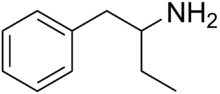
Phenylisobutylamine, also known as α-ethylphenethylamine, Butanphenamine, B or AEPEA,[1] is a stimulant drug of the phenethylamine class. It is a higher homologue of amphetamine, differing from amphetamine's molecular structure only by the substitution of the methyl group at the alpha position of the side chain with an ethyl group. Compared to amphetamine, phenylisobutylamine has strongly reduced dopaminergic effects, and instead acts as a selective norepinephrine releasing agent.[citation needed] The dextroisomer of phenylisobutylamine partially substitutes for dextroamphetamine in rats.[1]
A number of derivatives of phenylisobutylamine are known, including BDB, MBDB, EBDB, butylone (bk-MBDB), eutylone (bk-EBDB), Ariadne (α-Et-DOM), 4-CAB, and 4-MAB.
"Phenylisobutylamine" is in fact a chemical misnomer because isobutylamine itself contains a branched chain. The correct name after this style for this class of compound would be "phenylsecbutylamine".
See also
References
|
|---|
|
| |
| |
| |
| |
|---|
|
|
| |
|---|
| | |
|---|
| | |
|---|
| DBH | |
|---|
| |
- CGS-19281A
- SKF-64139
- SKF-7698
|
|---|
|
|---|
| |
|
* Note that MAO-B inhibitors also influence norepinephrine/epinephrine levels since they inhibit the breakdown of their precursor dopamine. |
|---|
| COMT | |
|---|
|
|---|
|
| |
| | |
|