Phrenicocolic ligament
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Ligament: Phrenicocolic ligament | ||
|---|---|---|
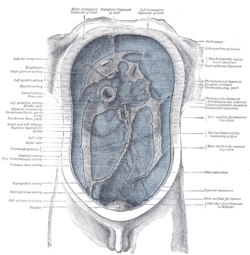 | ||
| Diagram to show the lines along which the peritoneum leaves the wall of the abdomen to invest the viscera. (Phrenicocolic ligament labeled at center right.) | ||
| Latin | Ligamentum phrenicocolicum | |
| Gray's | p.1158 | |
| From | ||
| To | ||
| Dorlands/Elsevier | l_09/12492796 | |
A fold of peritoneum, the phrenicocolic ligament is continued from the left colic flexure to the thoracic diaphragm opposite the tenth and eleventh ribs; it passes below and serves to support the spleen, and therefore has received the name of sustentaculum lienis.[1]
.jpg)
Friedrich Wilhelm Hensing
The phrenicocolic ligament is also called Hensing's ligament after Friedrich Wilhelm Hensing (* 1719; † 1745), a German professor for medicine in Gießen. [2][3]
References
- ↑ This article incorporates text from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy.
- ↑ Hensing ligament in The Free Dictionary by Farlex, Medical Eponyms, Farlex, 2012.
- ↑ Friedrich W. Hensing in The Free Dictionary by Farlex, Medical Eponyms, Farlex, 2012.
External links
- spleen at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
- "Phrenicocolic ligament". Medcyclopaedia. GE. Archived from the original on 2012-02-05.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.