Pandyan Dynasty
| Pandyan Empire பாண்டிய நாடு | |||||
| |||||
|
| |||||
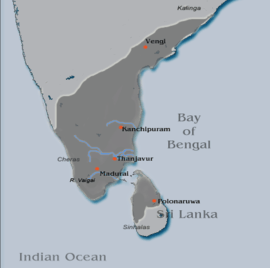 Extent of the Pandya Territories c. 1250 AD | |||||
| Capital | Madurai Korkai | ||||
| Languages | Tamil | ||||
| Religion | Hinduism Jain | ||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||
| King | |||||
| - | 560–590 AD | Kadungon | |||
| - | 1309–1345 AD | Vira Pandyan IV | |||
| Historical era | Iron Age | ||||
| - | Established | before 500 BC[11][12][13] | |||
| - | Early Pandyan Kingdom | 500 BC | |||
| - | Disestablished | 16th century AD[14] | |||
| Today part of | | ||||
| Part of a series on |
| History of Tamil Nadu |
|---|
 |
|
Main |
|
Medieval history Pallava Empire Pandya Empire |
| Outline of South Asian history History of Indian subcontinent |
|---|
|
7000–3000 BC: Stone Age
|
|
3000–1300 BC: Bronze Age
|
|
1700–26 BC: Iron Age
|
|
21–1279 AD: Middle Kingdoms
|
|
1206–1596: Late medieval age
|
|
1526–1858: Early modern period
|
|
1505–1961: Colonial period
|
|
Other states (1102–1947)
|
|
Kingdoms of Sri Lanka
|
|
Nation histories
|
|
Regional histories |
The Pandyan or Pandian dynasty was an ancient Tamil dynasty, one of the three Tamil dynasties, the other two being the Chola and the Chera). Even though the earliest extant Tamil literary works, such as the Kaliththokai, mention a Tamil continent called Kumari Kandam, which was ruled by Pandyas for 10,000 years, before getting submerged in the western Indian Ocean, the conventional historical evidences so far, suggest that they ruled parts of South India from around 600 BCE (Early Pandyan Kingdom)[15] to first half of 17th century AD. They initially ruled their country Pandya Nadu from Korkai, a seaport on the southernmost tip of the Indian Peninsula, and in later times moved to Madurai. Fish being their flag, Pandyas were experts in water management, agriculture(mostly near river banks) and fisheries and they were eminent sailors and sea traders too. Pandyan was well known since ancient times, with contacts, even diplomatic, reaching the Roman Empire. During the 13th century AD, Marco Polo mentioned it as the richest empire in existence.[16] The Pandyan empire was home to temples including Meenakshi Amman Temple in Madurai, and Nellaiappar Temple built on the bank of the river Thamirabarani in Tirunelveli. The Pandya kings were called either Jatavarman or Maravarman Pandyan. From being Jains in their early ages, they became Shaivaits after some centuries of rule.[17]
Pillaiyarpatti temple is a rock-cut temple located in Thiruppatthur, Sivagangai District. It was built after viewing a hillock by the early Pandiya kings. The image of Pillaiyarpatti Pillaiyar and that of a Siva Lingam were carved out of a stone by a sculptor named Ekkattur Koon Peruparanan who put his signature on a stone inscription, in Tamil Language used between the 2nd and 5th century AD, found even today in the sanctum. It can be concluded that the icon of Pillaiyarpatti Pillaiyar must have been carved around 4th century AD.
The Pandyas of Southern India are believed to have been founded at least five to six centuries before the Christian Era with a very strong possibility of a more ancient date of establishment.[18][19] Their recorded existence and mention are found in records dating to as early as 550 BC.[20] As recorded by Strabo, Emperor Augustus of Rome received at Antioch an ambassador from a South Indian King called Pandyan of Dramira. The country of the Pandyas, Pandi Mandala, was described as Pandyan Mediterranea in the Periplus and Modura Regia Pandyan by Ptolemy.[21]
The early Pandyan Dynasty of the Sangam Literature faded into obscurity upon the invasion of the Kalabhras. The dynasty revived under Kadungon in the early 6th century, pushed the Kalabhras out of the Tamil country and ruled from Madurai.[22] They again went into decline with the rise of the Cholas in the 9th century and were in constant conflict with them. The Pandyas allied themselves with the Sinhalese and the Cheras in harassing the Chola empire until they found an opportunity for reviving their fortunes during the late 13th century. The Later Pandyas (1216–1345) entered their golden age under Maravman Sundara Pandyan and Jatavarman Sundara Pandyan (c. 1251), who expanded the empire into Telugu country, conquered Kalinga (Orissa) and invaded and conquered Sri Lanka. They also had extensive trade links with the Southeast Asian maritime empires of Srivijaya and their successors. During their history, the Pandyas were repeatedly in conflict with the Pallavas, Cholas, Hoysalas and finally the Muslim invaders from the Delhi Sultanate. The Pandyan Kingdom finally became extinct after the establishment of the Madurai Sultanate in the 16th century.
The Pandyas excelled in both trade and literature before the Christian Era. They controlled the pearl fisheries along the South Indian coast, between Sri Lanka and India, which produced some of the finest pearls in the known ancient world. Traditionally, the legendary Sangams were held in Madurai under their patronage, and some of the Pandya Kings were poets themselves.
Etymology
The word Pandya is derived from the Tamil word "Pandu" meaning very old.
Son of Kulasekharan Pandya, the second king of Madurai, the legendary Malayadwaja Pandya, who sided with the Pandavas and took part in the Kurukshetra War of the Mahabharata, is described as follows in Karna Parva (verse 20.25):[23][24]
"Although knowing that the shafts (arrows) of the high souled son of Drona employed in shooting were really inexhaustible, yet Pandya, that bull among men, cut them all into pieces".
