Pacific War
| Pacific War | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of World War II | |||||||||
 A map showing the main areas of the conflict and Allied landings in the Pacific, 1942–45. |
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
| Allies[1]
| Axis and others [nb 2] |
||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
| Military deaths 4,000,000 (1937–45)[nb 3] Civilian deaths |
|||||||||
| |||||
| |||||
| History of Japan | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Periods
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Topics
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Pacific War, sometimes called the Asia-Pacific War,[4] was the theatre of World War II which was fought in the Pacific and East Asia. It was fought over a vast area which included the Pacific Ocean and islands, the South West Pacific, the South-East Asia, and in China (including the 1945 Soviet-Japanese conflict).
It is generally considered that the Pacific War began on 7/8 December 1941, on which dates the Empire of Japan invaded Thailand, attacked British possessions in Malaya, Singapore, and Hong Kong, and the United States military base in Pearl Harbor.[5][6][7][8] Some Historians contend that the conflict in Asia can be dated back to 7 July 1937 with the beginning of the Second Sino-Japanese War between the Empire of Japan and the Republic of China, or possibly 19 September 1931, beginning with the Japanese invasion of Manchuria.[9] However, it is more widely accepted that the Pacific War itself started in early December 1941, with the Sino-Japanese War then becoming part of it as a theater of the greater World War II.[10][11]
The Pacific War saw the Allied powers pitted against the Empire of Japan, the latter briefly aided by Thailand and to a much lesser extent by its Axis allies, Germany and Italy. The war culminated in the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, and other large aerial bombing attacks by the United States Army Air Forces, accompanied by the Soviet invasion of Manchuria on 8 August 1945, resulting in the Japanese announcement of intent to surrender on 15 August 1945. The formal and official surrender of Japan took place aboard the battleship USS Missouri in Tokyo Bay on 2 September 1945.
Overview
Names for the war
In Allied countries during the war, "The Pacific War" was not usually distinguished from World War II in general, or it was known simply as the War against Japan. In the United States, the term Pacific Theater was widely used, although technically this did not cover the South West Pacific Theatre (under the command of General Douglas MacArthur), the China-Burma-India Theater, or usually the Southeast Asian Theater. However, the aircraft carrier task forces of the U.S. Pacific Fleet did carry out large air raids on Vietnam – at Haiphong, Camranh Bay, and Saigon in early 1945.
Japan used the name Greater East Asia War (大東亜戦争 Dai Tō-A Sensō), as chosen by a cabinet decision on 10 December 1941, to refer to both the war with the Western Allies and the ongoing war in China. This name was released to the public on 12 December, with an explanation that it involved Asian nations achieving their independence from the Western powers through armed forces of the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere.[12] Japanese officials integrated what they called the Japan-Sino Incident (日支事変 Nisshi Jihen) into the Greater East Asia War.
During the American military occupation of Japan (1945–52), these Japanese terms were prohibited in official documents, although their informal usage continued, and the war became officially known as Pacific War (太平洋戦争 Taiheiyō Sensō). This latter term has later come into limited use in Occidental countries. In Japan, the Fifteen Year War (十五年戦争 Jūgonen Sensō) is also used, referring to the period from the Mukden Incident of 1931 through 1945.
Participants


The Axis states which assisted Japan included the authoritarian government of Thailand, which quickly formed a temporary alliance with the Japanese in 1941, as the Japanese forces were already invading the southern peninsula of Thailand. The Phayap Army sent troops to invade and occupy northeastern Burma, which was former Thai territory that had been forcibly taken away by the British Army much earlier. Also involved were the Japanese puppet states of Manchukuo and Mengjiang (consisting of most of Manchuria and parts of Inner Mongolia respectively), and the collaborationist Wang Jingwei regime (which controlled the coastal regions of China).
The official policy of the U.S. Government is that Thailand was not an ally of the Axis, and that the United States was not at war with Thailand. The policy of the U.S. Government ever since 1945 has been to treat Thailand not as a former enemy, but rather as a country which had been forced into certain actions by Japanese blackmail, before being occupied by Japanese troops. Thailand has been treated by the United States in the same way as such other Axis-occupied countries as Belgium, Czechoslovakia, Denmark, Greece, Korea, Norway, Poland, and the Netherlands.
Japan enlisted many soldiers from its colonies of Korea and Formosa (Taiwan). To a small extent, some Vichy French, Indian National Army, and Burmese National Army forces were active in the area of the Pacific War. Collaborationist units from Hong Kong (reformed ex-colonial police), Philippines, Dutch East Indies (the PETA) and Dutch Guinea, British Malaya and British Borneo, Inner Mongolia and former French Indochina (after the overthrow of Vichy French regime) as well as Timorese militia also assisted Japanese war efforts.
Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy both had limited involvement in the Pacific War. The German Navy (Kriegsmarine) and the Italian Royal Navy (Regia Marina) operated submarines and raiding ships in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. The Italians had access to "concession territory" naval bases in China, having been one of the Allies of World War I, while the Germans did not. After Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor and the subsequent declarations of war, both navies had access to Japanese naval facilities.
The major Allied participants were the United States, the Republic of China, the United Kingdom (including the armed forces of British India, the Fiji Islands, Samoa, etc.), Australia, the Commonwealth of the Philippines, the Netherlands (as the possessor of the Dutch East Indies and the western part of New Guinea), New Zealand, and Canada, all of whom were members of the Pacific War Council.[13] Mexico, Free France and many other countries also took part, especially forces from other British colonies.
The Soviet Union fought two short, undeclared border conflicts with Japan in 1938 and 1939, then remained neutral until August 1945, when it joined the Allies and invaded the territory of Manchukuo, Republic of China, Inner Mongolia, the Japanese protectorate of Korea and Japanese-claimed islands such as Sakhalin coordinated notably between the Red Banner Pacific Fleet and the US Navy's Task Force 38.[citation needed]
Theaters

Between 1942 and 1945, there were four main areas of conflict in the Pacific War: China, the Central Pacific, South East Asia and the South West Pacific. U.S. sources refer to two theaters within the Pacific War: the Pacific theater and the China Burma India Theater (CBI). However these were not operational commands.
In the Pacific, the Allies divided operational control of their forces between two supreme commands, known as Pacific Ocean Areas and Southwest Pacific Area.[14] In 1945, for a brief period just before the Japanese surrender, the Soviet Union and its Mongolian ally engaged Japanese forces in Manchuria and northeast China.
Historical Background
Conflict between China and Japan

By 1937, Japan controlled Manchuria and was ready to move deeper into China. The Marco Polo Bridge Incident on 7 July 1937 provoked full scale war between China and Japan. The Nationalist and Communist Chinese suspended their civil war to form a nominal alliance against Japan, and the Soviet Union quickly lent support by providing large amount of materiel to Chinese troops. The Japanese achieved major military victories in Shanghai, Nanjing, and Wuhan, but world opinion—in particular in the United States—condemned Japan, especially after Panay Incident.
In 1939, Japanese forces tried to push into the Soviet Far East from Manchuria. They were soundly defeated in the Battle of Khalkhin Gol by a mixed Soviet and Mongolian force led by Georgy Zhukov. This stopped Japanese expansion to the north, and Soviet aid to China ended as a result of the signing of the Soviet–Japanese Neutrality Pact at the beginning of its war against Nazi Germany.[15]
In September 1940, Japan decided to cut China's only land line to the outside world by seizing Indochina, which was controlled at the time by Vichy France. Japanese forces broke their agreement with the Vichy administration and fighting broke out, ending in a Japanese victory. On 27 September Japan signed a military alliance with Germany and Italy, becoming one of the three Axis Powers. In practice, there was little coordination between Japan and Germany until 1944, by which time the U.S. was deciphering their secret diplomatic correspondence.[16]
By 1941 the conflict had become a stalemate. Although Japan had occupied much of northern, central, and coastal China, the Nationalist Government had retreated to the interior with a provisional capital set up at Chungking while the Chinese communists remained in control of base areas in Shaanxi. In addition, Japanese control of northern and central China was somewhat tenuous, in that Japan was usually able to control railroads and the major cities ("points and lines"), but did not have a major military or administrative presence in the vast Chinese countryside. The Japanese found its aggression against the retreating and regrouping Chinese army was stalled by the mountainous terrain in southwestern China while the Communists organised widespread guerrilla and saboteur activities in northern and eastern China behind the Japanese front line.
Japan sponsored several puppet governments, one of which was headed by Wang Jingwei.[17] However, its policies of brutality toward the Chinese population, of not yielding any real power to these regimes, and of supporting several rival governments failed to make any of them a viable alternative to the Nationalist government led by Chiang Kai-shek. Conflicts between Chinese communist and nationalist forces vying for territory control behind enemy lines culminated in a major armed clash in January 1941, effectively ending their co-operation.[18]
Japanese strategic bombing[citation needed] efforts mostly targeted large Chinese cities such as Shanghai, Wuhan and Chongqing, with around 5,000 raids from February 1938 to August 1943 in the later case. "Japanese strategic bombing campaigns devastated Chinese cities, killing more than 260,000 noncombatants."[19]
Tensions between Japan and the West
In an effort to discourage Japanese militarism, Western powers including Australia, the United States, Britain, and the Dutch government in exile, which controlled the petroleum-rich Dutch East Indies, stopped selling iron ore, steel and oil to Japan, denying it the raw materials needed to continue its activities in China and French Indochina. In Japan, the government and nationalists viewed these embargos as acts of aggression; imported oil made up about 80% of domestic consumption, without which Japan's economy, let alone its military, would grind to a halt. The Japanese media, influenced by military propagandists,[nb 6] began to refer to the embargoes as the "ABCD ("American-British-Chinese-Dutch") encirclement" or "ABCD line".
Faced with a choice between economic collapse and withdrawal from its recent conquests (with its attendant loss of face), the Japanese Imperial General Headquarters began planning for a war with the western powers in April or May 1941.
The key objective was for the Southern Expeditionary Army Group to seize economic resources under the control of the United Kingdom and the Netherlands, most notably those in Malaya and the Dutch East Indies, known as the "Southern Plan". It was also decided—because of the close relationship between the UK and United States, and the (mistaken)[20][21] belief the US would inevitably become involved[20]—Japan would also require an "eastern plan".
The eastern plan required
- initial attacks on the US Pacific Fleet at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, with carrier-based aircraft of the Combined Fleet, and
- following this attack with
- seizure of the Philippines, and
- cutting the U.S. lines of communication by seizing Guam and Wake.
The southern plans called for:
- attacking Malaya and Hong Kong, and
- following with attacks against
- the Bismarck Archipelago,
- Java, and
- Sumatra.
- isolating Australia and New Zealand
Following completion of these objectives, the strategy would turn defensive, primarily holding their newly acquired territory while hoping for a negotiated peace.[22]
By November these plans were essentially complete, and were modified only slightly over the next month. Japanese military planners' expectation of success rested on the United Kingdom and the Soviet Union being unable to effectively respond to a Japanese attack because of the threat posed to each by Germany; the Soviet Union was even seen as unlikely to commence hostilities.
The Japanese leadership was aware that a total military victory in a traditional sense against the USA was impossible; the alternative would be negotiating for peace after their initial victories, which would recognize Japanese hegemony in Asia.[23] In fact, the Imperial GHQ noted, should acceptable negotiations be reached with the Americans, the attacks were to be canceled—even if the order to attack had already been given. The Japanese leadership looked to base the conduct of the war against America on the historical experiences of the successful wars against China (1894–95) and Russia (1904–5), in both of which a strong continental power was defeated by reaching limited military objectives, not by total conquest.[23]
They also planned, should the U.S. transfer its Pacific Fleet to the Philippines, to intercept and attack this fleet en route with the Combined Fleet, in keeping with all Japanese Navy prewar planning and doctrine.
Should the United States or Britain attack first, the plans further stipulated the military were to hold their positions and wait for orders from GHQ. The planners noted attacking the Philippines and Malaya still had possibilities of success, even in the worst case of a combined preemptive attack including Soviet forces.
Japanese offensives, 1941–42
On 7 December 1941 Japan attacked American bases in Pearl Harbor, Guam, and Wake Island. The same day (8 December on the other side of the International Date Line), Japanese forces attacked the British crown colony of Hong Kong, invaded the American controlled Philippines, invaded Thailand from bases in French Indochina and invaded Malaya.
Attack on Pearl Harbor
_burning_after_the_Japanese_attack_on_Pearl_Harbor_-_NARA_195617_-_Edit.jpg)
In the early hours of 7 December (Western Hemisphere time), Japan launched a major carrier-based air strike on Pearl Harbor, which crippled the US Naval forces leaving eight American battleships out of action.[24] The Japanese had gambled the United States, when faced with such a sudden and massive defeat, would agree to a negotiated settlement and allow Japan free rein in Asia. This gamble did not pay off. American losses were less serious than initially thought: The American aircraft carriers, far more important than battleships, were at sea, and vital naval infrastructure (fuel oil tanks, shipyard facilities, and a power station), submarine base, and signals intelligence units were unscathed.[24] Japan's fallback strategy, relying on a war of attrition to make the U.S. come to terms, was beyond the IJN's capabilities.[20][25]
When the attack on Pearl Harbor occurred, the U.S. was not officially at war anywhere in the world.[26] The 800,000-member America First Committee vehemently opposed any American intervention in the European conflict, even as America sold military aid to Britain and the Soviet Union through the Lend-Lease program. Opposition to war in the U.S. vanished after the attack. On 8 December, the Netherlands declared war on Japan,[27] followed by Australia the next day.[28] Four days after Pearl Harbor, Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy declared war on the United States, drawing the country into a two-theater war. This is widely agreed to be a grand strategic blunder, as it abrogated the benefit Germany gained by Japan's distraction of the U.S. (predicted months before in a memo by Commander Arthur McCollum)[nb 7] and the reduction in aid to Britain, which both Congress and Hitler had managed to avoid during over a year of mutual provocation, which would otherwise have resulted.
Attacks on South East Asia
| “ | I praise the Army for cutting down like weeds large numbers of the enemy... | ” |

