Phenylpropanoids metabolism
The metabolic pathway of phenylpropanoids involves a number of enzymes.
Biosynthesis
Shikimate pathway
The shikimate pathway is a seven step metabolic route used by bacteria, fungi, and plants for the biosythesis of aromatic amino acids (phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan).
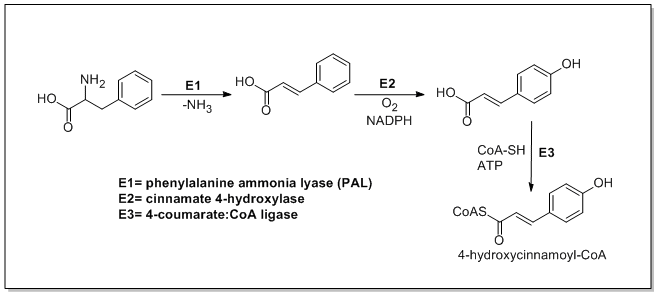
Cinnamic and p-coumaric acids biosynthesis
In plants, the biosynthesis of all phenylpropanoids begins with the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine.
Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL, a.k.a phenylalanine/tyrosine ammonia-lyase) is an enzyme responsible for the transformation of L-phenylalanine or tyrosine into trans-cinnamic acid or p-coumaric acid respectively and ammonia.
Trans-cinnamate 4-monooxygenase (cinnamate 4-hydroxylase) is the enzyme responsible for the transformation of trans-cinnamate into 4-hydroxycinnamate (p-coumaric acid). 4-Coumarate-CoA ligase is the enzyme responsible for the transformation of 4-coumarate (p-coumaric acid) into 4-coumaroyl-CoA.[1]
Other hydroxycinnamic acids biosynthesis
- Cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase (CAD), an enzyme responsible for the transformation of cinnamyl alcohol into cinnamaldehyde
- Sinapine esterase, an enzyme responsible for the transformation of sinapoylcholine into sinapate (sinapic acid) and choline
- Trans-cinnamate 2-monooxygenase, an enzyme responsible for the transformation of trans-cinnamate (cinnamic acid) into 2-hydroxycinnamate
- Caffeate O-methyltransferase, an enzyme responsible for the transformation of caffeic acid into ferulic acid
- Caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase, an enzyme responsible for the transformation of caffeoyl-CoA into feruloyl-CoA
- 5-O-(4-coumaroyl)-D-quinate 3'-monooxygenase, an enzyme responsible for the transformation of trans-5-O-(4-coumaroyl)-D-quinate into trans-5-O-caffeoyl-D-quinate
- Sinapoylglucose—choline O-sinapoyltransferase, an enzyme responsible for the transformation of 1-O-sinapoyl-beta-D-glucose into sinapoylcholine (sinapine)
- Sinapoylglucose—malate O-sinapoyltransferase, an enzyme responsible for the transformation of 1-O-sinapoyl-beta-D-glucose into sinapoyl-(S)-malate
Conjugation enzymes
- 2-coumarate O-beta-glucosyltransferase, an enzyme responsible for the transformation of trans-2-hydroxycinnamate into trans-beta-D-glucosyl-2-hydroxycinnamate
- Cinnamoyl-CoA reductase, an enzyme responsible for the production of cinnamoyl-CoA from cinnamaldehyde
- Hydroxycinnamate 4-beta-glucosyltransferase, an enzyme responsible for the transformation of p-coumaric acid into 4-O-beta-D-glucosyl-4-hydroxycinnamate
- Shikimate O-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase, an enzyme responsible for the transformation of 4-coumaroyl-CoA into 4-coumaroylshikimate
- Quinate O-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase, an enzyme responsible for the transformation of feruloyl-CoA into O-feruloylquinate
- Sinapate 1-glucosyltransferase, an enzyme responsible for the transformation of sinapate (sinapic acid) into 1-sinapoyl-D-glucose
- Coniferyl-alcohol glucosyltransferase, an enzyme responsible for the transformation of coniferyl alcohol into coniferin
Glucosidases
- Coniferin beta-glucosidase, an enzyme responsible for the transformation of coniferin into coniferol
Stilbenoids biosynthesis
- Pinosylvin synthase, an enzyme responsible for the formation of pinosylvin from cinnamoyl-CoA
- Trihydroxystilbene synthase, an enzyme responsible for the production of resveratrol from 4-coumaroyl-CoA
An alternative bacterial ketosynthase-directed stibenoids biosynthesis pathway exists in Photorhabdus bacterial symbionts of Heterorhabditis nematodes, producing 3,5-dihydroxy-4-isopropyl-trans-stilbene for antibiotic purposes.[2]
Coumarins biosynthesis
- Scopoletin glucosyltransferase, an enzyme responsible for the transformation of scopoletin into scopolin
Chalcones biosynthesis
4-Coumaroyl-CoA can be combined with malonyl-CoA to yield the true backbone of flavonoids, a group of compounds called chalconoids, which contain two phenyl rings. Naringenin-chalcone synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction 3 malonyl-CoA + 4-coumaroyl-CoA → 4 CoA + naringenin chalcone + 3 CO2.
Flavonoids biosynthesis
Conjugate ring-closure of chalcones results in the familiar form of flavonoids, the three-ringed structure of a flavone.
Biodegradation
Hydroxycinnamic acids degradation
- Caffeate 3,4-dioxygenase is an enzyme that uses 3,4-dihydroxy-trans-cinnamate (caffeic acid) and oxygen to produce 3-(2-carboxyethenyl)-cis,cis-muconate.
References
- ↑ Ververidis Filippos, F; Trantas Emmanouil, Douglas Carl, Vollmer Guenter, Kretzschmar Georg, Panopoulos Nickolas (October 2007). "Biotechnology of flavonoids and other phenylpropanoid-derived natural products. Part I: Chemical diversity, impacts on plant biology and human health". Biotechnology Journal 2 (10): 1214. doi:10.1002/biot.200700084. PMID 17935117.
- ↑ Joyce SA, Brachmann AO, Glazer I, Lango L, Schwär G, Clarke DJ, Bode HB (2008). "Bacterial biosynthesis of a multipotent stilbene". Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 47 (10): 1942–5. doi:10.1002/anie.200705148. PMID 18236486.