Silicate minerals
| Silicate minerals | |
|---|---|
 Copper silicate mineral chrysocolla | |
| Category | Mineral |
The silicate minerals make up the largest and most important class of rock-forming minerals, constituting approximately 90 percent of the crust of the Earth. They are classified based on the structure of their silicate group which contain different ratios of silicon and oxygen.
Nesosilicates or orthosilicates

Nesosilicates (from Greek νησος nēsos, island), or orthosilicates, have isolated (insular) [SiO4]4− tetrahedra that are connected only by interstitial cations. Nickel-Strunz classification: 09.A
- Phenakite group
- Olivine group
- Forsterite - Mg2SiO4
- Fayalite - Fe2SiO4
- Garnet group
- Pyrope - Mg3Al2(SiO4)3
- Almandine - Fe3Al2(SiO4)3
- Spessartine - Mn3Al2(SiO4)3
- Grossular - Ca3Al2(SiO4)3
- Andradite - Ca3Fe2(SiO4)3
- Uvarovite - Ca3Cr2(SiO4)3
- Hydrogrossular - Ca3Al2Si2O8(SiO4)3-m(OH)4m
- Zircon group

- Al2SiO5 group
- Andalusite - Al2SiO5
- Kyanite - Al2SiO5
- Sillimanite - Al2SiO5
- Dumortierite - Al6.5-7BO3(SiO4)3(O,OH)3
- Topaz - Al2SiO4(F,OH)2
- Staurolite - Fe2Al9(SiO4)4(O,OH)2
- Humite group - (Mg,Fe)7(SiO4)3(F,OH)2
- Norbergite - Mg3(SiO4)(F,OH)2
- Chondrodite - Mg5(SiO4)2(F,OH)2
- Humite - Mg7(SiO4)3(F,OH)2
- Clinohumite - Mg9(SiO4)4(F,OH)2
- Datolite - CaBSiO4(OH)
- Titanite - CaTiSiO5
- Chloritoid - (Fe,Mg,Mn)2Al4Si2O10(OH)4
- Mullite (aka Porcelainite) - Al6Si2O13
Sorosilicates

Sorosilicates (from Greek σωρός sōros, heap, mound) have isolated double tetrahedra groups with (Si2O7)6− or a ratio of 2:7. Nickel-Strunz classification: 09.B
- Hemimorphite (calamine) - Zn4(Si2O7)(OH)2·H2O
- Lawsonite - CaAl2(Si2O7)(OH)2·H2O
- Ilvaite - CaFe2+2Fe3+O(Si2O7)(OH)
- Epidote group (has both (SiO4)4− and (Si2O7)6− groups)
- Epidote - Ca2(Al,Fe)3O(SiO4)(Si2O7)(OH)
- Zoisite - Ca2Al3O(SiO4)(Si2O7)(OH)
- Clinozoisite - Ca2Al3O(SiO4)(Si2O7)(OH)
- Tanzanite - Ca2Al3O(SiO4)(Si2O7)(OH)
- Allanite - Ca(Ce,La,Y,Ca)Al2(Fe2+,Fe3+)O(SiO4)(Si2O7)(OH)
- Dollaseite-(Ce) - CaCeMg2AlSi3O11F(OH)
- Vesuvianite (idocrase) - Ca10(Mg,Fe)2Al4(SiO4)5(Si2O7)2(OH)4
Cyclosilicates

Cyclosilicates (from Greek κύκλος kuklos, circle), or ring silicates, have linked tetrahedra with (TxO3x)2x- or a ratio of 1:3. These exist as 3-member (T3O9)6- and 6-member (T6O18)12- rings, where T stands for a tetrahedrally coordinated cation. Nickel-Strunz classification: 09.C
- 3-member ring
- Benitoite - BaTi(Si3O9)
- 6-member ring
- Axinite - (Ca,Fe,Mn)3Al2(BO3)(Si4O12)(OH)
- Beryl/Emerald - Be3Al2(Si6O18)
- Cordierite - (Mg,Fe)2Al3(Si5AlO18)
- Tourmaline - (Na,Ca)(Al,Li,Mg)3-(Al,Fe,Mn)6(Si6O18(BO3)3(OH)4
Note that the ring in axinite contains two B and four Si tetrahedra and is highly distorted compared to the other 6-member ring cyclosilicates.
-
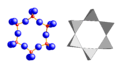
Cyclosilicate, [Si6O18]- 6-membered single rings, beryl (red: Si, blue: O)
-