British, Australian and Dutch forces, already drained of personnel and matériel by two years of war with Germany, and heavily committed in the Middle East, North Africa and elsewhere, were unable to provide much more than token resistance to the battle-hardened Japanese. The Allies suffered many disastrous defeats in the first six months of the war. Two major British warships the HMS Repulse and HMS Prince of Wales were sunk by a Japanese air attack off Malaya on 10 December 1941.[30]
Thailand, with its territory already serving as a springboard for the Malayan campaign, surrendered within 24 hours of the Japanese invasion. The government of Thailand formally allied itself with Japan on 21 December.
Hong Kong was attacked on 8 December and fell on 25 December 1941, with Canadian forces and the Royal Hong Kong Volunteers playing an important part in the defense. U.S. bases on Guam and Wake Island were lost at around the same time.
Following the 1 January 1942 Declaration by United Nations (the first official use of the term United Nations), the Allied governments appointed the British General Sir Archibald Wavell to the American-British-Dutch-Australian Command (ABDACOM), a supreme command for Allied forces in South East Asia. This gave Wavell nominal control of a huge force, albeit thinly spread over an area from Burma to the Philippines to northern Australia. Other areas, including India, Hawaii and the rest of Australia remained under separate local commands. On 15 January Wavell moved to Bandung in Java to assume control of ABDACOM.
In January, Japan invaded Burma, the Dutch East Indies, New Guinea, the Solomon Islands and captured Manila, Kuala Lumpur and Rabaul. After being driven out of Malaya, Allied forces in Singapore attempted to resist the Japanese during the Battle of Singapore but surrendered to the Japanese on 15 February 1942; about 130,000 Indian, British, Australian and Dutch personnel became prisoners of war.[31] The pace of conquest was rapid: Bali[32] and Timor[33] also fell in February. The rapid collapse of Allied resistance had left the "ABDA area" split in two. Wavell resigned from ABDACOM on 25 February, handing control of the ABDA Area to local commanders and returning to the post of Commander-in-Chief, India.

Meanwhile, Japanese aircraft had all but eliminated Allied air power in South-East Asia[34] and were making attacks on northern Australia, beginning with a psychologically devastating but militarily insignificant attack on the city of Darwin[34] on 19 February, which killed at least 243 people.
At the Battle of the Java Sea in late February and early March, the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) inflicted a resounding defeat on the main ABDA naval force, under Admiral Karel Doorman.[35] The Dutch East Indies campaign subsequently ended with the surrender of Allied forces on Java[36] and Sumatra.[37]
In March and April, a powerful IJN carrier force launched a raid into the Indian Ocean. British Royal Navy bases in Ceylon were hit and the aircraft carrier HMS Hermes as well as other Allied ships were sunk. The attack forced the Royal Navy to withdraw to the western part of the Indian Ocean.[38] This paved the way for a Japanese assault on Burma and India.

In Burma the British, under intense pressure, made a fighting retreat from Rangoon to the Indo-Burmese border. This cut the Burma Road which was the western Allies' supply line to the Chinese Nationalists. Cooperation between the Chinese Nationalists and the Communists had waned from its zenith at the Battle of Wuhan, and the relationship between the two had gone sour as both attempted to expand their area of operations in occupied territories. Most of the Nationalist guerrilla areas were eventually overtaken by the Communists. On the other hand, some Nationalist units were deployed to blockade the Communists and not the Japanese. Furthermore, many of the forces of the Chinese Nationalists were warlords allied to Chiang Kai-Shek, but not directly under his command. "Of the 1,200,000 troops under Chiang's control, only 650,000 were directly controlled by his generals, and another 550,000 controlled by warlords who claimed loyalty to his government; the strongest force was the Szechuan army of 320,000 men. The defeat of this army would do much to end Chiang's power."[39] The Japanese exploited this lack of unity to press ahead in their offensives.
Filipino and U.S. forces resisted in the Philippines until 8 May 1942, when more than 80,000 soldiers were ordered to surrender. By this time, General Douglas MacArthur, who had been appointed Supreme Allied Commander South West Pacific, had retreated to the safer confines of Australia. The U.S. Navy, under Admiral Chester Nimitz, had responsibility for the rest of the Pacific Ocean. This divided command had unfortunate consequences for the commerce war,[40] and consequently, the war itself.
Threat to Australia
In late 1941, as the Japanese struck at Pearl Harbor, most of Australia’s best forces were committed to the fight against Hitler in the Mediterranean Theatre. Australia was ill-prepared for an attack, lacking armaments, modern fighter aircraft, heavy bombers, and aircraft carriers. While still calling for reinforcements from Churchill, the Australian Prime Minister John Curtin called for American support with an historic announcement on 27 December 1941:[41][42]
The Australian Government...regards the Pacific struggle as primarily one in which the United States and Australia must have the fullest say in the direction of the democracies' fighting plan. Without inhibitions of any kind, I make it clear that Australia looks to America, free of any pangs as to our traditional links or kinship with the United Kingdom.— Prime Minister John Curtin

Australia had been shocked by the speedy collapse of British Malaya and Fall of Singapore in which around 15,000 Australian soldiers became prisoners of war. Curtin predicted that the "battle for Australia" would now follow. The Japanese established a major base in the Australian Territory of New Guinea in early 1942.[43] On 19 February, Darwin suffered a devastating air raid, the first time the Australian mainland had been attacked. Over the following 19 months, Australia was attacked from the air almost 100 times.

Two battle-hardened Australian divisions were steaming from the Mid-East for Singapore. Churchill wanted them diverted to Burma, but Curtin insisted on a return to Australia. In early 1942 elements of the Imperial Japanese Navy proposed an invasion of Australia. The Japanese Army opposed the plan and it was rejected in favour of a policy of isolating Australia from the United States via blockade by advancing through the South Pacific.[44] The Japanese decided upon a seaborne invasion of Port Moresby, capital of the Australian Territory of Papua which would put Northern Australia within range of Japanese bomber aircraft.
President Franklin Roosevelt ordered General Douglas MacArthur in the Philippines to formulate a Pacific defence plan with Australia in March 1942. Curtin agreed to place Australian forces under the command of MacArthur who became Supreme Commander, South West Pacific. MacArthur moved his headquarters to Melbourne in March 1942 and American troops began massing in Australia. Enemy naval activity reached Sydney in late May 1942, when Japanese midget submarines launched a daring raid on Sydney Harbour. On 8 June 1942, two Japanese submarines briefly shelled Sydney's eastern suburbs and the city of Newcastle.[45]
Allies re-group, 1942–43
In early 1942, the governments of smaller powers began to push for an inter-governmental Asia-Pacific war council, based in Washington, D.C.. A council was established in London, with a subsidiary body in Washington. However, the smaller powers continued to push for a U.S.-based body. The Pacific War Council was formed in Washington, on 1 April 1942, with President Franklin D. Roosevelt, his key advisor Harry Hopkins, and representatives from Britain, China, Australia, the Netherlands, New Zealand, and Canada. Representatives from India and the Philippines were later added. The council never had any direct operational control, and any decisions it made were referred to the U.S.-UK Combined Chiefs of Staff, which was also in Washington.
Allied resistance, at first symbolic, gradually began to stiffen. Australian and Dutch forces led civilians in a prolonged guerilla campaign in Portuguese Timor. The Doolittle Raid did minimal damage but was a huge morale booster for the Allies, especially the United States, and it caused repercussions throughout the Japanese military because they were sworn to protect the Japanese emperor and homeland, but did not shoot down a single bomber. The greatest effect of the raid, however, was that it caused the Japanese to launch the ultimately catastrophic assault on Midway.[46]
Coral Sea and Midway: the turning point

By mid-1942, the Japanese found themselves holding a vast area from the Indian Ocean to the Central Pacific, even though they lacked the resources to defend or sustain it. Moreover, Combined Fleet doctrine was inadequate to execute the proposed "barrier" defence.[20][25] Instead, Japan decided on additional attacks in both the south and central Pacific. While she had the element of surprise at Pearl Harbor, Allied codebreakers had now turned the tables. They discovered an attack was planned against Port Moresby; if it fell, Japan would control the seas to the north and west of Australia and could isolate the country. The carrier USS Lexington under Admiral Fletcher joined USS Yorktown and an American-Australian task force to stop the Japanese advance. The resulting Battle of the Coral Sea, fought in May 1942, was the first naval battle in which ships involved never sighted each other and only aircraft were used to attack opposing forces. Although Lexington was sunk and Yorktown seriously damaged, the Japanese lost the carrier Shōhō, and suffered extensive damage to Shōkaku and heavy losses to the air wing of Zuikaku, both of which missed the operation against Midway the following month. Although Allied losses were heavier than Japanese, the attack on Port Moresby was thwarted and the Japanese invasion force turned back, a strategic victory for the Allies. Moreover, Japan lacked the capacity to replace losses in ships, planes and trained pilots.

After Coral Sea, Yamamoto had four fleet carriers operational—Sōryū, Kaga, Akagi and Hiryū—and believed Nimitz had a maximum of two—Enterprise and Hornet. (Saratoga was out of action, undergoing repair after a torpedo attack, while Yorktown had been damaged at Coral Sea, and was believed sunk by Japanese navy intelligence; in the event, she sortied for Midway after just three days' of repairs involving her flight deck, with civilian work crews still aboard.)
Yamamoto's objective was to lure the American carriers into a trap,[47] leading to the destruction of United States strategic power in the Pacific.[48] He also intended to occupy Midway Atoll as part of an overall plan to extend Japan's defensive perimeter in response to the Doolittle Raid; afterward, it would be turned into a major airbase, giving Japan control of the central Pacific.
A Japanese force was sent north to attack the Aleutian Islands. The next stage of the plan called for the capture of Midway, which would give him an opportunity to destroy Nimitz's remaining carriers. In May, Allied codebreakers discovered his intentions. Nagumo was again in tactical command but was focused on the invasion of Midway; Yamamoto's complex plan had no provision for intervention by Nimitz before the Japanese expected him. Planned surveillance of the U.S. fleet by long range seaplane did not happen (as a result of an abortive identical operation in March), so Fletcher's carriers were able to proceed to a flanking position without being detected. Nagumo had 272 planes operating from his four carriers, the U.S. 348 (115 land-based).
As anticipated by Nimitz, the Japanese fleet arrived off Midway on 4 June and was spotted by PBY patrol aircraft.[49] Nagumo executed a first strike against Midway, while Fletcher launched his aircraft, bound for Nagumo's carriers. At 09:20 the first U.S. carrier aircraft arrived, TBD Devastator torpedo bombers from Hornet, but their attacks were poorly coordinated and ineffectual; thanks in part to faulty aerial torpedoes, they failed to score a single hit and all 15 were wiped out by defending Zero fighters. At 09:35, 15 additional TBDs from Enterprise attacked in which 14 were lost, again with no hits. Thus far, Fletcher's attacks had been disorganized and seemingly ineffectual, but they succeeded in drawing Nagumo's defensive fighters down to sea level where they expended much of their fuel and ammunition repulsing the two waves of torpedo bombers. As a result, when U.S. dive bombers arrived at high altitude, the Zeros were poorly positioned to defend. To make matters worse, Nagumo's four carriers had drifted out of formation in their efforts to avoid torpedoes, reducing the concentration of their anti-aircraft fire. Nagumo's indecision had also created confusion aboard his carriers. Alerted to the need of a second strike on Midway, but also wary of the need to deal with the American carriers that he now knew were in the vicinity, Nagumo twice changed the arming orders for his aircraft. As a result, the American dive bombers found the Japanese carriers with their decks cluttered with munitions as the crews worked hastily to properly re-arm their air groups.[21]

With the Japanese CAP out of position and the carriers at their most vulnerable, SBD Dauntlesses from Enterprise and Yorktown appeared at an altitude of 10,000 feet (3,000 m) and commenced their attack, quickly dealing fatal blows to three fleet carriers: Sōryū, Kaga, and Akagi. Within minutes, all three were ablaze and had to be abandoned with great loss of life. Hiryū managed to survive the wave of dive bombers and launched a counter-attack against the American carriers which caused severe damage to Yorktown (which was later finished off by a Japanese submarine). However, a second attack from the U.S. carriers a few hours later found and destroyed Hiryū, the last remaining fleet carrier available to Nagumo. With his carriers lost and the Americans withdrawn out of range of his powerful battleships, Yamamoto was forced to call off the operation, leaving Midway in enemy hands. The battle proved to be a decisive victory for the Allies. For the second time, Japanese expansion had been checked and its formidable Combined Fleet was significantly weakened by the loss of four fleet carriers and many highly trained, virtually irreplaceable, personnel. Japan would be largely on the defensive for the rest of the war.
New Guinea and the Solomons
Japanese land forces continued to advance in the Solomon Islands and New Guinea. From July 1942, a few Australian reserve battalions, many of them very young and untrained, fought a stubborn rearguard action in New Guinea, against a Japanese advance along the Kokoda Track, towards Port Moresby, over the rugged Owen Stanley Ranges. The militia, worn out and severely depleted by casualties, were relieved in late August by regular troops from the Second Australian Imperial Force, returning from action in the Mediterranean theater.

