (20.22 ± 0.13 ly; 1 star)
- HN Librae (20.29 ± 0.25 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 581 (20.38 ± 0.21 ly; 1 star, 4 (6?) planets: e
- b
- c
- g?
- d
- f?)
- EQ Pegasi (20.40 ± 0.20 ly; 2 stars)
- LHS 2090 (20.8 ± 0.4 ly; 1 star)
- LHS 337 (20.8 ± 0.3 ly; 1 star)
- Furuhjelm 46 (20.9 ± 0.2 ly; 2 stars)
- G 180-060 (20.9 ± 0.6 ly; 1 star)
- V1054 Ophiuchi (21.05 ± 0.07 ly; 5 stars: Ba
- Bb
- A
- Gl 643
- C (vB 8))
- LP 71-82 (~21.2 ly; 1 star)
- G 161-71 (~21.3 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 625 (21.3 ± 0.2 ly; 1 star)
- GJ 1128 (21.3 ± 0.4 ly; 1 star)
- GL Virginis (21.3 ± 0.4 ly; 1 star)
- LHS 3003 (21.4 ± 0.3 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 408 (21.8 ± 0.3 ly; 1 star)
- SCR J1546−5534 (~21.9 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 829 (21.9 ± 0.3 ly; 2 stars)
- G 41-14 (22.1 ± 0.3 ly; 3 stars)
- EE Leonis (22.2 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 880 (22.3 ± 0.2 ly; 2 stars)
- Gliese 299 (22.3 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star)
- LP 771-095 (22.7 ± 0.4 ly; 3 stars)
- GJ 1068 (22.7 ± 0.3 ly; 1 star)
- 2MASS J20360829-3607115 (~22.8 ly; 1 star)
- L 369-44 (~22.8 ly; 2 stars)
- 2MASS J18522528-3730363 (~22.8 ly; 1 star)
- G 161-7 (~22.8 ly; 2 stars)
- Gliese 809 (23.0 ± 0.1 ly; 2 stars)
- Gliese 393 (23.0 ± 0.4 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 54 (23.1 ± 0.6 ly; 2 stars)
- SCR J0740−4257 (~23.5 ly; 1 star)
- L 43-72 (23.5 ± 4.9 ly; 1 star)
- GJ 1286 (23.6 ± 0.6 ly; 1 star)
- GJ 4063 (23.6+9.6
−5.3 ly; 1 star)
- GJ 4053 (23.7 ± 0.9 ly; 1 star)
- GJ 4274 (24.3 ± 0.9 ly; 1 star)
- GJ 3991 (24.28 ± 0.36 ly; 2 stars)
- GJ 4248 (24.29 ± 0.24 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 109 (24.5 ± 0.4 ly; 1 star)
- GJ 1224 (24.6 ± 0.7 ly; 1 star)
- GJ 3378 (24.7 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 514 (24.97 ± 0.20 ly; 1 star)
|
|---|
| |
| |
|
| |
|
|---|
|
| |
| |
| |
K
(Orange) |
| |
|---|
| V |
- Gliese 673 (25.12 ± 0.14 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 884 (26.6 ± 0.3 ly; 1 star)
- p Eridani (26.57 ± 0.31 ly; 2 stars)
- Gliese 250 (28.4 ± 0.3 ly; 2 stars)
- HR 1614 (28.8 ± 0.3 ly; 1 star)
- HR 7722 (28.8 ± 0.3 ly; 1 star, 2 planets: b
- c)
|
|---|
|
|---|
| |
|
- LHS 1070 (25.2 ± 0.5 ly; 3 stars)
- Gliese 701 (25.3 ± 0.3 ly; 1 star)
- GJ 1093 (25.3 ± 0.7 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 480.1 (25.4 ± 0.8 ly; 1 star)
- SIPS 1259-4336 (25.4 ± 0.2 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 382 (25.48 ± 0.30 ly; 1 star)
- DG Canum Venaticorum (25.9+5.5
−3.8 ly; 1 star)
- Wolf 922 (25.9 ± 0.5 ly; 2 stars)
- Gliese 300 (25.97 ± 0.20 ly; 1 star)
- SSSPM J1138-7722 (26 ± 3 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 793 (26.08 ly; 1 star)
- 2MASS J12140866-2345172 (~26.1 ly; 1 star)
- 2MASS J19513587-3510375 (~26.1 ly; 1 star)
- SCR 0838-5855 (~26.1 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 257 (26.2 ± 0.6 ly; 2 stars)
- Gliese 623 (26.2 ± 0.3 ly; 2 stars)
- GJ 1289 (26.4 ± 0.6 ly; 1 star)
- GJ 1105 (26.4 ± 0.7 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 686 (26.5 ± 0.4 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 493.1 (26.6 ± 1.0 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 48 (26.6 ± 0.3 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 747 (26.6 ± 0.4 ly; 2 stars)
- SCR 1138-7721 (26.7 ± 0.7 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 486 (26.8 ± 0.6 ly; 1 star)
- GJ 1151 (26.8 ± 0.7 ly; 1 star)