Cyclosilicate, [Si3O9]- 3-membered single ring, benitoite
-

Cyclosilicate, [Si4O12]- 4-membered single ring, papagoite
-
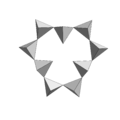
Cyclosilicate, [Si9O27]- 9-membered ring, eudialyte
-
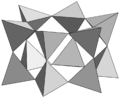
Cyclosilicate, [Si6O18]- 6-membered double ring, milarite
Inosilicates
Inosilicates (from Greek ις is [genitive: ινος inos], fibre), or chain silicates, have interlocking chains of silicate tetrahedra with either SiO3, 1:3 ratio, for single chains or Si4O11, 4:11 ratio, for double chains. Nickel-Strunz classification: 09.D
Single chain inosilicates
- Pyroxene group
- Pyroxenoid group
- Wollastonite - CaSiO3
- Rhodonite - MnSiO3
- Pectolite - NaCa2(Si3O8)(OH)
Double chain inosilicates
- Amphibole group
- Anthophyllite - (Mg,Fe)7Si8O22(OH)2
- Cumingtonite series
- Cummingtonite - Fe2Mg5Si8O22(OH)2
- Grunerite - Fe7Si8O22(OH)2
- Tremolite series
- Tremolite - Ca2Mg5Si8O22(OH)2
- Actinolite - Ca2(Mg,Fe)5Si8O22(OH)2
- Hornblende - (Ca,Na)2-3(Mg,Fe,Al)5Si6(Al,Si)2O22(OH)2
- Sodium amphibole group
- Glaucophane - Na2Mg3Al2Si8O22(OH)2
- Riebeckite (asbestos) - Na2Fe2+3Fe3+2Si8O22(OH)2
- Arfvedsonite - Na3(Fe,Mg)4FeSi8O22(OH)2
-
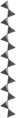
Inosilicate, pyroxene family, with 2-periodic single chain (Si2O6), diopside
-
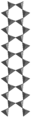
Inosilicate, clinoamphibole, with 2-periodic double chains (Si4O11), tremolite
-

Inosilicate, unbranched 3-periodic single chain of wollastonite
-
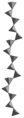
Inosilicate with 5-periodic single chain, rhodonite
-

Inosilicate with cyclic branched 8-periodic chain, pellyite
Phyllosilicates
Phyllosilicates (from Greek φύλλον phyllon, leaf), or sheet silicates, form parallel sheets of silicate tetrahedra with Si2O5 or a 2:5 ratio. Nickel-Strunz classification: 09.E

- Serpentine group
- Antigorite - Mg3Si2O5(OH)4
- Chrysotile - Mg3Si2O5(OH)4
- Lizardite - Mg3Si2O5(OH)4
- Clay mineral group
- Halloysite - Al2Si2O5(OH)4
- Kaolinite - Al2Si2O5(OH)4
- Illite - (K,H3O)(Al,Mg,Fe)2(Si,Al)4O10[(OH)2,(H2O)]
- Montmorillonite - (Na,Ca)0.33(Al,Mg)2Si4O10(OH)2·nH2O
- Vermiculite - (MgFe,Al)3(Al,Si)4O10(OH)2·4H2O
- Talc - Mg3Si4O10(OH)2
- Palygorskite - (Mg,Al)2Si4O10(OH)·4(H2O)
- Pyrophyllite - Al2Si4O10(OH)2
- Mica group
- Biotite - K(Mg,Fe)3(AlSi3)O10(OH)2
- Muscovite - KAl2(AlSi3)O10(OH)2
- Phlogopite - KMg3(AlSi3)O10(OH)2
- Lepidolite - K(Li,Al)2-3(AlSi3)O10(OH)2
- Margarite - CaAl2(Al2Si2)O10(OH)2
- Glauconite - (K,Na)(Al,Mg,Fe)2(Si,Al)4O10(OH)2
- Chlorite group
- Chlorite - (Mg,Fe)3(Si,Al)4O10(OH)2•(Mg,Fe)3(OH)6
-
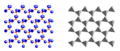
Phyllosilicate, mica group, muscovite (red: Si, blue: O)
-