Malayadwaja Pandya and his queen Kanchanamala had one daughter Thathagai alias Meenakshi who succeeded her father and reigned the kingdom successfully. The Madurai Meenakshi Amman temple was built after her. The city of Madurai was built around this temple.[25] It is also notable that the etymology of the name Meenakshi came from two Tamil words Meen(Fish) and Aatchi(Rule) which collectively means 'Rule of Fish'.
Another theory suggests that in Sangam Tamil lexicon the word Pandya means old country in contrast with Chola meaning new country, Chera meaning hill country and Pallava meaning branch in Sanskrit. The Chera, Chola and Pandya are the traditional Tamil siblings and together with the Pallavas are the major Kings that ruled ancient Tamilakam.
Historians have used several sources to identify the origins of the early Pandyan dynasty with the pre-Christian Era and also to piece together the names of the Pandyan kings. Pandyas were the longest ruling dynasty of Indian history.[26] Unfortunately, the exact genealogy of these kings has not been authoritatively established yet.
Sources
Sangam literature

Pandya kings find mention in a number of poems in the Sangam Literature. Among them Nedunjeliyan, 'the victor of Talaiyalanganam', and Mudukudimi Peruvaludi 'of several sacrifices' deserve special mention. Beside several short poems found in the Akananuru and the Purananuru collections, there are two major works — Mathuraikkanci and the Netunalvatai (in the collection of Pattupattu) — which give a glimpse into the society and commercial activities in the Pandyan kingdom during the Sangam age.
It is difficult to estimate the exact dates of these Sangam age Pandyas. The period covered by the extant literature of the Sangam is unfortunately not easy to determine with any measure of certainty. Except the longer epics Silapathikaram and Manimekalai, which by common consent belong to an age later than the Sangam age, the poems have reached us in the forms of systematic anthologies. Each individual poem has generally attached to it a colophon on the authorship and subject matter of the poem. The name of the king or chieftain to whom the poem relates and the occasion which called forth the eulogy are also found.
It is from these colophons, and rarely from the texts of the poems themselves, that we gather the names of many kings and chieftains and the poets and poetesses patronised by them. The task of reducing these names to an ordered scheme in which the different generations of contemporaries can be marked off one another has not been easy. To add to the confusions, some historians have even denounced these colophons as later additions and untrustworthy as historical documents.
Any attempt at extracting a systematic chronology from these poems should take into consideration the casual nature of these poems and the wide differences between the purposes of the anthologist who collected these poems and the historian’s attempts to arrive at a continuous history. Pandyas are also mentioned by Greek Megesthenes where he writes about southern kingdom being ruled by women.Huien tsang also mentions about it citing his Buddhist friend at Kanchi and callas it Malakutta or Malakotta but the capital city is not mentioned.
Epigraphy

The earliest Pandya to be found in epigraph is Nedunjeliyan, figuring in the Minakshipuram record assigned from the 2nd to the 1st centuries BC. The record documents a gift of rock-cut beds, to a Jain ascetic. Punch marked coins in the Pandya country dating from around the same time have also been found.
Pandyas are also mentioned in the Pillars of Ashoka (inscribed 273 – 232 BC). In his inscriptions Asoka refers to the peoples of south India – the Cholas, Cheras, Pandyas and Satiyaputras — as recipients of his Buddhist proselytism.[27][28] These kingdoms, although not part of the Mauryan Empire, were on friendly terms with Asoka:
- "The conquest by Dharma has been won here, on the borders, and even six hundred yojanas (5,400–9,600 km) away, where the Greek king Antiochos rules, beyond there where the four kings named Ptolemy, Antigonos, Magas and Alexander rule, likewise in the south among the Cholas, the Pandyas, and as far as Tamraparni (Sri Lanka)."[29]
Kharavela, the Kalinga king who ruled during the 2nd century BC, in his Hathigumpha inscription, claims to have destroyed a confederacy of Tamil states (‘’Tamiradesasanghatam'’) which had lasted 132 years, and to have acquired a large quantity of pearls from the Pandyas.[28]
Foreign sources

According to the Mahavamsa – a historical poem written in the Pali language, of the kings of Sri Lanka – King Vijaya (543 – 505 BC) married a Pandyan Princess. Along with Vijaya, all the men in his crew got married to Madurai girls and arrived Sri Lanka with a great celebration.

Megasthenes knew of the Pandyan kingdom around 300 BC. He described it in Indika as occupying the portion of India which lies southward and extends to the sea. According to his account, it had 365 villages, each of which was expected to meet the needs of the royal household for one day in the year. He described the Pandyan queen at the time, Pandaia as a daughter of Heracles.[30]
The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea (c. 60 – 100 AD) describes the riches of a 'Pandian Kingdom':
- ...Nelcynda is distant from Muziris by river and sea about five hundred stadia, and is of another Kingdom, the Pandian. This place also is situated on a river, about one hundred and twenty stadia from the sea.... [31]
The Chinese historian Yu Huan in his 3rd-century text, the Weilüe, mentions The Kingdom of Panyue:
- ...The kingdom of Panyue is also called Hanyuewang. It is several thousand li to the southeast of Tianzhu (Northern India)...The inhabitants are small; they are the same height as the Chinese...[32]
The Roman emperor Julian received an embassy from a Pandya about 361. A Roman trading centre was located on the Pandyan coast at the mouth of the Vaigai river, southeast of Madurai.
