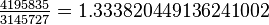Pentium FDIV bug

The Pentium FDIV bug was a bug in the Intel P5 Pentium floating point unit (FPU). Because of the bug, the processor would return incorrect results for many calculations used in math and science. Intel blamed the problem on a few missing entries in the lookup table used by the company.[1]
The error was discovered by Professor Thomas R. Nicely at Lynchburg College, Virginia, USA.[2]
The error was rarely encountered by users (Byte magazine estimated that 1 in 9 billion floating point divides with random parameters would produce inaccurate results).[3] However, both the flaw and Intel's initial handling of the matter were heavily criticized. Intel ultimately recalled the defective processors.
Chronology
Professor Thomas Nicely, a professor of mathematics at Lynchburg College, had written code to enumerate primes, twin primes, prime triplets, and prime quadruplets. Nicely noticed some inconsistencies in the calculations on June 13, 1994, shortly after adding a Pentium system to his group of computers, but was unable to eliminate other factors (such as programming errors, motherboard chipsets, etc.) until October 19, 1994. On October 24, 1994, he reported the issue to Intel. According to Nicely, his contact person at Intel later admitted that Intel had been aware of the problem since May 1994, when the flaw was discovered during testing of the FPU for its new P6 core, first used in the Pentium Pro.
On October 30, 1994, Nicely sent an email describing the error he had discovered in the Pentium floating point unit to various contacts, requesting reports of testing for the flaw on 486-DX4s, Pentiums and Pentium clones.[2]
This flaw in the Pentium FPU was quickly verified by other people around the Internet, and became known as the Pentium FDIV bug (FDIV is the x86 assembly language mnemonic for floating-point division). One example was found where the division result returned by the Pentium was off by about 61 parts per million.[2]
The story first appeared in the press on November 7, 1994, in an article in Electronic Engineering Times, "Intel fixes a Pentium FPU glitch" by Alexander Wolfe.[4]
The story was subsequently picked up by CNN in a segment aired on November 21, 1994.[2] This brought it into widespread public prominence.
Publicly, Intel acknowledged the floating point flaw, but claimed that it was not serious and would not affect most users. Intel offered to replace processors to users who could prove that they were affected. However, although most independent estimates found the bug to be of little importance and would have negligible effect on most users, it caused a great public outcry. Companies like IBM (whose IBM 5x86C microprocessor competed at that time with the Intel Pentium line) joined the condemnation.
On December 20, 1994, Intel offered to replace all flawed Pentium processors on the basis of request, in response to mounting public pressure.[5] Although it turned out that only a small fraction of Pentium owners bothered to get their chips replaced, the financial impact on the company was significant. On January 17, 1995, Intel announced a pre-tax charge of $475 million against earnings, ostensibly the total cost associated with replacement of the flawed processors.[2] Some of the defective chips were later turned into key rings by Intel.[6]
A 1995 article in Science describes the value of number theory problems in discovering computer bugs and gives the mathematical background and history of Brun's constant, the problem Nicely was working on when he discovered the bug.[7]
Affected models
This problem occurred only on some models of the original Pentium processor.[8] Any Pentium family processor with a clock speed of at least 120 MHz is new enough not to have this bug.[8]
On affected models, the Intel Processor Frequency ID Utility checks for the presence of this bug.
The ten affected processors are listed below. The 39 S-spec of those processors are not listed in the Intel processor specification finder web page.
| Family | Model | Stepping | Core stepping | Clock rate | FSB speed | S-spec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 1 | 3 | B1 | 60 MHz | 60 MHz | Q0352, Q0412, SX753 |
| 5 | 1 | 3 | B1 | 66 MHz | 66 MHz | Q0353, Q0413, SX754 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | C1 | 60 MHz | 60 MHz | Q0466, SX835, SZ949 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | C1 | 66 MHz | 66 MHz | Q0467, SX837, SZ950 |
| Family | Model | Stepping | Core stepping | Clock rate | FSB speed | S-spec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 2 | 1 | B1 | 75 MHz | 50 MHz | Q0601 |
| 5 | 2 | 1 | B1 | 90 MHz | 60 MHz | Q0542, Q0613, Q0543, SX879, SX885, SX909, SX874 |
| 5 | 2 | 1 | B1 | 100 MHz | 66 MHz | Q0563, Q0587, Q0614, SX886, SX910 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | B3 | 75 MHz | 50 MHz | Q0606, SX951 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | B3 | 90 MHz | 60 MHz | Q0628, Q0611, Q0612, SX923, SX922, SX921, SX942, SX943, SX944, SZ951 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | B3 | 100 MHz | 66 MHz | Q0677, SX960 |
The presence of the bug can be checked manually by performing the following calculation in any application that uses native floating point numbers, including the Windows Calculator or Microsoft Excel in Windows 95/98.
The correct value is
However, the value returned by the flawed Pentium is incorrect at or beyond four digits:[9]
Another way of detecting the bug is using the pentnt utility included with Windows NT 3.51, Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000, or Windows XP.[10]
See also
- Pentium F00F bug
- Anomaly in software
- MOS Technology 6502 bugs and quirks
- Accuracy problems in floating point operations
- SRT division
- Hardware Trojan
- Kill switch
References
- ↑ "FDIV Replacement Program: Description of the Flaw". Intel. 2004-07-09. Solution ID CS-013007. Retrieved 2006-12-19.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Professor Thomas Nicely. "Pentium FDIV flaw FAQ".
- ↑ Tom R. Halfhill (March 1995). "An error in a lookup table created the infamous bug in Intel's latest processor" (– Scholar search). BYTE (March 1995). Retrieved 2006-12-19.
- ↑ Alexander Wolfe. "Intel fixes a Pentium FPU glitch".
- ↑ "Intel adopts upon-request replacement policy on Pentium processors with floating point flaw; Will take Q4 charge against earnings". Business Wire. 1994-12-20. Retrieved 2006-12-24.
- ↑ "How many engineers does it take to change a lightbulb?". Boiledbeans. 20 April 2009. Retrieved 10 November 2009.
- ↑ Cipra, Barry (1995-01-13). "How number theory got the best of the Pentium chip". Science 267 (5195): 175. doi:10.1126/science.267.5195.175. PMID 17791336.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "FDIV Replacement Program: Frequently asked questions". Intel. 2009-03-20. Solution ID CS-012748. Retrieved 2009-11-10.
- ↑ "Pentium FDIV bug - a Picture". Kansas University Institute for Policy and Social Research. 1994-11-30. Retrieved 2010-11-03.
- ↑ "Pentnt".
External links
- Personal website of Dr. Nicely, who discovered the bug
- A page with precise information, also about the cause
- Ivars Peterson's Mathland on the bug
- A Tale of Two Numbers, by Cleve Moler of MathWorks
- ZIP-file containing more details (See ZIP file format for details on the file)
- Intel's official site
- Unopened Intel CPU box from the FDIV replacement program