In early September 1942 Japanese marines attacked a strategic Royal Australian Air Force base at Milne Bay, near the eastern tip of New Guinea. They were beaten back by the Australian Army, which inflicted the first outright defeat on Japanese land forces since 1939.
Guadalcanal
At the same time as major battles raged in New Guinea, Allied forces identified a Japanese airfield under construction at Guadalcanal. Sixteen thousand Allied infantry—primarily U.S. Marines—made an amphibious landing to capture the airfield in August.
Japanese and Allied forces occupied various parts of the island. Over the following six months, both sides fed resources into an escalating battle of attrition on the island, at sea, and in the sky. Most of the Japanese aircraft in the South Pacific were drafted into the Japanese defense of Guadalcanal, facing Allied air forces based at Henderson Field. Japanese ground forces launched attacks on US positions around Henderson Field, suffering high casualties. These offensives were resupplied by Japanese convoys known to the Allies as the "Tokyo Express", which often faced night battles with the Allied navies, and expended destroyers IJN could ill-afford to lose. Later fleet battles involving heavier ships and even daytime carrier battles resulted in a stretch of water near Guadalcanal becoming known as "Ironbottom Sound", from the severe losses to both sides. However, only the U.S. Navy could quickly replace and repair its losses. The Allies were victorious on Guadalcanal in February 1943. The Japanese lost the war of attrition as a result of failing to commit enough forces in sufficient time.[50]
Allied advances in New Guinea and the Solomons

By late 1942, Japanese headquarters decided to make Guadalcanal their priority. They ordered the Japanese on the Kokoda Track, within sight of the lights of Port Moresby, to retreat to the northeastern coast of New Guinea. Australian and U.S. attacked their fortified positions and after more than two months of fighting in the Buna-Gona area finally captured the key Japanese beachhead in early 1943.
In June 1943, the Allies launched Operation Cartwheel, which defined their offensive strategy in the South Pacific. The operation was aimed at isolating the major Japanese forward base at Rabaul and cutting its supply and communication lines. This prepared the way for Nimitz's island-hopping campaign towards Japan.
Stalemate in China and South-East Asia

In the aftermath of the Japanese conquest of Burma, there was widespread disorder in eastern India, and a disastrous famine in Bengal, which ultimately caused up to 3 million deaths. In spite of these, and inadequate lines of communication, British and Indian forces attempted limited counter-attacks in Burma in early 1943. An offensive in Arakan failed, while a long distance raid mounted by the Chindits under Brigadier Orde Wingate suffered heavy losses, but was publicized to bolster Allied morale. It also provoked the Japanese to mount major offensives themselves the following year.
In August 1943 the Allies formed a new South East Asia Command (SEAC) to take over strategic responsibilities for Burma and India from the British India Command, under Wavell. In October 1943 Winston Churchill appointed Admiral Lord Louis Mountbatten as its Supreme Commander. The British and Indian Fourteenth Army was formed to face the Japanese in Burma. Under Lieutenant General William Slim, its training, morale and health greatly improved. The American General Joseph Stilwell, who also was deputy commander to Mountbatten and commanded U.S. forces in the China Burma India Theater, directed aid to China and prepared to construct the Ledo Road to link India and China by land.
On 22 November 1943 U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill, and ROC Generalissimo Chiang Kai-shek, met in Cairo, Egypt, to discuss a strategy to defeat Japan. The meeting was also known as Cairo Conference and concluded with the Cairo Declaration.
Allied offensives, 1943–44

Midway proved to be the last great naval battle for two years. The United States used the ensuing period to turn its vast industrial potential into actual ships, planes, and trained aircrew.[51] At the same time, Japan, lacking an adequate industrial base or technological strategy, a good aircrew training program, or adequate naval resources and commerce defense, fell further and further behind. In strategic terms the Allies began a long movement across the Pacific, seizing one island base after another. Not every Japanese stronghold had to be captured; some, like Truk, Rabaul, and Formosa, were neutralized by air attack and bypassed. The goal was to get close to Japan itself, then launch massive strategic air attacks, improve the submarine blockade, and finally (only if necessary) execute an invasion.
In November 1943 U.S. Marines sustained high casualties when they overwhelmed the 4,500-strong garrison at Tarawa. This helped the Allies to improve the techniques of amphibious landings, learning from their mistakes and implementing changes such as thorough pre-emptive bombings and bombardment, more careful planning regarding tides and landing craft schedules, and better overall coordination.
The U.S. Navy did not seek out the Japanese fleet for a decisive battle, as Mahanian doctrine would suggest (and as Japan hoped); the Allied advance could only be stopped by a Japanese naval attack, which oil shortages (induced by submarine attack) made impossible.[25][40]
Submarine warfare
U.S. submarines, as well as some British and Dutch vessels, operating from bases at Cavite in the Philippines (1941–42); Fremantle and Brisbane, Australia; Pearl Harbor; Trincomalee, Ceylon; Midway; and later Guam, played a major role in defeating Japan, even though submarines made up a small proportion of the Allied navies—less than two percent in the case of the US Navy.[40][52] Submarines strangled Japan by sinking its merchant fleet, intercepting many troop transports, and cutting off nearly all the oil imports essential to weapons production and military operations. By early 1945 Japanese oil supplies were so limited that its fleet was virtually stranded.
The Japanese military claimed its defenses sank 468 Allied subs.[53] Only 42 U.S. submarines were sunk in the Pacific, with 10 others going down in accidents or as the result of friendly fire.[54]

U.S. submarines accounted for 56% of the Japanese merchantmen sunk; mines or aircraft destroyed most of the rest.[54] US submariners also claimed 28% of Japanese warships destroyed.[55] Furthermore, they played important reconnaissance roles, as at the battles of the Philippine Sea (June 1944) and Leyte Gulf (October 1944) (and, coincidentally, at Midway in June 1942), when they gave accurate and timely warning of the approach of the Japanese fleet. Submarines also rescued hundreds of downed fliers, including future U.S. president George H.W. Bush.
Allied submarines did not adopt a defensive posture and wait for the enemy to attack. Within hours of Pearl Harbor, Roosevelt promulgated a new doctrine: unrestricted submarine warfare against Japan. This meant sinking any warship, commercial vessel, or passenger ship in Axis-controlled waters, without warning and without help to survivors.[nb 8]
Allied surface fleets and aircraft gave good protection to Allied submarine bases.
While Japan had a large number of submarines, they did not make a significant impact on the war. In 1942, the Japanese fleet subs performed well, knocking out or damaging many Allied warships. However, Imperial Japanese Navy (and pre-war U.S.) doctrine stipulated that only fleet battles, not guerre de course (commerce raiding) could win naval campaigns. So, while the US had an unusually long supply-line between its west coast and frontline areas, leaving it vulnerable to submarine attack, Japan used its submarines primarily for long-range reconnaissance and only occasionally attacked U.S. supply-lines. The Japanese submarine offensive against Australia in 1942 and 1943 also achieved little.[56]
As the war turned against Japan, IJN submarines increasingly served to resupply strongholds which had been cut off, such as Truk and Rabaul. In addition, Japan honored its neutrality treaty with the Soviet Union and ignored U.S. freighters shipping millions of tons of war-supplies from San Francisco to Vladivostok,[57] much to the consternation of its German ally.

The U.S. Navy, by contrast, relied on commerce raiding from the outset. However, the problem of Allied forces surrounded in the Philippines, during the early part of 1942, led to diversion of boats to "guerrilla submarine" missions. As well, basing in Australia placed boats under Japanese aerial threat while en route to patrol areas, inhibiting effectiveness, and Nimitz relied on submarines for close surveillance of enemy bases. Furthermore, the standard-issue Mark 14 torpedo and its Mark VI exploder both proved defective, problems not corrected until September 1943. Worst of all, before the war, an uninformed US Customs officer had seized a copy of the Japanese merchant marine code (called the "maru code" in the USN), not knowing that the Office of Naval Intelligence (ONI) had broken it.[58] The Japanese promptly changed it, and the new code was not broken again by OP-20G until 1943.
Thus only in 1944 did the U.S. Navy begin to use its 150 submarines to maximum effect: installing effective shipboard radar, replacing commanders lacking in aggression, and fixing faults in torpedoes. Japanese commerce protection was "shiftless beyond description,"[nb 9] and convoys were poorly organised and defended compared to Allied ones, a product of flawed IJN doctrine and training – errors concealed by American faults as much as Japanese overconfidence. The number of U.S. submarines patrols (and sinkings) rose steeply: 350 patrols (180 ships sunk) in 1942, 350 (335) in 1943, and 520 (603) in 1944.[59] By 1945, sinkings of Japanese vessels had decreased because so few targets dared to move on the high seas. In all, Allied submarines destroyed 1,200 merchant ships – about five million tons of shipping. Most were small cargo-carriers, but 124 were tankers bringing desperately needed oil from the East Indies. Another 320 were passenger ships and troop transports. At critical stages of the Guadalcanal, Saipan, and Leyte campaigns, thousands of Japanese troops were killed or diverted before they arrived where they were needed. Over 200 warships were sunk, ranging from many auxiliaries and destroyers to one battleship and no fewer than eight carriers.
Underwater warfare was especially dangerous; of the 16,000 Americans who went out on patrol, 3,500 (22%) never returned, the highest casualty rate of any American force in World War II.[60] The Joint Army–Navy Assessment Committee assessed U.S. Submarine credits.[61][62] The Japanese losses, 130 submarines in all,[63] were even higher.[64]
Japanese counteroffensives in China, 1944
In mid-1944, Japan launched a massive invasion across China, under the code name Operation Ichi-Go. These attacks, the biggest in several years, gained much ground for Japan before they were stopped in Guangxi.
Japanese offensive in India 1944
Chinese forces on M3 Stuart tanks on the Ledo Road
After the Allied setbacks in 1943, the South East Asia command was preparing to launch offensives into Burma on several fronts. In the first months of 1944, the Chinese and American troops of the Northern Combat Area Command, commanded by the American Joseph Stilwell, began extending the Ledo Road from India into northern Burma, while the XV Corps began an advance along the coast in the Arakan Province. In February, the Japanese mounted a local counter-attack in the Arakan. After early success, this counter-attack was defeated when the Indian divisions of XV Corps stood firm, and relied on aircraft to drop supplies to isolated forward units until they could be relieved by reserve divisions.
The Japanese response to the Allied attacks was to launch an offensive of their own into India, across the mountainous and densely forested frontier. This attack, codenamed Operation U-Go, was advocated by Lieutenant General Renya Mutaguchi, the recently promoted commander of the Japanese Fifteenth Army, and was permitted to proceed by Imperial General Headquarters, despite misgivings at several intervening headquarters. The offensive was launched in mid-March. Although several units of the British Fourteenth Army were forced to fight their way out of encirclement, by early April they had concentrated around Imphal in Manipur state. A Japanese division which had advanced to Kohima in Nagaland cut the main road to Imphal, but failed to capture the whole of the defences at Kohima. During April, the Japanese attacks against Imphal failed, while fresh Allied formations drove the Japanese from the positions they had captured at Kohima.
As many Japanese had feared, their supply arrangements were inadequate to maintain their forces. Once Mutaguchi's hopes for an early victory were thwarted, his troops, particularly those at Kohima, starved. During May, while Mutaguchi continued to order attacks, the Allies were advancing southwards from Kohima and northwards from Imphal. The two Allied attacks met on 22 June, breaking the Japanese siege of Imphal. The Japanese finally broke off the operation on 3 July. They had lost over 50,000 troops, mainly to starvation and disease. It was the worst defeat suffered by the Japanese Army to that date.
Although the advance in the Arakan had been halted to release troops and aircraft for the Battle of Imphal, the Americans and Chinese had continued to advance in northern Burma, aided by the Chindits operating against the Japanese lines of communication. By the time campaigning ceased during the monsoon rains, the Americans had secured a vital airfield at Myitkyina, which eased the problems of the air resupply to China over The Hump.
Beginning of the end in the Pacific, 1944
Saipan and Philippine Sea

On 15 June 1944, 535 ships began landing 128,000 U.S. Army and Marine personnel on the island of Saipan. The Allied objective was the creation of airfields within B-29 range of Tokyo. The ability to plan and execute such a complex operation in the space of 90 days was indicative of Allied logistical superiority.
It was imperative for Japanese commanders to hold Saipan. The only way to do this was to destroy the U.S. Fifth Fleet, which had 15 fleet carriers and 956 planes, 7 battleships, 28 submarines, and 69 destroyers, as well as several light and heavy cruisers. Vice Admiral Jisaburo Ozawa attacked with nine-tenths of Japan's fighting fleet, which included nine carriers with 473 planes, 5 battleships, several cruisers, and 28 destroyers. Ozawa's pilots were outnumbered 2:1 and their aircraft were becoming or were already obsolete. The Japanese had considerable antiaircraft defenses but lacked proximity fuzes or good radar. With the odds against him, Ozawa devised an appropriate strategy. His planes had greater range because they were not weighed down with protective armor; they could attack at about 480 km (300 mi)[citation needed], and could search a radius of 900 km[citation needed] (560 mi). U.S. Navy Hellcat fighters could only attack within 200 miles (320 km) and only search within a 325-mile (523 km)[citation needed] radius. Ozawa planned to use this advantage by positioning his fleet 300 miles (480 km)[citation needed] out. The Japanese planes would hit the U.S. carriers, land at Guam to refuel, then hit the enemy again when returning to their carriers. Ozawa also counted on about 500 land-based planes at Guam and other islands.
Admiral Raymond A. Spruance was in overall command of Fifth Fleet. The Japanese plan would have failed if the much larger U.S. fleet had closed on Ozawa and attacked aggressively; Ozawa correctly inferred Spruance would not attack. U.S. Admiral Marc Mitscher, in tactical command of Task Force 58, with its 15 carriers, was aggressive but Spruance vetoed Mitscher's plan to hunt down Ozawa because Spruance's orders made protecting the landings on Saipan his first priority.