Pandyas also had trade contacts with Ptolemaic Egypt and, through Egypt, with Rome by the 1st century, and with China by the 3rd century. The 1st-century Greek historian Nicolaus of Damascus met, at Antioch, the ambassador sent by a king from Dramira "named Pandion or, according to others, Porus" to Caesar Augustus around 13 AD (Strabo XV.4 and 73).[33][34]
According to Xuanzang, the Pandya country was a depot for sea pearls, its people were harsh and of different religions. They were very good at trade.[22]
In the later part of the 13th century Venetian traveller Marco Polo visited the Pandyan kingdom and left a vivid description of the land and its people.[35][36] Polo exclaimed that:
- The darkest man is here the most highly esteemed and considered better than the others who are not so dark. Let me add that in very truth these people portray and depict their gods and their idols black and their devils white as snow. For they say that God and all the saints are black and the devils are all white. That is why they portray them as I have described.[37]
History
Myths and legends
Although there are many instances of the Pandyas being referred to in surviving ancient Hindu texts including the Mahabharata, we currently have no way of determining a cogent genealogy of these ancient kings. We have a connected history of the Pandyas from the fall of Kalabhras during the middle of the 6th century.
The earliest Tamil literary works, such as the Kaliththokai, mention a Tamil country called Kumari Kandam, located to the south of the present-day Kanyakumari tens of thousands of years ago, between the then Kumari and Pahruli rivers. Pandyan kings such as Chenkon, and the Cheras supposedly ruled this country, tens of thousands of years ago. They fought and defeated the Nagas. The Kaliththokai again mentions a war between the combined forces of Villavars (Cheras) and the Meenavars (Pandyas), and the Nagas, their arch-enemies, but eventually losing the war, and subsequently Central India to the Nagas. The Kaliththokai mentions that many Tamil Naga tribes such as Maravar, Eyinar, Oliar, Oviar, Aruvalur and Paravar migrated to the Pandyan kingdom and started living there in the Third Sangam in the first centuries AD.[38]
Also, the Pandyas, along with the Cheras and the Cholas, find mention as one of the three ruling dynasties of the southern region of the then Bharatavarsha in the Hindu epic Ramayana. They are also mentioned in the Aitareya Aranyaka, and the Mahabharata, where they are (along with the Cheras and the Cholas) believed to have been on the side of the Pandavas in the Great War.[39][40]
Early Pandyas (3rd century BC – 3rd century AD)
The following is a partial list of Pandyan emperors who ruled during the Sangam age:[41][42][43] The lists of the Pandya kings are based on the authoritative A History of South India from the Early Times to the Fall of Vijayanagar by K.A.N. Sastri, Oxford U Press, New Delhi (Reprinted 1998).
- Koon Pandiyan
- Nedunj Cheliyan I (Aariyap Padai Kadantha Nedunj Cheliyan)
- Pudappandiyan
- Mudukudumi Paruvaludhi
- Nedunj Cheliyan II
- Nan Maran
- Nedunj Cheliyan III (Talaiyaalanganathu Seruvendra Nedunj Cheliyan)
- Maran Valudi
- Kadalan valuthi
- Musiri Mutriya Cheliyan
- Kadalul Maintha Ukkirap Peruvaludi
First Pandya Empire (6th – 10th centuries AD)
After the close of the Sangam age, the first Pandyan empire was established by Kadungon in the 6th century by defeating the Kalabhras. The following chronological list of the Pandya emperors is based on an inscription found on the Vaigai riverbeds. Succeeding kings assumed the titles of "Sadayavaramban" and "Maaravaramban" alternately, denoting themselves as followers of Lord Sadaiyan (Sankan(r)/Sivan) and Lord Thiru Maal respectively.
After the defeat of the Kalabhras, the Pandya kingdom grew steadily in power and territory. With the Cholas in obscurity, the Tamil country was divided between the Pallavas and the Pandyas, the river Kaveri being the frontier between them.
After Vijayalaya Chola conquered Thanjavur by defeating the Muttarayar chieftains who were part of Pandya family tree around 850, the Pandyas went into a period of decline. They were constantly harassing their Chola overlords by occupying their territories. Parantaka I invaded the Pandya territories and defeated Rajasimha III. However, the Pandyas did not wholly submit to the Cholas despite loss of power, territory and prestige. They tried to forge various alliances with the Cheras and the Kings of Lanka and tried to engage the Cholas in war to free themselves from Chola supremacy. But right from the times of Parantaka I to the early 12th century up to the times of Kulottunga Chola I the Pandyas could not overpower the Cholas who right from AD 880–1215 remained the most powerful empire spread over South India, Deccan and the Eastern and Western Coast of India during this period.[44]
List of kings are given below;
- Kadungon (560–590 AD)
- Maravarman Avani Culamani (590–620 AD)
- Cezhiyan Cendan (620–640 AD)
- Arikesari Maravarman Nindraseer Nedumaaran (670–710 AD)
- Kochadaiyan Ranadhiran (710–735 AD)
- Arikesari Parankusa Maravarman Rajasimha I (735–765 AD)
- Parantaka Nedunjadaiyan (765–790 AD)
- Rasasingan II (790–800 AD)
- Varagunan I (800–830 AD)
- Sirmara Seervallabha (830–862 AD)
- Varagunavarman II (862–880 AD)
- Parantaka Viranarayana (880–900 AD)
- Maravarman Rajasimha II (900–920 AD)
Under the Cholas (10th – 13th centuries AD)
The Chola domination of the Tamil country began in earnest during the reign of Parantaka Chola II. Chola armies led by Aditya Karikala, son of Parantaka Chola II defeated Vira Pandya in battle. The Pandyas were assisted by the Sinhalese forces of Mahinda IV. Pandyas were driven out of their territories and had to seek refuge on the island of Sri Lanka. This was the start of the long exile of the Pandyas. They were replaced by a series of Chola viceroys with the title Chola Pandyas who ruled from Madurai from c. 1020.
