Phenylethanoid
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
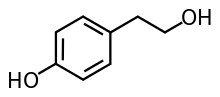
Tyrosol, a simple phenylethanoid.
Phenylethanoids are a type of phenolic compounds characterized by a phenethyl alcohol structure. Tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol are examples of such compounds.
Glycosides
The red deadnettle (Lamium purpureum) contains phenylethanoid glycosides named lamiusides A, B, C, D and E.[1] The aerial parts of Stachys officinalis contain phenylethanoid glycosides, (betonyosides A, B, C, D, E and F). Chemical investigation of methanol extracts from Pithecoctenium crucigerum (Bignoniaceae) showed the presence of five phenylethanoid glycosides (verbascoside, isoverbascoside, forsythoside B, jionoside D and leucosceptoside B), these all active against DPPH.[2]
Verbascoside and echinacoside are phenylethanoid and phenylpropanoid hybrids forming ester bonds with sugars.
References
- ↑ Ito, N; Nihei, T; Kakuda, R; Yaoita, Y; Kikuchi, M (2006). "Five new phenylethanoid glycosides from the whole plants of Lamium purpureum L". Chemical & pharmaceutical bulletin 54 (12): 1705–8. PMID 17139106.
- ↑ Martin, Frédéric; Hay, Anne-Emmanuelle; Corno, Laura; Gupta, Mahabir P.; Hostettmann, Kurt (May 2007). "Iridoid glycosides from the stems of Pithecoctenium crucigerum (Bignoniaceae)". Phytochemistry 68 (9): 1307–11. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2007.02.002. PMID 17382978.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.