The forces converged in the largest sea battle of World War II up to that point. Over the previous month American destroyers had destroyed 17 of 25 submarines out of Ozawa's screening force.[65][66] Repeated U.S. raids destroyed the Japanese land-based planes. Ozawa's main attack lacked coordination, with the Japanese planes arriving at their targets in a staggered sequence. Following a directive from Nimitz, the U.S. carriers all had combat information centers, which interpreted the flow of radar data and radioed interception orders to the Hellcats. The result was later dubbed the Great Marianas Turkey Shoot. The few attackers to reach the U.S. fleet encountered massive AA fire with proximity fuzes. Only one American warship was slightly damaged.
On the second day, U.S. reconnaissance planes located Ozawa's fleet, 275 miles (443 km)[citation needed] away, and submarines sank two Japanese carriers. Mitscher launched 230 torpedo planes and dive bombers. He then discovered the enemy was actually another 60 miles (97 km)[citation needed] further off, out of aircraft range (based on a roundtrip flight). Mitscher decided this chance to destroy the Japanese fleet was worth the risk of aircraft losses due to running out of fuel on the return flight. Overall, the U.S. lost 130 planes and 76 aircrew; however, Japan lost 450 planes, three carriers, and 445 aircrew. The Imperial Japanese Navy's carrier force was effectively destroyed.[67]
Leyte Gulf 1944
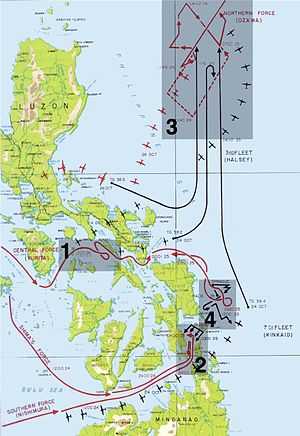
Sho-1 called for V. Adm. Jisaburo Ozawa's force to use an apparently vulnerable carrier force to lure the U.S. 3rd Fleet away from Leyte and remove air cover from the Allied landing forces, which would then be attacked from the west by three Japanese forces: V. Adm. Takeo Kurita's force would enter Leyte Gulf and attack the landing forces; R. Adm. Shoji Nishimura's force and V. Adm. Kiyohide Shima's force would act as mobile strike forces. The plan was likely to result in the destruction of one or more of the Japanese forces, but Toyoda justified it by saying that there would be no sense in saving the fleet and losing the Philippines.
Kurita's "Center Force" consisted of five battleships, 12 cruisers and 13 destroyers. It included the two largest battleships ever built: Yamato and Musashi. As they passed Palawan Island after midnight on 23 October the force was spotted, and U.S. submarines sank two cruisers. On 24 October, as Kurita's force entered the Sibuyan Sea, USS Intrepid and USS Cabot launched 260 planes, which scored hits on several ships. A second wave of planes scored many direct hits on Musashi. A third wave, from USS Enterprise and USS Franklin hit Musashi with 11 bombs and eight torpedoes. Kurita retreated but in the evening turned around to head for San Bernardino Strait. Musashi sank at about 19:30.
Meanwhile, V. Adm. Onishi Takijiro had directed his First Air Fleet, 80 land-based planes, against U.S. carriers, whose planes were attacking airfields on Luzon. The carrier USS Princeton was hit by an armor-piercing bomb and suffered a major explosion which killed 108 crew (out of 1,569) and 233 on the cruiser USS Birmingham (CL-62) which was fire-fighting alongside. Princeton sank, and the Birmingham was forced to retire.
Nishimura's force consisted of two battleships, one cruiser and four destroyers. Because they were observing radio silence, Nishimura was unable to synchronize with Shima and Kurita. Nishimura and Shima had failed to even coordinate their plans before the attacks – they were long-time rivals and neither wished to have anything to do with the other. When he entered the narrow Surigao Strait at about 02:00, Shima was 22 miles (40 km) behind him, and Kurita was still in the Sibuyan Sea, several hours from the beaches at Leyte. As they passed Panaon Island, Nishimura's force ran into a trap set for them by the U.S.-Australian 7th Fleet Support Force. R. Adm. Jesse Oldendorf had six battleships, four heavy cruisers, four light cruisers, 29 destroyers and 39 PT boats. To pass the strait and reach the landings, Nishimura had to run the gauntlet. At about 03:00 the Japanese battleship Fusō and three destroyers were hit by torpedoes and Fusō broke in two. At 03:50 the U.S. battleships opened fire. Radar fire control meant they could hit targets from a much greater distance than the Japanese. The battleship Yamashiro, a cruiser and a destroyer were crippled by 16-inch (406 mm) shells; Yamashiro sank at 04:19. Only one of Nishimura's force of seven ships survived the engagement. At 04:25 Shima's force of two cruisers and eight destroyers reached the battle. Seeing Fusō and believing her to be the wrecks of two battleships, Shima ordered a retreat, ending the last battleship-vs-battleship action in history.
Ozawa's "Northern Force" had four aircraft carriers, two obsolete battleships partly converted to carriers, three cruisers and nine destroyers. The carriers had only 108 planes. The force was not spotted by the Allies until 16:40 on 24 October. At 20:00 Soemu ordered all remaining Japanese forces to attack. Halsey saw an opportunity to destroy the remnants of the Japanese carrier force. The U.S. Third Fleet was formidable – nine large carriers, eight light carriers, six battleships, 17 cruisers, 63 destroyers and 1,000 planes – and completely outgunned Ozawa's force. Halsey's ships set out in pursuit of Ozawa just after midnight. U.S. commanders ignored reports that Kurita had turned back towards San Bernardino Strait. They had taken the bait set by Ozawa. On the morning of 25 October Ozawa launched 75 planes. Most were shot down by U.S. fighter patrols. By 08:00 U.S. fighters had destroyed the screen of Japanese fighters and were hitting ships. By evening, they had sunk the carriers Zuikaku, Zuiho, and Chiyoda, and a destroyer. The fourth carrier, Chitose, and a cruiser were disabled and later sank.

Kurita passed through San Bernardino Strait at 03:00 on 25 October and headed along the coast of Samar. The only thing standing in his path were three groups (Taffy 1, 2 and 3) of the Seventh Fleet, commanded by Admiral Thomas Kinkaid. Each group had six escort carriers, with a total of more than 500 planes, and seven or eight destroyers or destroyer escorts (DE). Kinkaid still believed that Lee's force was guarding the north, so the Japanese had the element of surprise when they attacked Taffy 3 at 06:45. Kurita mistook the Taffy carriers for large fleet carriers and thought he had the whole Third Fleet in his sights. Since escort carriers stood little chance against a battleship, Adm. Clifton Sprague directed the carriers of Taffy 3 to turn and flee eastward, hoping that bad visibility would reduce the accuracy of Japanese gunfire, and used his destroyers to divert the Japanese battleships. The destroyers made harassing torpedo attacks against the Japanese. For ten minutes Yamato was caught up in evasive action. Two U.S. destroyers and a DE were sunk, but they had bought enough time for the Taffy groups to launch planes. Taffy 3 turned and fled south, with shells scoring hits on some of its carriers and sinking one of them. The superior speed of the Japanese force allowed it to draw closer and fire on the other two Taffy groups. However, at 09:20 Kurita suddenly turned and retreated north. Signals had disabused him of the notion that he was attacking the Third Fleet, and the longer Kurita continued to engage, the greater the risk of major air strikes. Destroyer attacks had broken the Japanese formations, shattering tactical control. Three of Kurita's heavy cruisers had been sunk and another was too damaged to continue the fight. The Japanese retreated through the San Bernardino Strait, under continuous air attack. The Battle of Leyte Gulf was over.[68]
The battle secured the beachheads of the U.S. Sixth Army on Leyte against attack from the sea, broke the back of Japanese naval power and opened the way for an advance to the Ryukyu Islands in 1945. The only significant Japanese naval operation afterwards was the disastrous Operation Ten-Go, in April 1945. Kurita's force had begun the battle with five battleships; when he returned to Japan, only Yamato was combat-worthy. Nishimura's sunken Yamashiro was the last battleship in history to engage another in combat.
Philippines, 1944–45

On 20 October 1944 the U.S. Sixth Army, supported by naval and air bombardment, landed on the favorable eastern shore of Leyte, north of Mindanao. The U.S. Sixth Army continued its advance from the east, as the Japanese rushed reinforcements to the Ormoc Bay area on the western side of the island. While the Sixth Army was reinforced successfully, the U.S. Fifth Air Force was able to devastate the Japanese attempts to resupply. In torrential rains and over difficult terrain, the advance continued across Leyte and the neighboring island of Samar to the north. On 7 December U.S. Army units landed at Ormoc Bay and, after a major land and air battle, cut off the Japanese ability to reinforce and supply Leyte. Although fierce fighting continued on Leyte for months, the U.S. Army was in control.
On 15 December 1944 landings against minimal resistance were made on the southern beaches of the island of Mindoro, a key location in the planned Lingayen Gulf operations, in support of major landings scheduled on Luzon. On 9 January 1945, on the south shore of Lingayen Gulf on the western coast of Luzon, General Krueger's Sixth Army landed his first units. Almost 175,000 men followed across the twenty-mile (32 km) beachhead within a few days. With heavy air support, Army units pushed inland, taking Clark Field, 40 miles (64 km) northwest of Manila, in the last week of January.

Two more major landings followed, one to cut off the Bataan Peninsula, and another, that included a parachute drop, south of Manila. Pincers closed on the city and, on 3 February 1945, elements of the 1st Cavalry Division pushed into the northern outskirts of Manila and the 8th Cavalry passed through the northern suburbs and into the city itself.
As the advance on Manila continued from the north and the south, the Bataan Peninsula was rapidly secured. On 16 February paratroopers and amphibious units assaulted the island fortress of Corregidor, and resistance ended there on 27 February.
In all, ten U.S. divisions and five independent regiments battled on Luzon, making it the largest campaign of the Pacific war, involving more troops than the United States had used in North Africa, Italy, or southern France. Of the 250,000 Japanese troops defending Luzon, 80 percent died.[69] The last Japanese soldier in the Philippines to surrender was Hiroo Onoda on 9 March 1974.[70]
Palawan Island, between Borneo and Mindoro, the fifth largest and western-most Philippine Island, was invaded on 28 February with landings of the Eighth Army at Puerto Princesa. The Japanese put up little direct defense of Palawan, but cleaning up pockets of Japanese resistance lasted until late April, as the Japanese used their common tactic of withdrawing into the mountain jungles, dispersed as small units. Throughout the Philippines, U.S. forces were aided by Filipino guerrillas to find and dispatch the holdouts.
The U.S. Eighth Army then moved on to its first landing on Mindanao (17 April), the last of the major Philippine Islands to be taken. Mindanao was followed by invasion and occupation of Panay, Cebu, Negros and several islands in the Sulu Archipelago. These islands provided bases for the U.S. Fifth and Thirteenth Air Forces to attack targets throughout the Philippines and the South China Sea.
Final stages

Iwo Jima, February 1945
The battle of Iwo Jima ("Operation Detachment") in February 1945 was one of bloodiest battles fought by the Americans in the Pacific War. Iwo Jima was a 8 sq mile (21 km2) island situated halfway between Tokyo and the Mariana Islands. Holland Smith, the commander of the invasion force, aimed to capture the island, and utilize its three airfields as bases to carry out air attacks against the Home Islands. Lt. General Tadamichi Kuribayashi, the commander of the island's defense, knew that he could not win the battle, but he hoped to make the Americans suffer far more than they could endure.
From early 1944 until the days leading up to the invasion, Kuribayashi transformed the island into a massive network of bunkers, hidden guns, and 11 mi (18 km) of underground tunnels. The heavy American naval and air bombardment did little but drive the Japanese further underground, making their positions impervious to enemy fire. Their pillboxes and bunkers were all connected so that if one was knocked out, it could be reoccupied again. The network of bunkers and pillboxes greatly favored the defender.
Starting in mid-June 1944, Iwo Jima came under sustained aerial bombardment and naval artillery fire. However, Kuribayashi's hidden guns and defenses survived the constant bombardment virtually unscathed. On 19 February 1945, some 30,000 men of the 3rd, 4th, and 5th Marine Divisions landed on the southeast coast of Iwo, just under Mount Suribachi; where most of the island's defenses were concentrated. For some time, they did not come under fire. This was part of Kuribayashi's plan to hold fire until the landing beaches were full. As soon as the Marines pushed inland to a line of enemy bunkers, they came under devastating machine gun and artillery fire which cut down many of the men. By the end of the day, the Marines reached the west coast of the island, but their losses were appalling; almost 2,000 men killed or wounded.
On 23 February, the 28th Marine Regiment reached the summit of Suribachi, prompting the now famous Raising the Flag on Iwo Jima picture. Navy Secretary James Forrestal, upon seeing the flag, remarked "there will be a Marine Corps for the next 500 years." The flag raising is often cited as the most reproduced photograph of all time and became the archetypal representation not only of that battle, but of the entire Pacific War. For the rest of February, the Americans pushed north, and by 1 March, had taken two-thirds of the island. But it was not until 26 March that the island was finally secured. The Japanese fought to the last man, killing 6,800 Marines and wounding nearly 20,000 more. The Japanese losses totaled well over 20,000 men killed, and only 1,083 prisoners were taken. Historians debate whether it were strategically worth all those casualties.[71]
Allied offensives in Burma, 1944–45

In late 1944 and early 1945, the Allied South East Asia Command launched offensives into Burma, intending to recover most of the country, including Rangoon, the capital, before the onset of the monsoon in May.
The Indian XV Corps advanced along the coast in Arakan province, at last capturing Akyab Island after failures in the two previous years. They then landed troops behind the retreating Japanese, inflicting heavy casualties, and captured Ramree Island and Cheduba Island off the coast, establishing airfields on them which were used to support the offensive into Central Burma.
The Northern Combat Area Command resumed its advance in northern Burma, and in late January 1945, they linked up with Chinese armies attacking westwards from Yunnan province. The Ledo Road was completed, linking India and China, but too late in the war to have any significant effect.
The Japanese Burma Area Army attempted to forestall the main Allied attack on the central part of the front by withdrawing their troops behind the Irrawaddy River. Lieutenant General Heitarō Kimura, the new Japanese commander in Burma, hoped that the Allies' lines of communications would be overstretched trying to cross this obstacle. However, the advancing British Fourteenth Army under Lieutenant General William Slim switched its axis of advance to outflank the main Japanese armies.