The following list gives the names of the Pandya kings who were active during the 10th century and the first half of 11th century. It is difficult to give their dates of accession and the duration of their rule. Nevertheless, their presence in the southern country requires recognition.
- Sundara Pandya I
- Vira Pandya I
- Vira Pandya II
- Amarabhujanga Tivrakopa
- Jatavarman Sundara Chola Pandya
- Maravarman Vikrama Chola Pandya
- Maravarman Parakrama Chola Pandya
- Jatavarman Chola Pandya
- Seervallabha Manakulachala (1101–1124 AD)
- Maaravaramban Seervallaban (1132–1161 AD)
- Parakrama Pandyan I (1161–1162 AD)
- Kulasekara Pandyan III
- Vira Pandyan III
- Jatavarman Srivallaban (1175–1180 AD)
- Jatavarman Kulasekaran I (1190–1216 AD)
- Parakrama Pandyan II (Ceylon king) (1212–1215 AD)
- Maravarman Sundara Pandyan (1216–1238 AD)
- Sundaravaramban Kulasekaran II (1238–1240 AD)
- Maravarman Sundara Pandyan II (1238–1251 AD)
- Jatavarman Sundara Pandyan (1251–1268 AD)
- Maaravaramban Kulasekara Pandyan I (1268–1308 AD)
- Sundara Pandyan IV (1309–1327 AD)
- Vira Pandyan IV (1309–1345 AD)
Pandya revival and zenith (13th and 14th centuries AD)

The 13th century is the greatest period in the history of the Pandyan Empire. This period saw the rise of seven prime Lord Emperors (Ellarkku Nayanar – Lord of All) of Pandyan, who ruled the kingdom alongside Pandyan princes. Their power reached its zenith under Jatavarman Sundara Pandyan in the middle of the 13th century. The foundation for such a great empire was laid by Maravarman Sundara Pandyan early in the 13th century.
The Pandyan kingdom was replaced by the Chola princes who assumed the title as Chola Pandyas in the 11th century. After being overshadowed by the Pallavas and Cholas for centuries, Pandyan glory was briefly revived by Maravaramban Sundara Pandyan and by (probably his younger brother or son) the much celebrated Jatavarman Sundara Pandyan I in 1251. The Pandya power extended from the Telugu countries on banks of the Godavari river to the northern half of Sri Lanka, which was invaded by Sundara Pandyan I in 1258 and on his behalf by his younger brother Jatavarman Vira Pandyan I from 1262–1264. later Jatavarman Sundara Pandiyan appointed his brother to rule Kongu country, Chola nadu and Hoysala country. Jatavarman Vira Pandiyan's clan was later called as Kongu Pandiyar and he is the first Kongu Pandiya King.
The revival of the Pandyan dynasty was to coincide with the gradual but steady decline of the Chola empire. The last two or three Chola kings who followed Kulothunga III were either very weak or incompetent. The Cholas of course did not lack valour but had been unable to stop the revival of the Pandyan empire from the times of Maravaramban Sundara Pandyan, the revival of the Kadava Pallavas at Kanchi under Kopperinchunga I and indeed the growing power and status of the Telugu Cholas, the Renanti and the Irungola Cholas of the Telugu country; for the last three-named had been very trusted allies of the Cholas up to Kulothunga III, having helped him in conquering Kalinga. The marital alliance of Kulothunga III and one of his successors, Raja Raja III, with the Hoysalas did not yield any advantage, though (initially, at least) Kulothunga III took the help of the Hoysalas in countering the Pandiyan resurgence. Kulothunga III had even conquered Karur, the Cheras in addition to Madurai, Ilam and Kalinga. However, his strength rested on support from Hoysalas, whose king Veera Ballala II was his son-in-law. However, Veera Ballala II himself had lost quite a bit of his territories between 1208–1212 to his local adversaries in Kannada country, like the Kalachuris, Seunas etc.
The resurgent Pandiyans under Maravarman Sundara Pandyan went to war against Kulothunga and first at Kandai and then near Manaparai on the outskirts of modern Tiruchirappalli, the Pandiyans routed the Chola army and entered Tiruchy, Thiruvarangam and Thanjavur victorious in war. But it appears that in the Tiruchy and Thiruvarangam areas, there was renewed control of the Cholas, presumably with the help of the Hoysalas under Vira Someswara with the Hoysalas later shifting their allegiance to the Pandyans either during the last years of Maravarman Sundara Pandyan or the early years of his successor Jatavarman Sundara Pandyan.
Jatavarman Sundara Pandiyan was a very brave, ambitious warrior king, who wanted to completely subjugate the Cholas. He initially tolerated the presence of the Hoysalas under Vira Someshwara with his son Visvanatha or Ramanatha ruling from Kuppam near Samayapuram on the outskirts of Thiruvarangam. This was because other feudatories of the Hoysalas were also growing in power and threatening the Hoysala kingdom itself. Besides, the Delhi Sultanate invasion of the Deccan had started under Malik Kafur. The challenged Hoysalas did have a foothold in and around Tiruchy and Thiruvarangam for a few years and seemed to have indulged in some temple building activity at Thiruvarangam also. But Jatavarman Sundara Pandiyan, who subdued Rajendra Chola III in around 1258–1260 AD was an equal antagonist of the Hoysalas whose presence he absolutely disliked in the Tamil country. He first vanquished the Kadava Pallavas under Kopperinchungan-II, who had challenged the Hoysala army stationed in and around Kanchi and killed a few of their commanders.