Phyllosilicate, single net of tetrahedra with 4-membered rings, apophyllite-(KF)-apophyllite-(KOH) series
-

Phyllosilicate, single tetrahedral nets of 6-membered rings, pyrosmalite-(Fe)-pyrosmalite-(Mn) series
-

Phyllosilicate, single tetrahedral nets of 6-membered rings, zeophyllite
-
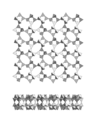
Phyllosilicate, double nets with 4- and 6-membered rings, carletonite
Tectosilicates
Tectosilicates, or "framework silicates," have a three-dimensional framework of silicate tetrahedra with SiO2 or a 1:2 ratio. This group comprises nearly 75% of the crust of the Earth. Tectosilicates, with the exception of the quartz group, are aluminosilicates. Nickel-Strunz classification: 09.F and 09.G, 04.DA (Quartz/ silica family)

- Quartz group
- Quartz - SiO2
- Tridymite - SiO2
- Cristobalite - SiO2
- Coesite - SiO2
- Feldspar family
- Alkali-feldspars (potassium-feldspars)
- Microcline - KAlSi3O8
- Orthoclase - KAlSi3O8
- Anorthoclase - (Na,K)AlSi3O8
- Sanidine - KAlSi3O8
- Albite - NaAlSi3O8
- Plagioclase feldspars
- Albite - NaAlSi3O8
- Oligoclase - (Na,Ca)(Si,Al)4O8 (Na:Ca 4:1)
- Andesine - (Na,Ca)(Si,Al)4O8 (Na:Ca 3:2)
- Labradorite - (Na,Ca)(Si,Al)4O8 (Na:Ca 2:3)
- Bytownite - (Na,Ca)(Si,Al)4O8 (Na:Ca 1:4)
- Anorthite - CaAl2Si2O8
- Alkali-feldspars (potassium-feldspars)
- Feldspathoid family
- Petalite - LiAlSi4O10
- Scapolite group
- Analcime - NaAlSi2O6•H2O
- Zeolite family
Gallery
-

Nesosilicate (SiO4)
-

Sorosilicate (Si2O7), as in suolunite
[Ca2Si2O5(OH)2·H2O] -

Tectosilicate, aluminosilicate 3-D network, zeolite family, synthetic zeolite ZSM-5
-
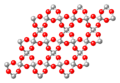
Silica family (SiO2 3-D-network), β-quartz
See also
- Classification of minerals - Non silicates
- Classification of minerals - Silicates
- Silicate mineral paint
Further references
- Deer, W.A.; Howie, R.A., & Zussman, J. (1992). An introduction to the rock-forming minerals (2nd ed.). London: Longman. ISBN 0-582-30094-0.
- Deer, W.A.; Howie, R.A., Wise, W.S. & Zussman, J. (2004). Rock-forming minerals. Volume 4B. Framework silicates: silica minerals. Feldspathoids and the zeolites (2nd ed.). London: Geological Society of London. p. 982 pp.
- Hurlbut, Cornelius S. (1966). Dana's Manual of Mineralogy (17th ed.). ISBN 0-471-03288-3.
- Hurlbut, Cornelius S.; Klein, Cornelis (1985). Manual of Mineralogy (20th ed.). Wiley. ISBN 0-471-80580-7.
External links
![]() Media related to Silicates at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Silicates at Wikimedia Commons
| ||||||||||||||
