Penile fracture
| Penile Fracture | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources | |
 Penile fracture | |
| ICD-9 | 959.13, 959.14 |
| eMedicine | med/3415 |
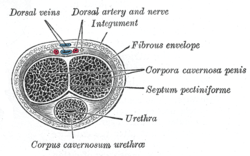
Penile fracture is rupture of one or both of the tunica albuginea, the fibrous coverings that envelop the penis's corpora cavernosa. It is caused by rapid blunt force to an erect penis, usually during vaginal intercourse or aggressive masturbation.[1] It sometimes also involves partial or complete rupture of the urethra or injury to the dorsal nerves, veins and arteries.[2]
Presentation
A popping or cracking sound, significant pain, immediate flaccidity, and skin hematoma of various sizes are commonly associated with the event.[1]
Treatment and prognosis
Penile fracture is a medical emergency, and emergency surgical repair is the usual treatment. Delay in seeking treatment increases the complication rate. Non-surgical approaches result in 10–50% complication rates including erectile dysfunction, permanent penile curvature, damage to the urethra and pain during sexual intercourse, while operatively treated patients experience an 11% complication rate.[1][3]
In some cases, retrograde urethrogram may be performed to rule out concurrent urethral injury.[3]
Causes
Vaginal intercourse, anal intercourse, and aggressive masturbation are the most common causes[1] but the practice of taqaandan (also taghaandan) also puts men at risk of penile fracture. Taqaandan, which comes from a Kurdish word meaning "to click," involves bending the top part of the erect penis while holding the lower part of the shaft in place, until a click is heard and felt. Taqaandan is said to be painless and has been compared to cracking one's knuckles, but the practice of taqaandan has led to an increase in the prevalence of penile fractures in western Iran.[4] Taqaandan may be performed to achieve detumescence.[5]
Legal issues
In America the case of Doe v. Moe, 63 Mass. App. Ct. 516, 827 N.E.2d 240 (2005), tested liability for a penile fracture injury caused during sexual intercourse. The court declined to find duty as between two consensual adults. The plaintiff in this case, a man who suffered a fractured penis, complained that the defendant, his ex-girlfriend, had caused his injury while she was on top of him during sexual intercourse. The court ruled in her favor, determining that her conduct was neither legally wanton nor reckless.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Greenberg's Text-Atlas of Emergency Medicine. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 22 November 2004. p. 318. ISBN 978-0-7817-4586-4. Retrieved 15 October 2012.
- ↑ Haas CA, Brown SL, Spirnak JP (April 1999). "Penile fracture and testicular rupture". World J Urol 17 (2): 101–6. PMID 10367369.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Andrew B. Peitzman; Michael Rhodes; C. William Schwab; Donald M Yealy, Timothy C Fabian (1 September 2007). The trauma manual: trauma and acute care surgery. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 305–. ISBN 978-0-7817-6275-5. Retrieved 18 April 2010.
- ↑ Nuzzo, Regina (9 February 2009). "Preventing penile fractures and Peyronie's disease - latimes.com". Los Angeles Times.
- ↑ Zargooshi J (August 2000). "Penile fracture in Kermanshah, Iran: report of 172 cases". J. Urol. 164 (2): 364–6. PMID 10893586.
External links
- A first-person account of the sensation on Everything2
- 2009 Scientific American article featuring interview with Hunter Wessells, chair of the urology department at the University of Washington School of Medicine in Seattle
- The NIH on Treatment options
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||