Though Rajendra III suffered another defeat at the hands of Vira Someshwara, because of the growing power of Pandiyans being felt by both Cholas and Hoysalas, there was a political affinity between the two which was cemented also by marital relations. At the time the Pandiyans and the Kadava Pallavas,with an earlier Chola, Raja Raja III, having been held in captivity by Kopperinchunga II and his release being secured by the Hoysalas. Ultimately, the Kadava Pallavas, Hoysalas and also the Telugu Choda Timma who invaded Kanchi were all one by one vanquished by Jatavarman Sundara Pandiyan with the Cholas finally becoming extinct after defeat of Hoysala Ramanatha as well as his ally Rajendra iii around 1279 by Maravarman Kulasekhara Pandiyan.

Jatavarman Sundara Pandiyan seized the opportunity with the Hoysalas being in Tiruchy and not having any ally, the rapidly weakening Cholas seeking alliance with the Kadava Pallavas who were themselves being threatened by the Telugu Cholas. In 1254 (or 1260) Jatavarman first dragged the Hoysalas into war by routing his son Ramanatha out of Tiruchy. Vira Someshwara Hoysala, who had given the control of the empire to his sons, had to come out of his slumber and tried to challenge Jatavarman. Between Samayapuram and Tiruchy, the armies of Vira Someshwara were routed with Vira Someshwara losing his life in this battle. This ended the presence of the Hoysalas in Tamil country. Jatavarman did not stop there: he went inside Kannada country after conquering Tiruchy and occupied parts of Hoysala territory up to the Konkana coast and established his son Vira Pandiyan as ruler of those territories. Temporarily, at least, the Hoysalas were in disarray in Kannada country itself.
Next the Pandiyan prince Jatavarman concentrated on completely wiping out the Chola empire. Rajadhiraja III had interfered in an earlier Pandiyan war of succession and defeated a confederation of Pandiyan princes. The predecessors of Jatavarman Sundara Pandiyan had suffered at the time of the Chola invasion and he wanted to take revenge. This was his opportunity. Rajendra III had been counting on Hoysala assistance in case he was challenged by the Pandiyans, keeping in mind the earlier marital alliance of the Cholas with the Hoysalas. Unfortunately for Rajendra III, the Hoysalas had lost any claim to regional power in Kannada and the Tamil countries, as they had been wiped out of Tamizhagam and indeed lost territories inside Kannada country itself to Jatavarman Sundara Pandiyan. Initially, Jatavarman consodlidated the Pandiyan hold on Tiruchy and Thiruvarangam and marched towards Tanjore and Kumbakonam. The Chola capital of Gangaikondacholapuram, too, was not far from reach. During the years 1270–1276 it appeared that Rajendra III ruled mainly in and around Gangaikondacholapuram and Tanjore. Tiruchy and Thiruvarangam had been lost to the Cholas forever, at least from 1254 AD. Though Rajendra III had been opposed to the Hoysalas due to their alliance with the Pandiyans, with new hostilities emerging between Hoysalas and the Pandiyans, Rajendra III had hoped for renewed friendship and military alliance with the Hoysalas.
When challenged by Jatavarman Sundara Pandiyan, the brave but tactically naive Rajendra III marched against the Pandiyans between Tanjore and Tiruchy, hoping for assistance and participation in war from the Hoysalas. However, the already vanquished Hoysalas were in a defensive position. They did not want to go to war and risk yet another defeat by the resurgent Pandiyans. Rajendra III, hopelessly isolated, was thoroughly routed and humiliated in this war, which is variously dated as between 1268–1270. The known rule of Jatavarman Sundara Pandiyan is of course, up to 1268 only. Probably Rajendra III fled the battlefield and had continued in obscurity up to 1279 but without any of the erstwhile Chola territories. By 1280 AD, the Chola empire was no more.
On the death of Maravarman Kulasekara Pandyan I in 1308, a conflict stemming from succession disputes arose amongst his sons. Sundara Pandyan and Vira Pandyan fought each other for the throne. Sundara Pandyan however with the help of his loyal generals and Veera Ballala III was successful in suppressing Vira Pandyan into a petty army chief with just 500 soldiers who was indeed supported for the throne by his father Maravarman Kulasekara Pandyan I and the people of madurai. Since then an uneasy truce existed between the two brothers. The Kingdom now under Sundara Pandyan revived its infrastructure and military strength to gain autonomy and drive out Hoysala Empire from its political affairs.
Raids by Malik Kafur
Defeat of Sundara Pandyan
Scenarios changed during 1311, when Alauddin Khilji of Khilji dynasty sent his general Malik Kafur on an expedition to the kingdoms of the south which led to the capture of Warangal, the overthrow of the Hoysala Empire south of the Krishna River, and the occupation of Madurai in the extreme south.[45] Malik Kafur was not seeking to expand the borders of the Delhi Sultanate; he was engaging in a military treasure-hunt on the Sultan's behalf. Malik's victory over Veera Ballala III and loot of Hindu temples at Halebidu sent alarming bells to the Pandyan Kingdom. Malik Kafur on the other hand, heard about the raised strength of the Pandyan army and its defensive position within the walls of Madurai was reluctant in carrying out his expedition further south. It was Alauddin Khilji himself ordered and sent reinforcements to Malik Kafur to attack Madurai after hearing the richness of it via Veera Virupaksha Ballala who was sent to Delhi as an act of peace by his defeated father Veera Ballala III.
