Perindopril
 | |
|---|---|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
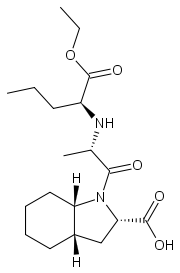
| (2S,3aS,7aS)-1-[(2S)-2-{[(2S)-1-ethoxy-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino}propanoyl]-octahydro-1H-indole-2-carboxylic acid | |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Coversyl, Coversum, Preterax, Aceon |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a602017 |
| Pregnancy cat. | D (US) |
| Legal status | ℞-only (US) |
| Routes | Oral |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 24% |
| Protein binding | 20% |
| Metabolism | Renal |
| Half-life | 1–17 hours for perindoprilat (active metabolite) |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 82834-16-0 |
| ATC code | C09AA04 C09BA04 (with diuretics) C09BB04 (with amlodipine) |
| PubChem | CID 107807 |
| DrugBank | DB00790 |
| ChemSpider | 96956 |
| UNII | 1964X464OJ |
| KEGG | D03753 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:8024 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1581 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C19H32N2O5 |
| Mol. mass | 368.468 g/mol |
| SMILES
| |
| |
| | |
Perindopril is a long-acting ACE inhibitor. It is used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure or stable coronary artery disease[1] in form of perindopril arginine (trade names include Coversyl, Coversum) or perindopril erbumine (trade name Aceon). According to the Australian government's Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme website, based on data provided to the Australian Department of Health and Aging by the manufacturer, perindopril arginine and perindopril erbumine are therapeutically equivalent and may be interchanged without differences in clinical effect.[2] However the dose prescribed to achieve the same effect will differ due to different molecular weights for the two forms.
Indications
- Essential hypertension.
- Stable coronary artery disease: reduction of risk of cardiac events in patients with a history of myocardial infarction and/or revascularization.
- Treatment of symptomatic heart disease or failure.
Dosage and administration
For Perindopril as treatment for hypertension, the initiation dose is 5 mg perindopril arginine (or 4 mg perindopril erbumine) once daily, then the dose may be increased to 10 mg perindopril arginine (or 8 mg perindopril erbumine) after 1 month of treatment to improve blood pressure control or in case of concomitant stable coronary artery disease.
The Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial showed the benefits of taking the two drugs Perindopril and Amlodipine together. The 9000 British patients aged 40 to 79 were involved in the five-year trial. Half were given the new drug combination, the rest were given traditional drugs. Perindopril and Amlodipine were found to be so effective that the trial was stopped early so that all patients could receive the combination.[3][4]
For stable coronary artery disease
A starting dose of 4 mg for two weeks is recommended, then uptitration to 8 mg once daily, depending on acceptability.
Congestive heart disease
Coversyl (perindopril) should be started under close medical supervision at a starting dose of 2 mg. This may be increased to 4 mg once blood pressure acceptability has been demonstrated.
Elderly patients should start treatment at 2 mg daily (2.5 mg daily of perindopril arginine in Australia).
Contraindications
- Children
- Pregnancy
- Lactation
- Situations where a patient has a history of hypersensitivity to Coversyl (perindopril).
- Renal failure
Precautions
- Assess renal function before and during treatment where appropriate.
- Renovascular hypertension.
- Surgery/anesthesia.
- Renal failure: the dose should be cautiously adjusted in accordance with the creatinine clearance (refer to complete data sheet).
- Symptomatic hypotension is rarely seen, but is more likely in volume-depleted patients, those receiving diuretics, or with the first two doses. In diuretic-treated patients, stop the diuretic 3 days before starting Coversyl (perindopril). A diuretic may later be given in combination if necessary; potassium-sparing diuretics are not recommended. Combination with neuroleptics or imipramine-type drugs may increase the hypotensive effect. Serum lithium concentrations may rise during lithium therapy.
Side effects
Rare and mild, usually at the start of treatment.
- Cough
- fatigue
- asthenia
- headache
- disturbances of mood and/or sleep
Less often
- taste impairment
- epigastric discomfort
- nausea
- abdominal pain
- rash.
Reversible increases in blood urea and creatinine may be observed. Proteinuria has occurred in some patients. Rarely, angioneurotic edema and decreases in hemoglobin, red cells, and platelets have been reported.
Composition
Each tablet contains 2 mg, 4 mg or 8 mg of the tert-butylamine salt of perindopril. Perindopril is also available under the trade name Coversyl Plus, containing 4 mg of perindopril combined with 1.25 mg indapamide.
In Australia, each tablet contains 2.5 mg, 5 mg or 10 mg of perindopril arginine. Perindopril is also available under the trade name Coversyl Plus, containing 5 mg of perindopril arginine combined with 1.25 mg indapamide and Coversyl Plus LD, containing 2.5 mg of perindopril arginine combined with 0.625 mg indapamide.
The efficacy and tolerability of a fixed-dose combination of 4 mg perindopril and 5 mg amlodipine, a calcium channel antagonist, has been confirmed in a prospective, observational multicenter trial of 1,250 hypertensive patients.[5] A preparation of the two drugs is available commercially as Coveram.
Presentation
Packs of 30 tablets of Coversyl (perindopril) 2.5 mg. Packs of 30 tablets of Coversyl (perindopril) 5 mg (scored). Packs of 30 tablets of Coversyl (perindopril) 10 mg.
Also available under the brand names:
- Aceon
- Acertil
- Actiprex
- Armix
- Coverene
- Coverex
- Coversum
- Prenessa
- Prestarium
- Prexanil
- Prexum
- Procaptan
- Provinace
- Covinace
- Pericard
References
- Bounhoure JP, Bottineau G, Lechat P, et al.. "Value of perindopril in the treatment of chronic congestive heart failure: multicentre double-blind placebo-controlled study." Clin Exp Hypertens. 1989;A11(suppl 2):575-586.
- Lechat P, Granham SP, Desche P, et al.. "Efficacy and acceptability of perindopril in mild-to-moderate chronic congestive heart failure." Am Heart J. 1993;126:798-806.
- Morgan T and Anderson A; "Clinical efficacy of perindopril in hypertension." Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1992;19:61-65.
- Myers MG; (on behalf of the perindopril multicentre dose-response study group) "A dose-response study of perindopril in hypertension: effects on blood pressure 6 and 24h after dosing." Can J Cardiol. 1996;12:1191-1196.
- "The European trial On reduction of cardiac events with Perindopril in stable coronary Artery disease Investigators. Efficacy of perindopril in reduction of cardiovascular events among patients with stable coronary artery disease: randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled, multicentre trial (the EUROPA study)." The Lancet 2003;362:782-788.
Citations
- ↑ Royal Australian College of General Practitioners. "Consumer Medicine Information, GenRx Perindopril". Clinical Resources, Medicine information for health professionals.
- ↑ Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing (2008). "PBS For Health Professionals". Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme. Retrieved 2008-09-04.
- ↑ Charlotte Harding (2005). "What you need to know about the new wonder drug cocktail for high blood pressure...". JADN Repository. Retrieved 2007-07-01.
- ↑ Linda Brookes (2003). "ASCOT: Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial -- Results From The Lipid-Lowering Arm". Medscape Today. Retrieved 2007-07-01.
- ↑ Bahl VK, Jadhav UM, Thacker HP. Management of Hypertension with the Fixed Combination of Perindopril and Amlodipine in Daily Clinical Practice: Results from the STRONG Prospective, Observational, Multicenter Study. American Journal of Cardiovascular Drugs May 22, 2009; 9 (3): 135-42 Link text
External links
| ||||||||||||||||||||