Phellamurin
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Phellamurin | ||
|---|---|---|
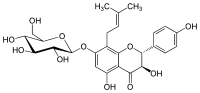 | ||
| IUPAC name (2R,3R)-3,5-Dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-8-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)-7-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-2,3-dihydrochromen-4-one | ||
| Other names Fellavine | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| CAS number | 52589-11-4 | |
| PubChem | 193876 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:8048 | |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:CC(=CCC1=C(C=C(C2=C1O[C@@H]([C@H](C2=O)O)C3=CC=C(C=C3)O)O)O[C@H]4[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O4)CO)O)O)O)C|Image 1 | |
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C26H30O11 | |
| Molar mass | 518.51 g mol−1 | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Phellamurin is a flavanonol, a type of flavonoid. It can be found in Commiphora africana[1] and in Phellodendron amurense.[2]
Related compounds
6"′-O-acetyl phellamurin is found in the leaves of Phellodendron japonicum.[3]
References
- ↑ A Dihydroflavonol Glucoside from Commiphora africana that Mediates DNA Strand Scission, Ji Ma, Shannon H. Jones, and Sidney M. Hecht, 2005
- ↑ A flavonoid glucoside, phellamurin, regulates differential oviposition on a rutaceous plant, Phellodendron amurense, by two sympatric swallowtail butterflies, Papilio protenor and P. xuthus: The front line of a coevolutionary arms race? Keiichi Honda and Nanao Hayashi, 1995
- ↑ Constituents of Leaves of Phellodendron japonicum MAXIM. and Their Antioxidant Activity, Chih-Yang Chiu, Chia-Ying Li, Chao-Chen Chiu, Masatake Niwa, Susumu Kitanaka, Amooru Gangaiah Damu, E-Jian Lee and Tian-Shung Wu, 2005
| |||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.