Being a strong Saivite, Sundara Pandyan was enraged by the destruction of the Hindu temples by the Muslim armies. He assembled his army and planned to march them at once to face the invading armies of the Delhi Sultanate. This idea was however opposed by Vira Pandyan who felt that taking a defensive position might be more advantageous. Sundara Pandyan ignored his words and ordered his army to march leaving Vira Pandyan to safeguard Madurai with his men. The Pandyan army managed to march well intact till Melaithirukattupalli. But their reliance on the river Kaveri as the water source turned disastrous as the river ran dry during the hot summer of 1311. The already exhausted Pandyan army planned to march west in search of nearby water source. Their speed was drastically reduced due to the general's decision of marching on the dried beds of River Kaveri. Malik Kafur's forces on the other hand tactically planned on their ration and water supplies, met Sundara Pandyan much before Thiruchirapalli. The physically exhausted Pandyan infantry easily fell prey for the Sultanate's army. However, the Pandyan cavalry revived its attack on the Delhi Sultanate cavalry. But, the cavaliers were well armed with turcopoles and chain mail armours while Pandyan horsemen were inferiorly armoured and heavily relied on heavy swords. Tactical strikes by Malik Kafur's crossbow men over the Pandya cavalry, followed by the Delhi Sultanate infantry's attack blocked any possible retreat for the Sundara Pandyan's army. The generals of Kafur's army took Sundara Pandyan as captive and beheaded all the others captured. Few Pandyan cavaliers managed to escape to Madurai to report their defeat to Vira Pandya. The victorious Sultanate went on plundering the temples of Thiruchirapalli and Thiruvarangam.
Siege of Madurai

The walled city of Madurai was now left only with the Vira Pandyan's men. Their sole aim was to safeguard Meenakshi Sundareswarar Temple. Understanding the fact that they were largely outnumbered, the defenders' only hope is to delay their enemies long enough for them to negotiate. Kafur's siege on Madurai continued for weeks, however, it turned futile as his army lacked any Ballistas or Trebuchets and relied on Battering Rams of inferior quality. On the other hand, continuous archery attack by Pandyan soldiers and surprise cavalry attacks on the Delhi Sultanate infantry during night times tremendously increased the casualties on Kafur's side. Malik Kafur lost about half of his army, and then managed to breach the wall after weeks of siege. Vira Pandyan and his soldiers still managed to hold the line, thus making Malik Kafur to finally come down for negotiation.
Malik Kafur offered the following terms to Vira Pandyan:
1. Hand over all the treasures belonging to the Meenakshi Temple and Madurai Treasury which included 96,000 gold coins and precious stones
2. Half of the rice rationed inside the walls of Madurai
3. All the elephants and horses available with Pandyas.[citation needed]
In return, Vira Pandyan was promised the release of his brother, Sundara Pandyan and safety of the deities in the inner sanctum of the Meenakshi Temple.
Later Expeditions and Capture by Vijayanagara Empire
Following this there were two other expeditions from the Khilji Sultanate in 1314 AD led by Khusro Khan (later Sultan Nasir-ud-din) and in 1323 AD by Ulugh Khan (later Sultan Muhammad bin Tughluq) under Sultan Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq. No inscriptions about Pandyas are known since then. Sayyid Jalal-ud-Din Ahsan was appointed Governor of the newly created southern-most Ma'bar province of the Delhi sultanate by Muhammad bin Tughluq. In 1333 AD, Sayyid declared his independence and created Madurai Sultanate. Vijayanagara Empire conquered Madurai and replaced the Sultanate by Nayak governors in 1378. These Nayaks continued to govern Madurai until the arrival of British forces.
Government and Society
Trade
Megasthenes reported about the pearl fisheries of the Pandyas, indicating that the Pandyas derived great wealth from the pearl trade.[46][47]
Religion
Historical Madurai was a stronghold of Saivism. Following the invasion of Kalabhras, Jainism gained a foothold in the Pandyan kingdom. With the advent of Bhakti movements, Saivism and Vaishnavism resurfaced. The latter-day Pandyas after 600 AD were Saivites who claimed to descend from Lord Shiva and Goddess Parvati. Pandyan Nedumchadayan was a staunch Vaishnavite.[48]
See also
| Classical India | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Timeline and cultural period |
Northwestern India (Punjab-Sapta Sindhu) |
Indo-Gangetic Plain | Central India | Southern India | ||||
| Western Gangetic Plain | Northern India (Central Gangetic Plain) |
Northeastern India | ||||||
| IRON AGE | ||||||||
| Culture | Late Vedic Period | Late Vedic Period (Brahmin ideology)[lower-alpha 1] |
Late Vedic Period (Kshatriya/Shramanic culture)[lower-alpha 2] |
Pre-history | ||||
| 6th century BCE | Gandhara | Kuru-Panchala | Magadha | Adivasi (tribes) | ||||
| Culture | Persian-Greek influences | "Second Urbanisation" Rise of Shramana movements |
Pre-history | |||||
| 5th century BCE | (Persian rule) | Shishunaga dynasty | Adivasi (tribes) | |||||
| 4th century BCE | (Greek conquests) |
