Persona (satellite)
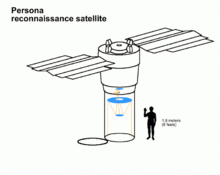 Artist's impression of a Persona satellite | |
| General information | |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer |
TsSKB Progress LOMO Vavilov State Optical Institute NPO Opteks |
| Country of origin | Russia |
| Applications | Optical imaging |
| Orbit regimes | Sun-synchronous |
| Operator |
VKS (2008-2011) VKO (2011-) |
| Lifetime | 3-5 years |
| Derived from | Yantar |
| Production | |
| Status | In production |
| Built | 2 |
| Launched | 2 |
| Operational | 1 |
| Failed | 1 |
| First launch |
Kosmos 2441 26 July 2008 |
| Typical spacecraft | |
| Average mass | 7,000 kg (15,000 lb) |
Persona is a class of Russian reconnaissance satellites, derived from the Resurs DK class of remote sensing satellite, itself derived from the Soviet Yantar reconnaissance satellites. The satellites are built by TsSKB-Progress, and the optics by LOMO and the Vavilov State Optical Institute.
The first satellite, identified as Kosmos 2441, was launched into a 750 km sun synchronous orbit on 26 July 2008, atop a Soyuz-2.1b carrier rocket from LC-43/4 at the Plesetsk Cosmodrome[1] It reportedly failed to return useful imagery due to an electrical malfunction.[2]
A second satellite, Kosmos 2486, was launched on 7 June 2013.[3]
The satellites have a mass of 6,500 kilograms (14,300 lb), are 7 metres (23 ft) long, and 2.7 metres (8.9 ft) in diameter. [citation needed]

The satellites optical subsystems are believed to be based on a 3-mirror Korsch type telescope with a primary mirror diameter of 1.5 metres (4.9 ft) and focal length of 20 metres (66 ft).[4]
The CCD sensor is probably ELCT1080v1U[citation needed] with a pixel size of 9 µm.[5] The CCD is produced by ELAR, previously known as ELECTRON-OPTRONIC.[6] The focal plane unit is manufactured by NPO Opteks.
The satellites have a nadir image resolution of 33 centimetres (13 in), using panchromatic imagery. They are planned to operate for 7 years.[citation needed]
External links
- Electro-optical systems for Earth remote sensing developed by LOMO (In Russian)
- Gunter Krebs (2008-04-09). "Persona". Gunter's Space Page. Retrieved 2008-04-10.
References
- ↑ Clark, Stephen (2008-07-26). "Soyuz 2-1b rocket launches classified military payload". Spaceflight Now. Retrieved 2008-10-27.
- ↑ "Шпион на связь не вышел" (in Russian). Российская газета. Retrieved 2009-02-11.
- ↑ Graham, William. "Russian spy satellite launched via Soyuz 2-1B". NASASpaceflight.com. Retrieved 8 June 2013.
- ↑ "ОПТИКО-ЭЛЕКТРОННЫЕ СИСТЕМЫ ДЛЯ ДИСТАНЦИОННОГО ЗОНДИРОВАНИЯ ЗЕМЛИ" (in Russian). LOMO. Retrieved 2008-10-27.
- ↑ Разработки и производство ФПЗС и цифровых камер на их основе. // Интернет-журнал "ТелеФото Техника", 01.11.2008 (russian): "Тип ФПЗС ELCT1080v1U ... Размеры элемента, µм 9х9"
- ↑ "ФПЗС с временной задержкой и накоплением" (in Russian). NPP-ELAR. Retrieved 2008-10-27.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||