During February, Fourteenth Army secured bridgeheads across the Irrawaddy on a broad front. On 1 March, units of IV Corps captured the supply centre of Meiktila, throwing the Japanese into disarray. While the Japanese attempted to recapture Meiktila, XXXIII Corps captured Mandalay. The Japanese armies were heavily defeated, and with the capture of Mandalay, the Burmese population and the Burma National Army (which the Japanese had raised) turned against the Japanese.
During April, Fourteenth Army advanced 300 miles (480 km) south towards Rangoon, the capital and principal port of Burma, but was delayed by Japanese rearguards 40 miles (64 km) north of Rangoon at the end of the month. Slim feared that the Japanese would defend Rangoon house-to-house during the monsoon, placing his army in a disastrous supply situation, and in March he had asked that a plan to capture Rangoon by an amphibious force, Operation Dracula, which had been abandoned earlier, be reinstated.[72] Dracula was launched on 1 May, but Rangoon was found to have been abandoned. The troops which occupied Rangoon linked up with Fourteenth Army five days later, securing the Allies' lines of communication.
The Japanese forces which had been bypassed by the Allied advances attempted to break out across the Sittang River during June and July to rejoin the Burma Area Army which had regrouped in Tenasserim in southern Burma. They suffered 10,000 casualties, half their strength. Overall, the Japanese lost some 150,000 men in Burma. Only 1,700 prisoners were taken.[73]
The Allies were preparing to make amphibious landings in Malaya when word of the Japanese surrender arrived.
Liberation of Borneo
.jpg)
The Borneo Campaign of 1945 was the last major campaign in the South West Pacific Area. In a series of amphibious assaults between 1 May and 21 July, the Australian I Corps, under General Leslie Morshead, attacked Japanese forces occupying the island. Allied naval and air forces, centered on the U.S. 7th Fleet under Admiral Thomas Kinkaid, the Australian First Tactical Air Force and the U.S. Thirteenth Air Force also played important roles in the campaign.
The campaign opened with a landing on the small island of Tarakan on 1 May. This was followed on 1 June by simultaneous assaults in the north west, on the island of Labuan and the coast of Brunei. A week later the Australians attacked Japanese positions in North Borneo. The attention of the Allies then switched back to the central east coast, with the last major amphibious assault of World War II, at Balikpapan on 1 July.
Although the campaign was criticized in Australia at the time, and in subsequent years, as pointless or a "waste" of the lives of soldiers, it did achieve a number of objectives, such as increasing the isolation of significant Japanese forces occupying the main part of the Dutch East Indies, capturing major oil supplies and freeing Allied prisoners of war, who were being held in deteriorating conditions.[74] At one of the very worst sites, around Sandakan in Borneo, only six of some 2,500 British and Australian prisoners survived.[73]
Okinawa

The largest and bloodiest American battle came at Okinawa, as the U.S. sought airbases for 3000 B-29 bombers and 240 squadrons of B-17 bombers for the intense bombardment of Japan's home islands in preparation for a full-scale invasion in late 1945. The Japanese, with 115,000 troops augmented by thousands of civilians on the heavily populated island, did not resist on the beaches—their strategy was to maximize the number of soldier and Marine casualties, and naval losses from Kamikaze attacks. After an intense bombardment the Americans landed on 1 April 1945 and declared victory on 21 June.[75] The supporting naval forces were the targets for 4,000 sorties, many by Kamikaze suicide planes. U.S. losses totaled 38 ships of all types sunk and 368 damaged with 4,900 sailors killed. The Americans suffered 75,000 casualties on the ground; 94% of the Japanese soldiers died along with many civilians.[76]
Landings in the Japanese home islands
Hard-fought battles on the Japanese home islands of Iwo Jima, Okinawa, and others resulted in horrific casualties on both sides but finally produced a Japanese defeat. Of the 117,000 Japanese troops defending Okinawa, 94 percent died.[69] Faced with the loss of most of their experienced pilots, the Japanese increased their use of kamikaze tactics in an attempt to create unacceptably high casualties for the Allies. The U.S. Navy proposed to force a Japanese surrender through a total naval blockade and air raids.[77]
Towards the end of the war as the role of strategic bombing became more important, a new command for the U.S. Strategic Air Forces in the Pacific was created to oversee all U.S. strategic bombing in the hemisphere, under United States Army Air Forces General Curtis LeMay. Japanese industrial production plunged as nearly half of the built-up areas of 67 cities were destroyed by B-29 firebombing raids. On 9–10 March 1945 alone, about 100,000 people were killed in a firestorm caused by an attack on Tokyo. In addition, LeMay also oversaw Operation Starvation, in which the inland waterways of Japan were extensively mined by air, which disrupted the small amount of remaining Japanese coastal sea traffic.
Soviet invasion and the Atomic bomb

On 3 February 1945 the Soviet Union agreed with Roosevelt to enter the Pacific conflict. It promised to act 90 days after the war ended in Europe and did so exactly on schedule on 9 August by invading Manchuria. A battle-hardened, one million-strong Soviet force, transferred from Europe,[citation needed] attacked Japanese forces in Manchuria and quickly defeated the Japanese Kantōgun (Kwantung Army group).[78]
On 6 August 1945, the U.S. B-29 Enola Gay dropped an atomic bomb on the Japanese city of Hiroshima, in the first nuclear attack in history. On 9 August another was dropped on Nagasaki. This was the last nuclear attack. More than 240,000 people died as a direct result of these two bombings.[79] The necessity of the atomic bombings has long been debated, with detractors claiming that a naval blockade and bombing campaign had already made invasion, hence the atomic bomb, unnecessary.[80] However, other scholars have argued that the bombings did obviate invasion, including a planned Soviet invasion of Hokkaidō, or a prolonged blockade and bombing campaign, any of which would have exacted much higher casualties among Japanese civilians.[79] Historian Richard B. Frank wrote that a Soviet invasion was never likely because they had insufficient naval capability to mount an amphibious invasion of Hokkaidō.[81]
Surrender

The effects of the "Twin Shocks"—the Soviet entry and the atomic bombing—were profound. On 10 August the "sacred decision" was made by Japanese Cabinet to accept the Potsdam terms on one condition: the "prerogative of His Majesty as a Sovereign Ruler". At noon on 15 August, after the American government's intentionally ambiguous reply, stating that the "authority" of the emperor "shall be subject to" the Supreme Commander of the Allied Powers", the Emperor broadcast to the nation and to the world at large the rescript of surrender,[82] ending the Second World War.
"Should We continue to fight, it would not only result in an ultimate collapse and obliteration of the Japanese nation, but also it would lead to the total extinction of human civilization." -Emperor Hirohito.[83]
In Japan, 14 August is considered to be the day that the Pacific War ended. However, as Imperial Japan actually surrendered on 15 August, this day became known in the English-speaking countries as "V-J Day" (Victory in Japan).[84] The formal Japanese Instrument of Surrender was signed on 2 September 1945, on the battleship USS Missouri, in Tokyo Bay. The surrender was accepted by General Douglas MacArthur as Supreme Commander for the Allied Powers, with representatives of several Allied nations, from a Japanese delegation led by Mamoru Shigemitsu and Yoshijiro Umezu.
Following this period, MacArthur went to Tokyo to oversee the postwar development of the country. This period in Japanese history is known as the occupation.
War crimes

Japanese soldiers killed millions of civilians and prisoners of war from surrounding nations.[85] At least 20 million Chinese died during the Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945).[86][87]
Unit 731 was one example of wartime atrocities committed on a civilian population during World War II, where experiments were performed on thousands of Chinese civilians and Allied prisoners of war. In military campaigns, the Japanese army used biological weapons on Chinese, killing around 400,000 Chinese civilians.[88] The Rape of Nanking is another example of atrocity committed by Japanese soldiers on a civilian population.[89]
According to the findings of the Tokyo tribunal, the death rate of Western prisoners was 27.1%, seven times that of POWs under the Germans and Italians.[73] The most notorious use of forced labour was in the construction of the Burma–Thailand Death Railway.
A widely publicised example of institutionalised sexual slavery are "comfort women", a euphemism for the 200,000 women, mostly from Korea and China, who served in the Japanese army's camps during World War II. Some 35 Dutch comfort women brought a successful case before the Batavia Military Tribunal in 1948.[90] To this day, Japan still denies these war crimes; then-Prime Minister Shinzō Abe claimed in 2007, "The fact is, there is no evidence to prove there was coercion."[91]
The Three Alls Policy (Sankō Sakusen) was a Japanese scorched earth policy adopted in China, the three alls being: "Kill All, Burn All and Loot All". Initiated in 1940 by Ryūkichi Tanaka, the Sankō Sakusen was implemented in full scale in 1942 in north China by Yasuji Okamura. According to historian Mitsuyoshi Himeta, the scorched earth campaign was responsible for the deaths of "more than 2.7 million" Chinese civilians.[92]
Pacific War campaigns
(Flags indicate the country, or countries, winning the offensive.)
Second Sino-Japanese war
Before 1942 and inclusion in the Pacific War:
-
.svg.png) 1937-07-07 – 1937-07-09 Marco Polo Bridge Incident
1937-07-07 – 1937-07-09 Marco Polo Bridge Incident -
.svg.png) 1937-08-13 – 1937-11-26 Battle of Shanghai
1937-08-13 – 1937-11-26 Battle of Shanghai -
.svg.png) 1937-09-01 – 1937-11-09 Battle of Taiyuan
1937-09-01 – 1937-11-09 Battle of Taiyuan -
.svg.png) 1937-12-09 – 1938-01-31 Battle of Nanjing
1937-12-09 – 1938-01-31 Battle of Nanjing -
.svg.png) 1938-03-24 – 1938-05-01 Battle of Xuzhou
1938-03-24 – 1938-05-01 Battle of Xuzhou -
.svg.png) 1938-06-11 – 1938-10-27 Battle of Wuhan
1938-06-11 – 1938-10-27 Battle of Wuhan -
.svg.png) 1939-03-17 – 1939-05-09 Battle of Nanchang
1939-03-17 – 1939-05-09 Battle of Nanchang -
 1939-04-20 – 1939-05-24 Battle of Suixian-Zaoyang
1939-04-20 – 1939-05-24 Battle of Suixian-Zaoyang -
 1939-09-13 – 1939-10-08 Battle of Changsha (1939)
1939-09-13 – 1939-10-08 Battle of Changsha (1939) -
 1939-11-15 – 1940-11-30 Battle of South Guangxi
1939-11-15 – 1940-11-30 Battle of South Guangxi -
 1940-05-01 – 1940-06-18 Battle of Zaoyang-Yichang
1940-05-01 – 1940-06-18 Battle of Zaoyang-Yichang -
 1940-08-20 – 1940-12-05 Hundred Regiments Offensive
1940-08-20 – 1940-12-05 Hundred Regiments Offensive -
 1941-01-30 – 1941-03-01 Battle of South Henan
1941-01-30 – 1941-03-01 Battle of South Henan -
 1941-03-14 – 1941-04-09 Battle of Shanggao
1941-03-14 – 1941-04-09 Battle of Shanggao -
.svg.png) 1941-05-07 – 1941-05-27 Battle of South Shanxi
1941-05-07 – 1941-05-27 Battle of South Shanxi -
 1941-09-06 – 1941-10-08 Battle of Changsha (1941)
1941-09-06 – 1941-10-08 Battle of Changsha (1941)
After inclusion in the Pacific War:
-
 1941-12-24 – 1942-01-15 Battle of Changsha (1942)
1941-12-24 – 1942-01-15 Battle of Changsha (1942) -
 1942-05-14 – 1942-09-07 Zhejiang-Jiangxi Campaign
1942-05-14 – 1942-09-07 Zhejiang-Jiangxi Campaign -
 1943-05-12 – 1943-06-03 Battle of West Hubei
1943-05-12 – 1943-06-03 Battle of West Hubei -
 1943-11-02 – 1943-12-20 Battle of Changde
1943-11-02 – 1943-12-20 Battle of Changde -
.svg.png) 1944-04-17 – 1944-12-10 Operation Ichi-Go
1944-04-17 – 1944-12-10 Operation Ichi-Go -

