Patellar tendinitis
| Patellar tendinitis | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources | |
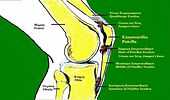 | |
| ICD-10 | M76.5 |
| ICD-9 | 726.64 |
| DiseasesDB | 9704 |
| eMedicine | sports/56 |
Patellar tendinitis (patellar tendinopathy, also known as jumper's knee), is a relatively common cause of pain in the inferior patellar region in athletes. It is common with frequent jumping and studies have shown it may be associated with stiff ankle movement and ankle sprains.[1][2]
Presentation
Jumper's knee (patellar tendinopathy, patellar tendinosis, patellar tendinitis) commonly occurs in athletes who are involved in jumping sports such as basketball and volleyball. Patients report anterior knee pain, often with an aching quality. The symptom onset is insidious. Rarely is a discrete injury described. Usually, involvement is infrapatellar at or near the infrapatellar pole, but it may also be suprapatellar.
Depending on the duration of symptoms, jumper's knee can be classified into 1 of 4 stages, as follows:
Stage 1 – Pain only after activity, without functional impairment
Stage 2 – Pain during and after activity, although the patient is still able to perform satisfactorily in his or her sport
Stage 3 – Prolonged pain during and after activity, with increasing difficulty in performing at a satisfactory level
Stage 4 – Complete tendon tear requiring surgical repair
It begins as inflammation in the patellar tendon where it attaches to the patella and may progress by tearing or degenerating the tendon. Patients present with an ache over the patella tendon. Most patients are between 10 and 16 years old. Magnetic resonance imaging can reveal edema (increased T2 signal intensity) in the proximal aspect of the patellar tendon.
Causes
It is an overuse injury from repetitive overloading of the extensor mechanism of the knee. The microtears exceed the body's healing mechanism unless the activity is stopped.
Among the risk factors for patellar tendonitis are low ankle dorsiflexion, weak gluteal muscles, and muscle tightness, particularly in the calves, quadriceps muscle, and hamstrings.[3]
The injury occurs to athletes in many sports.
Treatment

Early stages may be treated conservatively using the R.I.C.E methods.
- Rest
- Ice
- Compression
- Elevation
A physical therapist may also recommend specific exercises and stretches to strengthen the muscles and tendons. Should this fail, autologous blood injection, or injection of platelet rich plasma may be performed and is typically successful though not as successful as high volume saline injection (Crisp et al.). Uncommonly it may require surgery to remove myxoid degeneration in the tendon. This is reserved for patients with debilitating pain for 6–12 months despite conservative measures. Novel treatment modalities targeting the abnormal blood vessel growth which occurs in the condition are currently being investigated.
References
- ↑ http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/news/fullstory_117344.html
- ↑ Backman, Ludvig J.; Danielson, Patrik (2011). "Low Range of Ankle Dorsiflexion Predisposes for Patellar Tendinopathy in Junior Elite Basketball Players: A 1-Year Prospective Study". Am J Sports Med. doi:10.1177/0363546511420552.
- ↑ Koban, Martin (2013). Beating Patellar Tendonitis. pp. 20–25. ISBN 978-1491049730.
Further reading
- Kaplan, Helms, Dussault, Anderson, and Major Musculoskeletal MRI 2001 .
- Khan KM, Bonar F, Desmond PM, et al. (1996). "Patellar tendinosis (jumper's knee): findings at histopathologic examination, US, and MR imaging. Victorian Institute of Sport Tendon Study Group". Radiology 200 (3): 821–7. PMID 8756939.
- Kettunen JA, Kvist M, Alanen E, Kujala UM (2002). "Long-term prognosis for jumper's knee in male athletes. A prospective follow-up study". Am J Sports Med 30 (5): 689–92. PMID 12239003.
- Tom Crisp, Faisal Khan, Nat Padhiar,et al. (2008). "High volume ultrasound guided injections at the interface between the patellar tendon and Hoffa's body are effective in chronic patellar tendinopathy: A pilot study". Disability and rehabilitation. 30 (20–22): 1625–34. doi:10.1080/09638280701830936. PMID 18608403.
External links
- Jumpers Knee & Acrobatics
- Patellar Tendinitis, Musculoskeletal Consumer Review
- Ultrasound images demonstrating patella tendinosis and an autologous blood injection
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||