Nanda empire |
||||||
| HISTORICAL AGE | ||||||||
| Culture | Spread of Buddhism | Pre-history | Sangam period (300 BCE – 200 CE) | |||||
| 3rd century BCE | Maurya Empire | Early Cholas Cheras 46 other small kingdoms in Ancient Thamizhagam | ||||||
| Culture | Preclassical Hinduism[lower-alpha 3] - "Hindu Synthesis"[lower-alpha 4] (ca. 200 BCE-300 CE)[lower-alpha 5][lower-alpha 6] Epics - Puranas - Ramayana - Mahabharata - Bhagavad Gita - Brahma Sutras - Smarta Tradition Mahayana Buddhism |
Sangam period (continued) | ||||||
| 2nd century BCE | Indo-Greek Kingdom | Sunga Empire | Adivasi (tribes) | Early Cholas Cheras 46 other small kingdoms in Ancient Thamizhagam | ||||
| 1st century BCE | Yona | Maha-Meghavahana Dynasty | ||||||
| 1st century CE | Kuninda Kingdom | |||||||
| 2nd century | Pahlava | Varman dynasty | ||||||
| 3rd century | Kushan Empire | Western Satraps | Kamarupa kingdom | Kalabhras dynasty Pandyan Kingdom(Under Kalabhras) | ||||
| Culture | "Golden Age of Hinduism"(ca. 320-650 CE)[lower-alpha 7] Puranas Co-existence of Hinduism and Buddhism | |||||||
| 4th century | Gupta Empire | Kalabhras dynasty Pandyan Kingdom(Under Kalabhras) Kadamba Dynasty Western Ganga Dynasty | ||||||
| 5th century | Maitraka | Adivasi (tribes) | Kalabhras dynasty Pandyan Kingdom(Under Kalabhras) | |||||
| 6th century | Kalabhras dynasty Pandyan Kingdom(Under Kalabhras) | |||||||
| Culture | Late-Classical Hinduism (ca. 650-1100 CE)[lower-alpha 8] Advaita Vedanta - Tantra Decline of Buddhism in India | |||||||
| 7th century | Indo-Sassanids | Vakataka dynasty, Harsha | Mlechchha dynasty | Adivasi (tribes) | Pandyan Kingdom(Under Kalabhras) Pandyan Kingdom(Revival) | |||
| 8th century | Kidarite Kingdom | Pandyan Kingdom Kalachuri | ||||||
| 9th century | Indo-Hephthalites (Huna) | Gurjara-Pratihara | Pandyan Kingdom Pandyan Kingdom(Under Cholas) Chera Perumals of Makkotai | |||||
| 10th century | Pala dynasty Kamboja-Pala dynasty |
Medieval Cholas Pandyan Kingdom(Under Cholas) Chera Perumals of Makkotai Rashtrakuta | ||||||
| Culture | Islamic rule and "Sects of Hinduism" (ca. 1100-1850 CE)[lower-alpha 9] - Medieval and Late Puranic Period (500–1500 CE)[lower-alpha 10] | |||||||
| 11th century | (Islamic conquests) Kabul Shahi (Islamic Empire) |
Pala Empire |
Adivasi (tribes) | Medieval Cholas Pandyan Kingdom(Under Cholas) Later Cholas Chera Perumals of Makkotai Yadava dynasty | ||||
| 12th century | Later Cholas Pandyan Kingdom(Under Cholas) Chera Perumals of Makkotai Alupa Dynasty Chera-Ai Dynasty Venadu Cheras | |||||||
| 13th century | Later Cholas Pandyan Kingdom(Under Cholas) Pandyan Kingdom(Revival) Venadu Cheras | |||||||
| 14th century | Pandyan Kingdom(Ruled from Madurai) Khilji Dynasty Pandyan Kingdom(Thenkaasi Pandiyar(Ruled from Thenkaasi after conquest)) | |||||||
| 15th century | Pandyan Kingdom(Thenkaasi Pandiyar) | |||||||
| 16th century | Pandyan Kingdom(Thenkaasi Pandiyar) | |||||||
| 17th century | Pandyan Kingdom(Thenkaasi Pandiyar) | |||||||
| ||||||||
Notes
- ↑ Kishore, Kavita (15 October 2010). "States / Tamil Nadu: Porunthal excavations prove existence of Indian scripts in 5th century BC: expert". The Hindu. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- ↑ "Government Museum Chennai". Chennaimuseum.org. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- ↑ "History – Ancient History in depth: The Story of India". BBC. 17 February 2011. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- ↑ Kishore, Kavita (15 October 2010). "States / Tamil Nadu: Porunthal excavations prove existence of Indian scripts in 5th century BC: expert". The Hindu. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- ↑ "Government Museum Chennai". Chennaimuseum.org. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- ↑ "History – Ancient History in depth: The Story of India". BBC. 17 February 2011. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- ↑ Kishore, Kavita (15 October 2010). "States / Tamil Nadu: Porunthal excavations prove existence of Indian scripts in 5th century BC: expert". The Hindu. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- ↑ "Government Museum Chennai". Chennaimuseum.org. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- ↑ "History – Ancient History in depth: The Story of India". BBC. 17 February 2011. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- ↑ "Pandya dynasty (Indian dynasty) – Britannica Online Encyclopedia". Britannica.com. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- ↑ Kishore, Kavita (15 October 2010). "States / Tamil Nadu: Porunthal excavations prove existence of Indian scripts in 5th century BC: expert". The Hindu. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- ↑ "Government Museum Chennai". Chennaimuseum.org. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- ↑ "History – Ancient History in depth: The Story of India". BBC. 17 February 2011. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- ↑ "Pandya dynasty (Indian dynasty) – Britannica Online Encyclopedia". Britannica.com. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- ↑ Geological Survey of India. p. 80. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑
- ↑ Pandya dynasty (Indian dynasty) – Encyclopedia Britannica. Britannica.com. Retrieved on 12 July 2013.