 1945-04-09 – 1945-06-07 Battle of West Hunan
1945-04-09 – 1945-06-07 Battle of West Hunan
![]() Franco-Japanese Border War
Franco-Japanese Border War
- 1940-09-22 – 1940-09-25 Battle of Lạng Sơn
- 1940-09-24 – 1940-09-26 Bombing of Hải Phòng
- October 1940 – 9 May 1941
![]() Soviet–Japanese border conflicts
Soviet–Japanese border conflicts
- 1938-07-29 – 1938-08-11 Battle of Lake Khasan
- 1939-05-11 – 1939-09-16 Battles of Khalkhin Gol
Japanese conquest of Southeast Asia and Pacific
-
.svg.png) 1941-12-07 (12-08 Asian Time) Attack on Pearl Harbor
1941-12-07 (12-08 Asian Time) Attack on Pearl Harbor -
.svg.png) 1941-12-08 Japanese invasion of Thailand
1941-12-08 Japanese invasion of Thailand -
.svg.png) 1941-12-08 Battle of Guam (1941)
1941-12-08 Battle of Guam (1941) - 1941-12-07 Japan declares war on the United States and the United Kingdom; 1941-12-08 The United States and the United Kingdom declare war on Japan
-
.svg.png) 1941-12-08 – 1941-12-25 Battle of Hong Kong
1941-12-08 – 1941-12-25 Battle of Hong Kong -
.svg.png) 1941-12-08 – 1942-01-31 Malayan Campaign
1941-12-08 – 1942-01-31 Malayan Campaign -
.svg.png) 1941-12-10 Sinking of HMS Prince of Wales and HMS Repulse
1941-12-10 Sinking of HMS Prince of Wales and HMS Repulse -
.svg.png) 1941-12-11 – 1941-12-24 Battle of Wake Island
1941-12-11 – 1941-12-24 Battle of Wake Island -
.svg.png) 1941-12-16 – 1942-04-01 Battle of Borneo (1941–42)
1941-12-16 – 1942-04-01 Battle of Borneo (1941–42) -
.svg.png) 1941-12-22 – 1942-05-06 Battle of the Philippines
1941-12-22 – 1942-05-06 Battle of the Philippines - 1942-01-01 – 1945-10-25 Transport of POWs via hell ships
-
.svg.png) 1942-01-11 – 1942-01-12 Battle of Tarakan[93]
1942-01-11 – 1942-01-12 Battle of Tarakan[93] -
.svg.png) 1942-01-23 Battle of Rabaul (1942)
1942-01-23 Battle of Rabaul (1942) -
.svg.png) 1942-01-24 Battle of Balikpapan (1942)[94]
1942-01-24 Battle of Balikpapan (1942)[94] - 1942-01-25 Thailand declares war on the Allies
-
.svg.png) 1942-01-30 – 1942-02-03 Battle of Ambon[95]
1942-01-30 – 1942-02-03 Battle of Ambon[95] -
.svg.png) 1942-01-30 – 1942-02-15 Battle of Singapore
1942-01-30 – 1942-02-15 Battle of Singapore -
.svg.png) 1942-02-04 Battle of Makassar Strait
1942-02-04 Battle of Makassar Strait -
.svg.png) 1942-02-14 – 1942-02-15 Battle of Palembang[96]
1942-02-14 – 1942-02-15 Battle of Palembang[96] -
.svg.png) 1942-02-19 Air raids on Darwin, Australia
1942-02-19 Air raids on Darwin, Australia -
.svg.png) 1942-02-19 – 1942-02-20 Battle of Badung Strait[97]
1942-02-19 – 1942-02-20 Battle of Badung Strait[97] -
.svg.png) 1942-02-19 – 1943-02-10 Battle of Timor (1942-43)[33][98]
1942-02-19 – 1943-02-10 Battle of Timor (1942-43)[33][98] -
.svg.png) 1942-02-27 – 1942-03-01 Battle of the Java Sea[35]
1942-02-27 – 1942-03-01 Battle of the Java Sea[35] -
.svg.png) 1942-03-01 Battle of Sunda Strait[99]
1942-03-01 Battle of Sunda Strait[99] -
.svg.png) 1942-03-01 – 1942-03-09 Battle of Java[36]
1942-03-01 – 1942-03-09 Battle of Java[36] -
.svg.png) 1942-03-31 Battle of Christmas Island[100]
1942-03-31 Battle of Christmas Island[100] -
.svg.png) 1942-03-31 – 1942-04-10 Indian Ocean raid
1942-03-31 – 1942-04-10 Indian Ocean raid - 1942-04-09 Bataan Death March begins
-
 1942-04-18 Doolittle Raid
1942-04-18 Doolittle Raid -
.svg.png) 1942-05-03 Japanese invasion of Tulagi
1942-05-03 Japanese invasion of Tulagi 
 1942-05-04 – 1942-05-08 Battle of the Coral Sea
1942-05-04 – 1942-05-08 Battle of the Coral Sea-
.svg.png) 1942-05-31 – 1942-06-08 Attacks on Sydney Harbour area, Australia
1942-05-31 – 1942-06-08 Attacks on Sydney Harbour area, Australia -
 1942-06-04 – 1942-06-06 Battle of Midway
1942-06-04 – 1942-06-06 Battle of Midway
Allied offensives
| See Atlas of the World Battle Fronts | ||
|---|---|---|
 1943-07-01 |
 1943-12-01 |
 1944-05-01 |
 1944-11-01 |
 1945-03-01 |
 1945-08-01 |
South East Asian campaigns: 1941-12-08 – 1945-08-15
-

 [101]
[101]  Burma Campaign: 1941-12-16 – 1945-08-15
Burma Campaign: 1941-12-16 – 1945-08-15 -
 1945-05-15 – 1945-05-16 Battle of the Malacca Strait
1945-05-15 – 1945-05-16 Battle of the Malacca Strait
-
.svg.png) 1942-01-23 – Battle of Rabaul
1942-01-23 – Battle of Rabaul - 1942-03-07 – Operation Mo (Japanese invasion of mainland New Guinea)
-

 1942-05-04 – 1942-05-08 Battle of the Coral Sea
1942-05-04 – 1942-05-08 Battle of the Coral Sea -
 1942-07-01 – 1943-01-31 Kokoda Track Campaign
1942-07-01 – 1943-01-31 Kokoda Track Campaign -

 1942-08-25 – 1942-09-05 Battle of Milne Bay
1942-08-25 – 1942-09-05 Battle of Milne Bay -

 1942-11-19 – 1943-01-23 Battle of Buna-Gona
1942-11-19 – 1943-01-23 Battle of Buna-Gona -

 1943-01-28 – 1943-01-30 Battle of Wau
1943-01-28 – 1943-01-30 Battle of Wau -

 1943-03-02 – 1943-03-04 Battle of the Bismarck Sea
1943-03-02 – 1943-03-04 Battle of the Bismarck Sea -

 1943-06-29 – 1943-09-16 Battle of Lae
1943-06-29 – 1943-09-16 Battle of Lae -


 1943-06-30 – 1944-03-25 Operation Cartwheel
1943-06-30 – 1944-03-25 Operation Cartwheel -

 1943-09-19 – 1944-04-24 Finisterre Range campaign
1943-09-19 – 1944-04-24 Finisterre Range campaign -

 1943-09-22 – 1944-01-15 Huon Peninsula campaign
1943-09-22 – 1944-01-15 Huon Peninsula campaign -


 1943-11-01 – 1943-11-11 Attack on Rabaul
1943-11-01 – 1943-11-11 Attack on Rabaul -


 1943-12-15 – 1945-08-15 New Britain campaign
1943-12-15 – 1945-08-15 New Britain campaign -
 1944-02-29 – 1944-03-25 Admiralty Islands campaign
1944-02-29 – 1944-03-25 Admiralty Islands campaign -

 1944-04-22 – 1945-08-15 Western New Guinea campaign
1944-04-22 – 1945-08-15 Western New Guinea campaign
-



 1942-05-05 – 1942-11-06 Battle of Madagascar
1942-05-05 – 1942-11-06 Battle of Madagascar
-

 1942-06-06 – 1943-08-15 Battle of the Aleutian Islands
1942-06-06 – 1943-08-15 Battle of the Aleutian Islands -

 1942-06-07 – 1943-08-15 Battle of Kiska
1942-06-07 – 1943-08-15 Battle of Kiska -
 1943-03-26 – Battle of the Komandorski Islands
1943-03-26 – Battle of the Komandorski Islands
-



 1942-08-07 – 1943-02-09 Battle of Guadalcanal
1942-08-07 – 1943-02-09 Battle of Guadalcanal -
.svg.png) 1942-08-09 Battle of Savo Island
1942-08-09 Battle of Savo Island -

 1942-08-24 – 1942-08-25 Battle of the Eastern Solomons
1942-08-24 – 1942-08-25 Battle of the Eastern Solomons -
 1942-10-11 – 1942-10-12 Battle of Cape Esperance
1942-10-11 – 1942-10-12 Battle of Cape Esperance - 1942-10-25 – 1942-10-27 Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands
-

 1942-11-13 – 1942-11-15 Naval Battle of Guadalcanal
1942-11-13 – 1942-11-15 Naval Battle of Guadalcanal -
.svg.png) 1942-11-30 Battle of Tassafaronga
1942-11-30 Battle of Tassafaronga
-
.svg.png) 1943-01-29 – 1943-01-30 Battle of Rennell Island
1943-01-29 – 1943-01-30 Battle of Rennell Island -
 1943-03-06 Battle of Blackett Strait
1943-03-06 Battle of Blackett Strait -



 1943-06-10 – 1943-08-25 New Georgia Campaign
1943-06-10 – 1943-08-25 New Georgia Campaign - 1943-07-06 Battle of Kula Gulf
-
.svg.png) 1943-07-12 – 1943-07-13 Battle of Kolombangara
1943-07-12 – 1943-07-13 Battle of Kolombangara -
 1943-08-06 – 1943-08-07 Battle of Vella Gulf
1943-08-06 – 1943-08-07 Battle of Vella Gulf -
 1943-08-17 – 1943-08-18 Battle off Horaniu
1943-08-17 – 1943-08-18 Battle off Horaniu -


 1943-08-15 – 1943-10-09 Land Battle of Vella Lavella
1943-08-15 – 1943-10-09 Land Battle of Vella Lavella -
.svg.png) 1943-10-06 Naval Battle of Vella Lavella
1943-10-06 Naval Battle of Vella Lavella -



 1943-11-01 – 1945-08-21 Battle of Bougainville
1943-11-01 – 1945-08-21 Battle of Bougainville -
 1943-11-01 – 1943-11-02 Battle of Empress Augusta Bay
1943-11-01 – 1943-11-02 Battle of Empress Augusta Bay -
 1943-11-26 Battle of Cape St. George
1943-11-26 Battle of Cape St. George
Gilbert and Marshall Islands campaign
-
 1943-11-20 – 1943-11-23 Battle of Tarawa
1943-11-20 – 1943-11-23 Battle of Tarawa -
 1943-11-20 – 1943-11-24 Battle of Makin
1943-11-20 – 1943-11-24 Battle of Makin -
 1944-01-31 – 1944-02-07 Battle of Kwajalein
1944-01-31 – 1944-02-07 Battle of Kwajalein -
 1944-02-16 – 1944-02-17 Attack on Truk
1944-02-16 – 1944-02-17 Attack on Truk -
 1944-02-16 – 1944-02-23 Battle of Eniwetok
1944-02-16 – 1944-02-23 Battle of Eniwetok
Bombing of South East Asia, 1944-45
-

 Operation Cockpit 1944-04-19
Operation Cockpit 1944-04-19 -

 Operation Transom 1944-05-17
Operation Transom 1944-05-17 -

 Bombing of Bangkok 1944-05-20
Bombing of Bangkok 1944-05-20 -
 Operation Matterhorn 1944-06-05 – May 1945
Operation Matterhorn 1944-06-05 – May 1945 -
 Operation Meridian 1945-01-24 – 1945-01-29
Operation Meridian 1945-01-24 – 1945-01-29
Mariana and Palau Islands campaign
-
 1944-06-15 – 1944-07-09 Battle of Saipan
1944-06-15 – 1944-07-09 Battle of Saipan -
 1944-06-19 – 1944-06-20 Battle of the Philippine Sea
1944-06-19 – 1944-06-20 Battle of the Philippine Sea -
 1944-07-21 – 1944-08-10 Battle of Guam[102]
1944-07-21 – 1944-08-10 Battle of Guam[102] -
 1944-07-24 – 1944-08-01 Battle of Tinian[102]
1944-07-24 – 1944-08-01 Battle of Tinian[102] -
 1944-09-15 – 1944-11-25 Battle of Peleliu[103]
1944-09-15 – 1944-11-25 Battle of Peleliu[103] -
 1944-09-17 – 1944-09-30 Battle of Angaur[103]
1944-09-17 – 1944-09-30 Battle of Angaur[103]
Philippines campaign
-

.svg.png)
 1944-10-20 – 1944-12-10 Battle of Leyte
1944-10-20 – 1944-12-10 Battle of Leyte -

 1944-10-24 – 1944-10-25 Battle of Leyte Gulf
1944-10-24 – 1944-10-25 Battle of Leyte Gulf -
 1944-11-11 – 1944-12-21 Battle of Ormoc Bay
1944-11-11 – 1944-12-21 Battle of Ormoc Bay -

.svg.png)
 1944-12-15 – 1945-07-04 Battle of Luzon
1944-12-15 – 1945-07-04 Battle of Luzon -

 1945-01-09 Invasion of Lingayen Gulf
1945-01-09 Invasion of Lingayen Gulf -
.svg.png)
 1945-01-31 – 1945-02-08 Recapture of Bataan
1945-01-31 – 1945-02-08 Recapture of Bataan -
.svg.png)
 1945-02-03 – 1945-03-03 Battle of Manila
1945-02-03 – 1945-03-03 Battle of Manila -
.svg.png)
 1945-03-18 – 1945-07-30 Battle of the Visayas
1945-03-18 – 1945-07-30 Battle of the Visayas -
.svg.png)
 1945-03-10 – 1945-08-15 Battle of Mindanao
1945-03-10 – 1945-08-15 Battle of Mindanao
Volcano and Ryukyu Islands campaign
-
 1945-02-16 – 1945-03-26 Battle of Iwo Jima
1945-02-16 – 1945-03-26 Battle of Iwo Jima -




