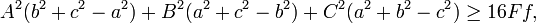Pedoe's inequality
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In geometry, Pedoe's inequality, named after Daniel Pedoe, states that if a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides of a triangle with area ƒ, and A, B, and C are the lengths of the sides of a triangle with area F, then
with equality if and only if the two triangles are similar.
The expression on the left is not only symmetric under any of the six permutations of the set { (A, a), (B, b), (C, c) } of pairs, but also—perhaps not so obviously—remains the same if a is interchanged with A and b with B and c with C. In other words, it is a symmetric function of the pair of triangles.
Pedoe's inequality is a generalization of Weitzenböck's inequality and of the Hadwiger–Finsler inequality.
References
- "A Two-Triangle Inequality", Daniel Pedoe, The American Mathematical Monthly, volume 70, number 9, page 1012, November, 1963.
- "An Inequality for Two Triangles", D. Pedoe, Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, volume 38, part 4, page 397, 1943.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.