- GJ 1227 (26.9 ± 0.4 ly; 1 star)
- GJ 1230 (27.0+1.7
−1.5 ly; 3 stars)
- Gliese 232 (27.2 ± 0.4 ly; 1 star)
- AP Columbae (27.4 ± 0.2 ly; 1 star)
- GJ 3146 (27.6 ± 1.7 ly; 1 star)
- GJ 1154 (27.6 ± 0.9 ly; 1 star)
- GJ 1057 (27.6 ± 0.9 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 618 (27.6 ± 0.6 ly; 2 stars)
- GJ 3076 (27.6+6.0
−4.2 ly; 1 star)
- SCR 0640-0552 (~27.7 ly; 1 star)
- HD 32450 (27.8 ± 0.4 ly; 2 stars)
- Gliese 450 (27.9 ± 0.3 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 877 (28.1 ± 0.3 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 745 (28.1 ± 0.6 ly; 2 stars)
- Gliese 867 (28.2 ± 0.4 ly; 2 stars)
- GJ 3454 (28.2 ± 0.2 ly; 2 stars)
- SCR 0630-7643 (28.6 ± 0.5 ly; 2 stars)
- HU Delphini (28.6 ± 0.5 ly; 2 stars)
- LDS 169 (28.6 ± 0.8 ly; 2 stars)
- Gliese 849 (28.6 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star, 2 planets: b
- c)
- GJ 1103 (28.7 ± 0.8 ly; 2 stars)
- GJ 1207 (28.8 ± 0.4 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 465 (29.0 ± 0.7 ly; 1 star)
- GJ 1277 (29.0 ± 4.6 ly; 1 star)
- GJ 3128 (29.1 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star)
- V374 Pegasi (29.1 ± 0.9 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 357 (29.3 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 595 (29.4 ± 3.5 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 433 (29.5 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star, 2 planets: b
- c)
- Gliese 424 (29.7 ± 0.3 ly; 1 star)
- GJ 3801 (29.7 ± 0.9 ly; 1 star)
- GJ 2066 (29.9 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star)
- LHS 224 (29.9 ± 0.8 ly; 2 stars)
- SCR 1826-6542 (~30 ly; 1 star)
|
|---|
| |
|
DA |
- G 99-47 (26.1 ± 0.8 ly; 1 star)
- WD 2359-434 (26.7 ± 0.3 ly; 1 star)
- Gliese 318 (28.7 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star)
|
|---|
| DC | |
|---|
| DQ |
- LHS 1126 (29.5 ± 0.3 ly; 1 star)
|
|---|
| DZ |
- Wolf 489 (26.9 ± 0.8 ly; 1 star)
- LP 701-29 (27.9 ± 0.2 ly; 1 star)
- L 745-46 (29.7 ± 0.2 ly; 2 stars)
|
|---|
|
|---|
| |
|
M |
- DENIS 0334-49 (27.04 ± 0.83 ly; 1 brown dwarf)
- GJ 3517 (27.8 ± 0.4 ly; 1 brown dwarf)
|
|---|
| L | |
|---|
| T |
- 2MASS 0348-6022 (~25.4 ly; 1 brown dwarf)
- 2MASS 0729-39 (25.8 ± 1.8 ly; 1 brown dwarf)
- UGPS J0521+3640 (26.7+3.9
−3.2 ly; 1 brown dwarf)
- WISE 0313+7807 (~28.0 ly; 1 brown dwarf)
- 2MASS 0727+1710 (29.0 ± 0.2 ly; 1 brown dwarf)
|
|---|
| Y |
- WISE 1405+5534 (25.3+4.4
−3.2 ly; 1 brown dwarf)
- WISE 2220-3628 (~26.4 ly; 1 brown dwarf)
- WISE 0647-6232 (28.4+3.3
−2.7 ly; 1 brown dwarf)
|
|---|
|
|---|
|
| |
In left column are stellar classes of primary members of star systems. Bold are systems containing at least one component with absolute magnitude of +8.5 or brighter. Italic are systems without known trigonometric parallax. |
|
|
|---|
| | Bayer | |
|---|
| | Flamsteed | |
|---|
| | Variable |
- S
- T
- U
- W
- Z
- RS
- UX
- VV
- YY
- AN
- BF
- BL
- BM
- BN
- BQ
- CK
- CN
- CO
- CZ
- DN
- DY
- ER
- EW
- EY
- FH
- FT
- FU
- FZ
- GG
- GP
- GU
- GW
- HK
- KX
- V346
- V351
- V359
- V371
- V372
- V380
- V586
- V901
- V1031
- V1046
- V1051
- V1107
- V1118
- V1149
- V1155
- V1156
- V1159
- V1162
- V1179
- V1192
- V1197
- V1261
- V1307
- V1309
- V1355
- V1357
- V1366
- V1369
- V1377
- V1389
- V1647
- V1649
- V1788
|
|---|
| | HR | |
|---|
| | HD |
- 30869
- 31253
- 31423
- 33636
- 34445
- 35575
- 35775
- 36150
- 36558
- 36629
- 36814
- 36840
- 37605
- 37806
- 37903
- 38087
- 38801
- 290327
|
|---|
| | Gliese | |
|---|
| | Other | |
|---|
| |
|