 1945-04-01 – 1945-06-21 Battle of Okinawa
1945-04-01 – 1945-06-21 Battle of Okinawa -
 1945-04-07 Operation Ten-Go
1945-04-07 Operation Ten-Go
-


 1945-05-01 – 1945-05-25 Battle of Tarakan
1945-05-01 – 1945-05-25 Battle of Tarakan -
 1945-06-10 – 1945-06-15 Battle of Brunei
1945-06-10 – 1945-06-15 Battle of Brunei -
 1945-06-10 – 1945-06-22 Battle of Labuan
1945-06-10 – 1945-06-22 Battle of Labuan -
 1945-06-17 – 1945-08-15 Battle of North Borneo
1945-06-17 – 1945-08-15 Battle of North Borneo -

 1945-07-07 – 1945-07-21 Battle of Balikpapan
1945-07-07 – 1945-07-21 Battle of Balikpapan
-
 1945-07-22 Battle of Tokyo Bay
1945-07-22 Battle of Tokyo Bay -
 1945-08-06 – 1945-08-09 Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
1945-08-06 – 1945-08-09 Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
-
.svg.png) 1945-08-08 – 1945-09-02 Soviet invasion of Manchuria
1945-08-08 – 1945-09-02 Soviet invasion of Manchuria
Command areas
The command structures of the Pacific War varied, reflecting the different roles of various belligerent nations, and often involving different geographic scopes. These included the following:
- American commands:
- Pacific Ocean Areas
- South West Pacific Area
- British and Allied commands:
- GHQ India, commanding the British Army in India
- Eastern Fleet
- American-British-Dutch-Australian Command
- South East Asia Command
- Far East Command (Soviet Union), the Soviet command during the war against Japan in 1945
- Japanese commands:
- Japanese Combined Fleet, the Japanese command which oversaw naval operations
- Southern Expeditionary Army Group, the Japanese army command in the South West Pacific and South East Asia
See also
- European Theatre of World War II
- Japanese holdout
- Operation Downfall
- Timeline WW II – Pacific Theater
- Yasukuni Shrine
Footnotes
- ↑ Complete list of nations which fought on the Allied side in the Pacific War: The Republic of China, The United States, The United Kingdom (including the Fiji Islands, the Straits Settlements and other colonial forces), Tonga (a British protectorate), Australia (including the Territory of New Guinea), the Commonwealth of the Philippines (a United States protectorate), British India, the Netherlands (including Dutch East Indies colonial forces), the Soviet Union, New Zealand, Canada, Mexico, and Mongolia. Free French Naval Forces contributed several warships, such as the Triomphant. After the Liberation of France, the French battleship Richelieu was sent to the Pacific. From 1943, the commando group Corps Léger d'Intervention took part in resistance operations in Indochina.
Guerrilla Organizations which fought for the Allies include Chinese Red Army, Hukbalahap, Malayan People's Anti-Japanese Army, Manchurian Anti-Japanese Volunteer Armies, the Korean Liberation Army, and the Viet Minh - ↑ Complete list of nations and groups which fought on the Axis side in the Pacific War: The Empire of Japan (including Thailand, the puppet government of Manchukuo, Mengjiang, Wang Jingwei regime, and other Chinese collaborationist governments and organizations, the State of Burma, the Provisional Government of Free India, the puppet Second Philippine Republic, and other states in the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere). The Vichy French allowed the Japanese to use bases in French Indochina beginning in 1941. In addition, Nazi Germany and Italy both contributed small naval forces.
- ↑ 3.8 million Chinese military casualties (1937–45; 3.2 million Nationalist/-allied and 580,000 Communist),[3] 354,523 United States casualties (106,207 killed, 248,316 wounded and missing),[5] 52,000 British casualties including 12,000 deaths in captivity,[citation needed] 86,838 British Indian casualties (this casualty figure is for all theatres of World War Two that Indian troops fought in),[1] 17,501 Australian casualties,[6] 57,000 casualties from the Philippine Commonwealth,[citation needed] around 9,400 Dutch casualties including 8,500 who died in captivity (likely not including colonial forces),[citation needed] 578 New Zealander casualties,[7] 63,225 Soviet casualties (20,797 killed and missing, 42,428 wounded and sick), 5000 French military casualties in Indochina, 300 Mongolian casualties[8] and 5 Mexican deaths[9] Malaria was the most important health hazard encountered by U.S. troops in the South Pacific during World War II, where about 500,000 men were infected.[10]
- ↑ Over 17 million Chinese civilian deaths (1937–45);[3] around 4 million civilian deaths from the Dutch East Indies;[1], 2 million Indochinese civilians;[4] around 1.5 million British Indian civilian deaths; 0.5 to 1 million Filipino civilian deaths; and hundreds of thousands of Burmese, Malayan, Pacific and other civilian deaths.[1]
n Pear
Military deaths
2,000,000 (1937–45)[nb 1] 1.18 million Chinese collaborator casualties 1937–45 (432.000 dead),[citation needed] 22,000 Burmese casualties,[citation needed] 5,600 Thai casualties,[citation needed] and 2,615 Indian casualties.[citation needed] - ↑ 580,000 Japanese civilian deaths,[1], 378,000 Korean and 300 Thai civilian deaths.[citation needed]
- ↑
- ↑ This is the same McCollum conspiracy theorists accuse of providing a blueprint for provoking Japan.
- ↑ The U.S. thereby reversed its opposition to unrestricted submarine warfare. After the war, when moralistic doubts about Hiroshima and other raids on civilian targets were loudly voiced, no-one criticized Roosevelt's submarine policy. (Two German admirals, Erich Raeder and Karl Dönitz, faced charges at the Nuremberg War Crimes Trials of violating international law through unrestricted submarine warfare; the court acquitted them after they proved that Allied merchant ships were legitimate military targets, under the rules in force at the time.)
- ↑ Chihaya went on to note that when the IJN belatedly improved its ASW methods, the U.S. submarine force responded by increasing Japanese losses.[2]
Citations
- ↑ A Decade of American Foreign Policy 1941–1949 Interim Meeting of Foreign Ministers, Moscow. Retrieved 30 September 2009.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 At war since 1937.
- ↑ L, Klemen (1999-2000). "Lieutenant-General Hein Ter Poorten". Forgotten Campaign: The Dutch East Indies Campaign 1941–1942.
- ↑ Williamson Murray, Allan R. Millett A War to be Won: Fighting the Second World War, Harvard University Press, 2001, p. 143
- ↑ John Costello, The Pacific War: 1941–1945, Harper Perennial, 1982
- ↑ B. H. Liddell Hart, History of the Second World War, Putnum, New York, 1971
- ↑ Japan Economic Foundation, Journal of Japanese Trade & Industry, Volume 16, 1997
- ↑ David Williams, Defending Japan's Pacific War: The Kyoto Philosophers and the Idea of a Post-White World, RoutledgeCurzon, 2004
- ↑ Roy M. MacLeod, Science and the Pacific War: Science and Survival in the Pacific, 1939–1945, Kluwer Academic Publishing, p. 1, 1999
- ↑ "For fifty-three long months, beginning in July 1937, China stood alone, single-handedly fighting an undeclared war against Japan. On 9 December 1941, after Japan's surprise attack on Pearl Harbor, China finally declared war against Japan. What had been for so long a war between two countries now became part of a much wider Pacific conflict." Hsi-sheng Ch'i, in James C. Hsiung and Steven I. Levine, China's Bitter Victory: The War with Japan 1937–1945, M.E. Sharpe, 1992, p. 157
- ↑ Youli Sun, China and the Origins of the Pacific War, 1931–41, Palgrave MacMillan, p. 11
- ↑ Jansen 2002, p. 626.
- ↑ "WW2 People's War – Timeline". BBC. Retrieved 31 October 2010.
- ↑ "Map of the Pacific Theater". Retrieved 31 October 2010.
- ↑ Edward J. Drea, Nomonhan: Japanese-Soviet Tactical Combat, 1939 (2005)
- ↑ Boyd, Carl. Hitler's Japanese confidant: General Ōshima Hiroshi and MAGIC intelligence, 1941–1945 (1993)
- ↑ Jansen 2002, p. 636.
- ↑ Fairbank, John King; Goldman, Merle (1994). China: A New History. Harvard University Press. p. 320. ISBN 0-674-11673-9.
- ↑ Lind Jennifer M. (2010). "Sorry States: Apologies in International Politics". Cornell University Press, p.28. ISBN 0-8014-7628-3
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 Peattie & Evans, Kaigun
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Willmott, Barrier and the Javelin (Annapolis: Naval Institute Press, 1983).
- ↑ Wilmott, H. P. Barrier and the Javelin (Annapolis, 1983).
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Boog et al (2006) "Germany and the Second World War: The Global War", p. 175
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 Evans & Peattie 1997, p. 488.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 25.2 Parillo, Mark P. Japanese Merchant Marine in World War II. (United States Naval Institute Press, 1993).
- ↑ The Neutrality Patrol had U.S. destroyers effectively at war, but no state of war had been declared by Congress.
- ↑ "The Kingdom of the Netherlands Declares War with Japan", Inter-Allied Review (Inter-Allied Review via publisher=[Pearl Harbor History Associates Inc. http://www.ibiblio.org/pha/] hosted at ibiblio), (purportedly) 15 December 1941, retrieved 3 October 2009
- ↑ "Australia Declares War on Japan", Inter-Allied Review (Inter-Allied Review via publisher=[Pearl Harbor History Associates Inc. http://www.ibiblio.org/pha/] hosted at ibiblio), 15 December 1941, retrieved 3 October 2009
- ↑ H. Bix, "The Shōwa Emperor's Monologue and the Problem of War Responsibility", Journal of Japanese Studies, Vol. 18, No. 2, 1992, p. 344.
- ↑ Peattie 2007, pp. 168–169.
- ↑ "Remembering 1942, The fall of Singapore, 15 February 1942". Awm.gov.au. Retrieved 31 October 2010.
- ↑ Klemen, L (1999-2000). "The capture of Bali Island, February 1942". Forgotten Campaign: The Dutch East Indies Campaign 1941–1942.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 Klemen, L (1999-2000). "The Japanese Invasion of Dutch West Timor Island, February 1942". Forgotten Campaign: The Dutch East Indies Campaign 1941–1942.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 Peattie 2007, pp. 170–172.
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 Klemen, L (1999-2000). "The Java Sea Battle, February 1942". Forgotten Campaign: The Dutch East Indies Campaign 1941–1942.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 Klemen, L (1999-2000). "The conquest of Java Island, March 1942". Forgotten Campaign: The Dutch East Indies Campaign 1941–1942.
- ↑ Womack, Tom (1999-2000). "An Abandoned Army – The KNIL and The Japanese Invasion of Northern Dutch Sumatra". Dutch East Indies Campaign website.
- ↑ Peattie 2007, p. 172.
- ↑ Hoyt, Edwin P. (1986). Japan's War. Da Capo. pp. 262–263. ISBN 0-306-80348-8.
- ↑ 40.0 40.1 40.2 Blair, Silent Victory
- ↑ "In office – John Curtin – Australia's PMs – Australia's Prime Ministers". Primeministers.naa.gov.au. Retrieved 2013-04-20.
- ↑ Cited in Frank Crowley (1973) Vol 2, p.51
- ↑ "Remembering the war in New Guinea – Rabaul". Ajrp.awm.gov.au. Retrieved 2013-04-20.
- ↑ "Remembering the war in New Guinea – Were the Japanese going to invade?". Ajrp.awm.gov.au. 1942-02-19. Retrieved 2013-04-20.
- ↑ "Midget Submarines history at". Home.st.net.au. Retrieved 29 April 2010.
- ↑ Wilmott, Barrier and the Javelin
- ↑ Parshall, Jonathan; Tully, Anthony (2005). Shattered Sword: The Untold Story of the Battle of Midway. Potomac Books. pp. 19–38. ISBN 1-57488-923-0.
- ↑ Parshall, Jonathan; Tully, Anthony (2005). Shattered Sword: The Untold Story of the Battle of Midway. Potomac Books. p. 33. ISBN 1-57488-923-0.
- ↑ "Battle of Midway-Scouting and Early Attacks from Midway, 3–4 June 1942". History.navy.mil. Retrieved 31 October 2010.
- ↑ Evans & Peattie 1997, pp. 490.
- ↑ Evans & Peattie 1997, p. 491.
- ↑ Theodore Roscoe, United States Submarine Operations in World War II (US Naval Institute Press, 1949).
- ↑ Prange et al. Pearl Harbor Papers
- ↑ 54.0 54.1 Roscoe, Theodore. Pig Boats (Bantam Books, 1958); Blair, Silent Victory, pp.991–2.
- ↑ Larry Kimmett and Margaret Regis, U.S. Submarines in World War II