- ↑ Page vi, Mackenzie collection: a descriptive catalogue of the oriental manuscripts and other articles illustrative of the literature, history, statistics and antiquities of the south of India collected by the late Lieut.-Col. Colin Mackenzie, surveyor general of India, Volume 1
- ↑ "The ordinary enumeration is above Seventy, but some accounts with more consistency if the origin be so remote, assert that the whole number was Three hundred and fifty seven, down to Kuna Pandya, with whom all the lists close", Pages xxiv & xxv, Mackenzie collection: a descriptive catalogue of the oriental manuscripts and other articles illustrative of the literature, history, statistics and antiquities of the south of India collected by the late Lieut.-Col. Colin Mackenzie, surveyor general of India, Volume 1
- ↑ The First Spring: The Golden Age of India – Abraham Eraly – Google Books. Books.google.co.in. Retrieved on 12 July 2013.
- ↑ The cyclopædia of India and of Eastern and Southern Asia By Edward Balfour
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Ancient Indian History and Civilization By Sailendra Nath Sen
- ↑ Mahabhrata Book Eight: Karna By Adam Bowles
- ↑ The Mahabharata of Krishna-Dwaipayana Vyasa translated into ..., Volume 8 By Kisari Mohan Ganguli
- ↑ Let's go: India & Nepal, 2004 By Let's Go, Inc.
- ↑ AALAVAI by KRA NARASIAH
- ↑ Kulke and Rothermund, p104
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 Keay, p119
- ↑ S. Dhammika, The Edicts of King Asoka: An English Rendering; Buddhist Publication Sosciety, Kandy (1994). Also ISBN 955-24-0104-6
- ↑ India By John Keay
- ↑ Periplus 54. Original Greek: "Ἡ δὲ Νέλκυνδα σταδίους μὲν ἀπὸ Μουζιρέως ἀπέχει σχεδὸν πεντακοσίους, ὁμοίως διά τε ποταμοῦ (καὶ πεζῇ) καὶ διὰ θαλάσσης, βασιλείας δέ ἐστιν ἑτέρας, τῆς Πανδίονος· κεῖται δὲ καὶ αὐτὴ παρὰ ποταμὸν, ὡσεὶ ἀπὸ σταδίων ἑκατὸν εἴκοσι τῆς θαλάσσης."
- ↑ Hill, John
- ↑ Strabo, Geography, BOOK XV., CHAPTER I., section 73. Perseus.tufts.edu. Retrieved on 12 July 2013.
- ↑ Keay, p121
- ↑ Travel and ethnology in the Renaissance: South India through European eyes, Joan-Pau Rubiés
- ↑ Muslim identity, print culture, and the Dravidian factor in Tamil Nadu, J. B. Prashant More
- ↑ Layers of blackness: colourism in the African diaspora, Deborah Gabriel
- ↑ The Tamils Eighteen Hundred Years Ago By V. Kanakasabhai
- ↑ "Mahabharata: The Great War and World History". Bvashram.org. 29 October 2005. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- ↑ "The Sampradaya Sun – Independent Vaisnava News – Feature Stories – October 2007". Harekrsna.com. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- ↑ Husaini, AQ, p 8-17
- ↑ Sastri, KAN, pp 22–25
- ↑ Purushottam, Vi.Pi, pp 42
- ↑ K.A.Nilakanta Sastry, "Advanced History of India" (1970), Allied Publishers Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi
- ↑ Sastri (1955), pp 206–208
- ↑ Kulke and Rothermund, p99
- ↑ Kulke and Rothermund, p107
- ↑ Lloyd V. J. Ridgeon, Major World Religions: From Their Origins to the Present
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Pandyan Dynasty. |
- Carswell, John. 1991. "The Port of Mantai, Sri Lanka." RAI, pp. 197–203.
- Hill, John E. 2004. The Peoples of the West from the Weilüe 魏略 by Yu Huan 魚豢: A Third Century Chinese Account Composed between 239 and 265 CE. Draft annotated English translation.
- Husaini, A.Q. (1972). History of The Pandya Country.
- Keay, John (2000) [2001]. India: A history. India: Grove Press. ISBN 0-8021-3797-0.
- Nagasamy, R (1981). Tamil Coins — A study. Institute of Epigraphy, Tamilnadu State Dept. of Archaeology.
- Sastri, K. A. Nilakanta. The Pandyan Kingdom: From the Earliest Times to the Sixteenth Century.
- Purushottam, Vi. Pi. (1989). Cankakala Mannar Kalanilai Varalaru.
- Ray, Himanshu Prabha, ed. 1996. Tradition and Archaeology: Early Maritime Contacts in the Indian Ocean. Proceedings of the International Seminar Techno-Archaeological Perspectives of Seafaring in the Indian Ocean 4th cent. B.C. – 15th cent. A.D. New Delhi, 28 February – 4 March 1994. New Delhi, and Jean-François SALLES, Lyon. First published 1996. Reprinted 1998. Manohar Publishers & Distributors, New Delhi.
- Reddy, P. Krishna Mohan. 2001. "Maritime Trade of Early South India: New Archaeological Evidences from Motupalli, Andhra Pradesh." East and West Vol. 51 – Nos. 1–2 (June 2001), pp. 143–156.
- Shaffer, Lynda (1996). Maritime Southeast Asia to 1500 (Sources and Studies in World History). Armonk, N.Y: M.E. Sharpe. ISBN 1-56324-144-7.
- Tripathi, Rama Sankar (1967). History of Ancient India. India: Motilal Banarsidass Publications. ISBN 81-208-0018-4.