- ↑ David Stevens. Japanese submarine operations against Australia 1942–1944. Retrieved 18 June 2007.
- ↑ Carl Boyd, "The Japanese Submarine Force and the Legacy of Strategic and Operational Doctrine Developed Between the World Wars", in Larry Addington ed. Selected Papers from the Citadel Conference on War and Diplomacy: 1978 (Charleston, 1979) 27–40; Clark G. Reynolds, Command of the Sea: The History and Strategy of Maritime Empires (1974) 512.
- ↑ Farago, Ladislas. Broken Seal.
- ↑ Blair, Silent Victory, pp.359–60, 551–2, & 816.
- ↑ RD Designs (7 December 1941). "Sinkings By Boat". Pigboats.com. Retrieved 31 October 2010.
- ↑ "Japanese Naval and Merchant Vessels Sunk During World War II By All U.S. Submarines". Valoratsea.com. Retrieved 31 October 2010.
- ↑ Roscoe, op. cit.
- ↑ Blair, p.877.
- ↑
- ↑ Blair, Clay, Jr. Silent Victory (New York: Bantam, 1976).
- ↑ Morison, S. E. U.S. Navy in World War Two.
- ↑ Peattie 2007, p. 188-189.
- ↑ L, Klemen (1999-2000). "Rear-Admiral Takeo Kurita". Forgotten Campaign: The Dutch East Indies Campaign 1941–1942.
- ↑ 69.0 69.1 "Creating military power: the sources of military effectiveness". Risa Brooks, Elizabeth A. Stanley (2007). Stanford University Press. p.41. ISBN 0-8047-5399-7
- ↑ Powers, D. (2011): Japan: No Surrender in World War Two BBC History (17 February 2011).
- ↑ Robert S. Burrell, "Breaking the Cycle of Iwo Jima Mythology: A Strategic Study of Operation Detachment," Journal of Military History Volume 68, Number 4, October 2004, pp. 1143–1186 and rebuttal in Project MUSE
- ↑ Slim, William (1956). Defeat into Victory. Cassell. pp. 468–469. ISBN 0-552-08757-2.
- ↑ 73.0 73.1 73.2 "Japanese prisoners of war". Philip Towle, Margaret Kosuge, Yōichi Kibata (2000). Continuum International Publishing Group. pp.47–48. ISBN 1-85285-192-9
- ↑ Grey, Jeffrey (1999). A Military History of Australia. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-64483-6.. Pages 184–186.
- ↑ Joseph H. Alexander, The final campaign: Marines in the victory on Okinawa (1996) short official history online
- ↑ Hiromichi Yahara, The Battle For Okinawa (1997), Japanese perspective excerpt and text search
- ↑ Skates, James. Invasion of Japan.
- ↑ Raymond L. Garthoff. The Soviet Manchurian Campaign, August 1945. Military Affairs, Vol. 33, No. 2 (Oct. 1969), pp. 312–336
- ↑ 79.0 79.1 Professor Duncan Anderson, 2005,"Nuclear Power: The End of the War Against Japan" (World War Two, BBC History website) Access date: 11 September 2007.
- ↑ See, for example, Alperowitz, G., The Decision to Use the Atomic Bomb (1995; New York, Knopf; ISBN 0-679-44331-2) for this argument.
- ↑ Frank, Richard B. (2007). Tsuyoshi Hasegawa, ed. The End of the Pacific War: Reappraisals. Stanford University Press. p. 89. ISBN 978-0-8047-5427-9.
- ↑ Sadao Asada. The Shock of the Atomic Bomb and Japan's Decision to Surrender: A Reconsideration. The Pacific Historical Review, Vol. 67, No. 4 (Nov. 1998), pp. 477–512.
- ↑ Patrick Clancey. "The Voice of the Crane: The Imperial Rescript of 15Aug45". ibiblio. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Retrieved 27 September 2012.
- ↑ "Chronology of Japanese Holdouts". Wanpela.com. Retrieved 31 October 2010.
- ↑ "Rummel, R.J. '''Statistics of Democide: Genocide and Mass Murder since 1900''' Chapter 3. LIT Verlag Münster-Hamburg-Berlin-Wien-London-Zürich (1999)". Hawaii.edu. Retrieved 31 October 2010.
- ↑ Nuclear Power: The End of the War Against Japan
- ↑ Remember role in ending fascist war
- ↑ Christopher Hudson (2 March 2007). "Doctors of Depravity". Daily Mail.
- ↑ Chapel, Joseph (2004). "Denial of the Holocaust and the Rape of Nanking".
- ↑ de Brouwer, Anne-Marie (2005). Supranational Criminal Prosecution of Sexual Violence. Intersentia. p. 8. ISBN 90-5095-533-9.
- ↑ "No government coercion in war's sex slavery: Abe", The Japan Times, 2 March 2007
- ↑ Himeta, Mitsuyoshi (姫田光義) (日本軍による『三光政策・三光作戦をめぐって』) (Concerning the Three Alls Strategy/Three Alls Policy By the Japanese Forces), Iwanami Bukkuretto, 1996, Bix, Hirohito and the Making of Modern Japan, 2000
- ↑ L, Klemen (1999-2000). "The capture of Tarakan Island, January 1942". Forgotten Campaign: The Dutch East Indies Campaign 1941–1942.
- ↑ L, Klemen (1999-2000). "The capture of Balikpapan, January 1942". Forgotten Campaign: The Dutch East Indies Campaign 1941–1942.
- ↑ L, Klemen (1999-2000). "The Japanese Invasion of Ambon Island, January 1942". Forgotten Campaign: The Dutch East Indies Campaign 1941–1942.
- ↑ L, Klemen (1999-2000). "The battle for Palembang, February 1942". Forgotten Campaign: The Dutch East Indies Campaign 1941–1942.
- ↑ L, Klemen (1999-2000). "The Badung Strait Battle". Forgotten Campaign: The Dutch East Indies Campaign 1941–1942.
- ↑ L, Klemen (1999-2000). "The fighting on Portuguese East Timor, 1942". Forgotten Campaign: The Dutch East Indies Campaign 1941–1942.
- ↑ Visser, Jan (1999-2000). "The Sunda Strait Battle". Forgotten Campaign: The Dutch East Indies Campaign 1941–1942.
- ↑ L, Klemen (1999-2000). "The Mystery of Christmas Island, March 1942". Forgotten Campaign: The Dutch East Indies Campaign 1941–1942.
- ↑ http://www.veterans.gc.ca/eng/remembrance/medals-decorations/campaign-stars-medals-1939-1954/pstar
- ↑ 102.0 102.1 Potter & Nimitz, 1960, p.770
- ↑ 103.0 103.1 Ofstie(1946)p.275
References
- Eric M. Bergerud, Fire in the Sky: The Air War in the South Pacific (2000)
- Blair, Jr., Clay. Silent Victory. Philadelphia: Lippincott, 1975 (submarine war).
- Buell, Thomas. Master of Seapower: A Biography of Admiral Ernest J. King Naval Institute Press, 1976.
- Buell, Thomas. The Quiet Warrior: A Biography of Admiral Raymond Spruance. 1974.
- Costello, John. The Pacific War. 1982, overview
- Craven, Wesley, and James Cate, eds. The Army Air Forces in World War II. Vol. 1, Plans and Early Operations, January 1939 to August 1942. University of Chicago Press, 1958. Official history; Vol. 4, The Pacific: Guadalcanal to Saipan, August 1942 to July 1944. 1950; Vol. 5, The Pacific: Matterhorn to Nagasaki. 1953.
- Dunnigan, James F., and Albert A. Nofi. The Pacific War Encyclopedia. Facts on File, 1998. 2 vols. 772p.
- Evans, David C; Peattie, Mark R (1997). Kaigun: strategy, tactics, and technology in the Imperial Japanese Navy, 1887–1941. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-87021-192-7.
- Gailey, Harry A. The War in the Pacific: From Pearl Harbor to Tokyo Bay (1995) online
- Gordon, David M. "The China-Japan War, 1931–1945" Journal of Military History (January 2006) v 70#1, pp 137–82. Historiographical overview of major books
- Seki, Eiji. (2006). Mrs. Ferguson's Tea-Set, Japan and the Second World War: The Global Consequences Following Germany's Sinking of the SS Automedon in 1940. London: Global Oriental. 10-ISBN 1-905246-28-5; 13- ISBN 978-1-905246-28-1 (cloth) (reprinted by University of Hawaii Press), Honolulu, 2007. previously announced as Sinking of the SS Automedon and the Role of the Japanese Navy: A New Interpretation.
- Saburo Hayashi and Alvin Coox. Kogun: The Japanese Army in the Pacific War. Quantico, Virginia: Marine Corps Assoc., 1959.
- Hopkins, William B. The Pacific War: The Strategy, Politics, and Players that Won the War (2010)
- Hsiung, James C. and Steven I. Levine, eds. China's Bitter Victory: The War with Japan, 1937–1945 M. E. Sharpe, 1992
- Hsi-sheng, Ch'i. Nationalist China at War: Military Defeats and Political Collapse, 1937–1945 University of Michigan Press, 1982
- Inoguchi, Rikihei, Tadashi Nakajima, and Robert Pineau. The Divine Wind. Ballantine, 1958. Kamikaze.
- Jansen, Marius B. (2002). The Making of Modern Japan. Cambridge, Mass: Harvard University Press. ISBN 0-674-00334-9.
- Kirby, S. Woodburn The War Against Japan. 4 vols. London: H.M.S.O., 1957–1965. Official Royal Navy history.
- L, Klemen (1999-2000). "Forgotten Campaign: The Dutch East Indies Campaign 1941–1942".
- Leary, William M. We Shall Return: MacArthur's Commanders and the Defeat of Japan. University Press of Kentucky, 1988.
- Long, Gavin. Australia in the War of 1939–45, Army. Vol. 7, The Final Campaigns. Canberra: Australian War Memorial, 1963.
- McCarthy, Dudley. Australia in the War of 1939–45, Army. Vol. 5, South-West Pacific Area—First Year: Kokoda to Wau. Canberra: Australian War Memorial, 1959.
- James, D. Clayton. The Years of MacArthur. Vol. 2. Houghton Mifflin, 1972.
- Maurice Matloff and Edwin M. Snell Strategic Planning for Coalition Warfare 1941–1942, United States Army Center of Military History, Washington, D. C., 1990
- Miller, Edward S. (2007). War Plan Orange: The U.S. Strategy to Defeat Japan, 1897–1945. US Naval Institute Press. ISBN 1-59114-500-7.
- Peattie, Mark R (2007). Sunburst: The Rise of Japanese Naval Air Power, 1909–1941. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 1-59114-664-X.
- Samuel Eliot Morison, History of United States Naval Operations in World War II. Vol. 3, The Rising Sun in the Pacific. Boston: Little, Brown, 1961; Vol. 4, Coral Sea, Midway and Submarine Actions. 1949; Vol. 5, The Struggle for Guadalcanal. 1949; Vol. 6, Breaking the Bismarcks Barrier. 1950; Vol. 7, Aleutians, Gilberts, and Marshalls. 1951; Vol. 8, New Guinea and the Marianas. 1962; Vol. 12, Leyte. 1958; vol. 13, The Liberation of the Philippines: Luzon, Mindanao, the Visayas. 1959; Vol. 14, Victory in the Pacific. 1961.
- Masatake Okumiya, and Mitso Fuchida. Midway: The Battle That Doomed Japan. Naval Institute Press, 1955.
- E. B. Potter, and Chester W. Nimitz. Triumph in the Pacific. Prentice Hall, 1963. Naval battles
- E. B. Potter, Bull Halsey Naval Institute Press, 1985.
- E. B. Potter, Nimitz. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press, 1976.
- John D. Potter, Yamamoto 1967.
- Gordon W. Prange, Donald Goldstein, and Katherine Dillon. At Dawn We Slept. Penguin, 1982. Pearl Harbor
- ——, et al. Miracle at Midway. Penguin, 1982.
- ——, et al. Pearl Harbor: The Verdict of History.
- Seki, Eiji (2007). Sinking of the SS Automedon And the Role of the Japanese Navy: A New Interpretation. University of Hawaii Press. ISBN 1-905246-28-5.
- Henry Shaw, and Douglas Kane. History of U.S. Marine Corps Operations in World War II. Vol. 2, Isolation of Rabaul. Washington, D.C.: Headquarters, U.S. Marine Corps, 1963
- Henry Shaw, Bernard Nalty, and Edwin Turnbladh. History of U.S. Marine Corps Operations in World War II. Vol. 3, Central Pacific Drive. Washington, D.C.: Office of the Chief of Military History, 1953.
- E.B. Sledge, With the Old Breed: At Peleliu and Okinawa. Presidio, 1981. Memoir.
- J. Douglas Smith, and Richard Jensen. World War II on the Web: A Guide to the Very Best Sites. (2002)
- Ronald Spector, Eagle Against the Sun: The American War with Japan Free Press, 1985.
- John Toland, The Rising Sun. 2 vols. Random House, 1970. Japan's war.
- Ian W. Toll. Pacific Crucible: War at Sea in the Pacific, 1941–1942 (2011)
- H. P. Willmott. Empires in the Balance. Annapolis: United States Naval Institute Press, 1982.
- H. P. Willmott. The Barrier and the Javelin. Annapolis: United States Naval Institute Press, 1983.
- Gerhard L. Weinberg, A World at Arms: A Global History of World War II, Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-44317-2. (2005).
- William Y'Blood, Red Sun Setting: The Battle of the Philippine Sea. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press, 1980.
- Harries, Meirion; Susie Harries (1994). Soldiers of the Sun : The Rise and Fall of the Imperial Japanese Army. New York: Random House. ISBN 0-679-75303-6.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Pacific War. |
- Film Footage of the Pacific War
- La politique de la sphère de coprospérité de la grande Asie orientale au Japon (French)
- Animated History of the Pacific War
- Canada in the Pacific War — Canadians in Asia & the Pacific
- The Pacific War Series – at The War Times Journal
- Morinoske: Japanese Pilot testimonials – and more
- Imperial Japanese Navy Page
- The Atomic Bomb and the End of World War II
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||


